Jean-Louis Reymond
Mapping the Space of Chemical Reactions Using Attention-Based Neural Networks
Dec 09, 2020
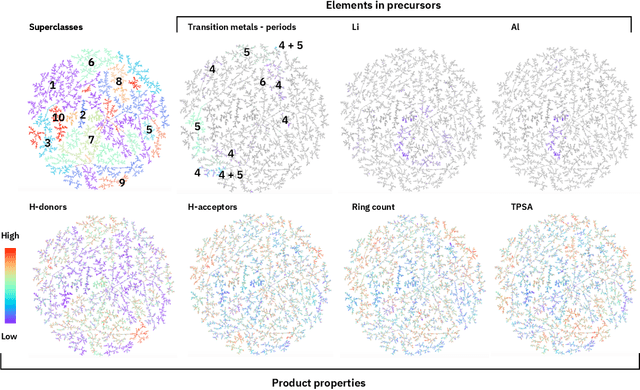
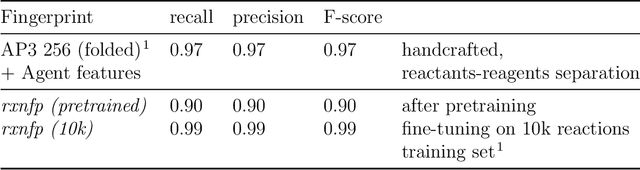
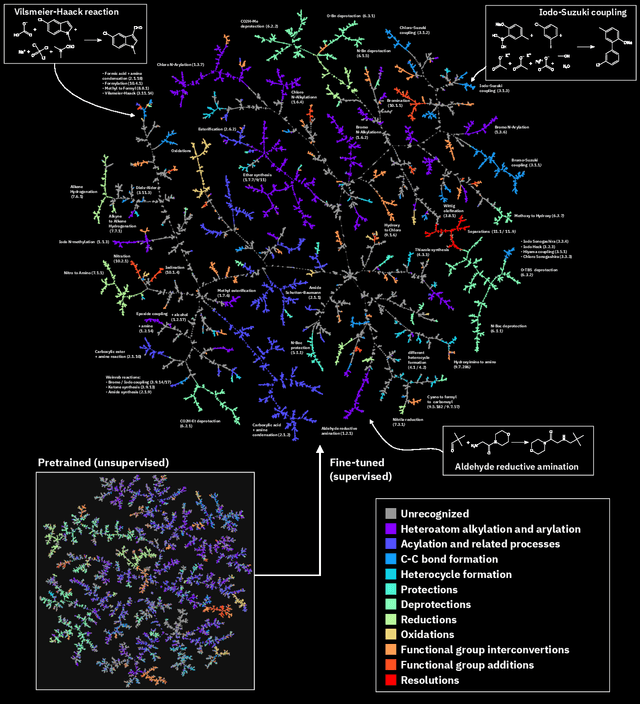
Abstract:Organic reactions are usually assigned to classes containing reactions with similar reagents and mechanisms. Reaction classes facilitate the communication of complex concepts and efficient navigation through chemical reaction space. However, the classification process is a tedious task. It requires the identification of the corresponding reaction class template via annotation of the number of molecules in the reactions, the reaction center, and the distinction between reactants and reagents. This work shows that transformer-based models can infer reaction classes from non-annotated, simple text-based representations of chemical reactions. Our best model reaches a classification accuracy of 98.2%. We also show that the learned representations can be used as reaction fingerprints that capture fine-grained differences between reaction classes better than traditional reaction fingerprints. The insights into chemical reaction space enabled by our learned fingerprints are illustrated by an interactive reaction atlas providing visual clustering and similarity searching.
Visualization of Very Large High-Dimensional Data Sets as Minimum Spanning Trees
Aug 16, 2019



Abstract:Here, we introduce a new data visualization and exploration method, TMAP (tree-map), which exploits locality sensitive hashing, Kruskal's minimum-spanning-tree algorithm, and a multilevel multipole-based graph layout algorithm to represent large and high dimensional data sets as a tree structure, which is readily understandable and explorable. Compared to other data visualization methods such as t-SNE or UMAP, TMAP increases the size of data sets that can be visualized due to its significantly lower memory requirements and running time and should find broad applicability in the age of big data. We exemplify TMAP in the area of cheminformatics with interactive maps for 1.16 million drug-like molecules from ChEMBL, 10.1 million small molecule fragments from FDB17, and 131 thousand 3D- structures of biomolecules from the PDB Databank, and to visualize data from literature (GUTENBERG data set), cancer biology (PANSCAN data set) and particle physics (MiniBooNE data set). TMAP is available as a Python package. Installation, usage instructions and application examples can be found at http://tmap.gdb.tools.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge