Jean-Francois Mari
INRIA Lorraine - LORIA
Temporal and Spatial Data Mining with Second-Order Hidden Models
May 09, 2005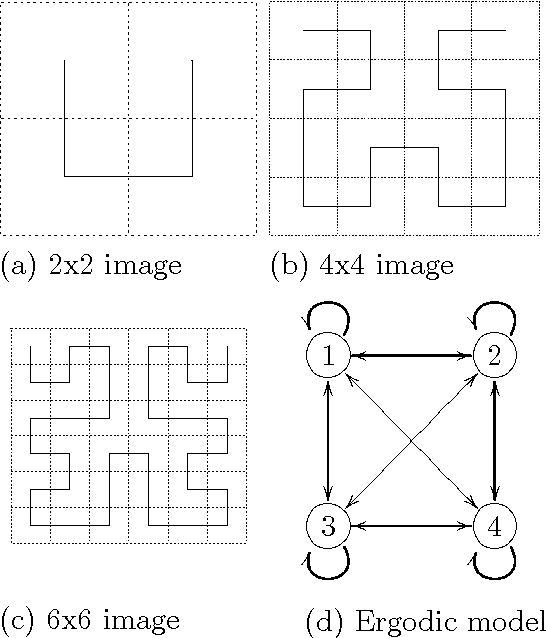

Abstract:In the frame of designing a knowledge discovery system, we have developed stochastic models based on high-order hidden Markov models. These models are capable to map sequences of data into a Markov chain in which the transitions between the states depend on the \texttt{n} previous states according to the order of the model. We study the process of achieving information extraction fromspatial and temporal data by means of an unsupervised classification. We use therefore a French national database related to the land use of a region, named Teruti, which describes the land use both in the spatial and temporal domain. Land-use categories (wheat, corn, forest, ...) are logged every year on each site regularly spaced in the region. They constitute a temporal sequence of images in which we look for spatial and temporal dependencies. The temporal segmentation of the data is done by means of a second-order Hidden Markov Model (\hmmd) that appears to have very good capabilities to locate stationary segments, as shown in our previous work in speech recognition. Thespatial classification is performed by defining a fractal scanning ofthe images with the help of a Hilbert-Peano curve that introduces atotal order on the sites, preserving the relation ofneighborhood between the sites. We show that the \hmmd performs aclassification that is meaningful for the agronomists.Spatial and temporal classification may be achieved simultaneously by means of a 2 levels \hmmd that measures the \aposteriori probability to map a temporal sequence of images onto a set of hidden classes.
Learning to automatically detect features for mobile robots using second-order Hidden Markov Models
Jan 24, 2005



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a new method based on Hidden Markov Models to interpret temporal sequences of sensor data from mobile robots to automatically detect features. Hidden Markov Models have been used for a long time in pattern recognition, especially in speech recognition. Their main advantages over other methods (such as neural networks) are their ability to model noisy temporal signals of variable length. We show in this paper that this approach is well suited for interpretation of temporal sequences of mobile-robot sensor data. We present two distinct experiments and results: the first one in an indoor environment where a mobile robot learns to detect features like open doors or T-intersections, the second one in an outdoor environment where a different mobile robot has to identify situations like climbing a hill or crossing a rock.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge