Jay W. McMahon
PoleStack: Robust Pole Estimation of Irregular Objects from Silhouette Stacking
Feb 05, 2025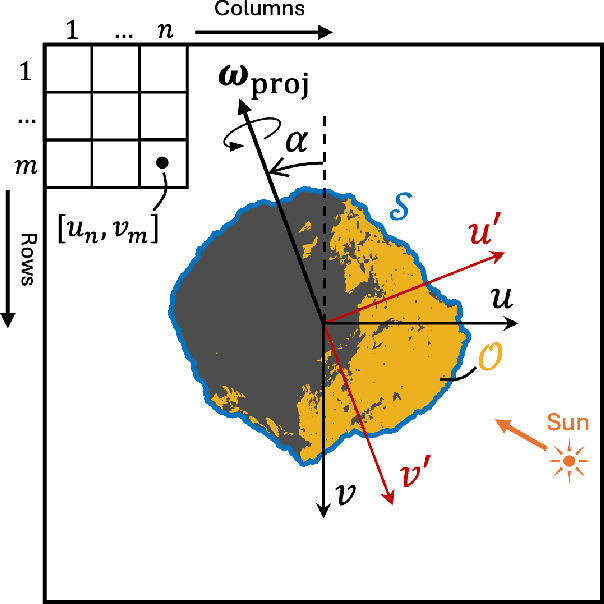
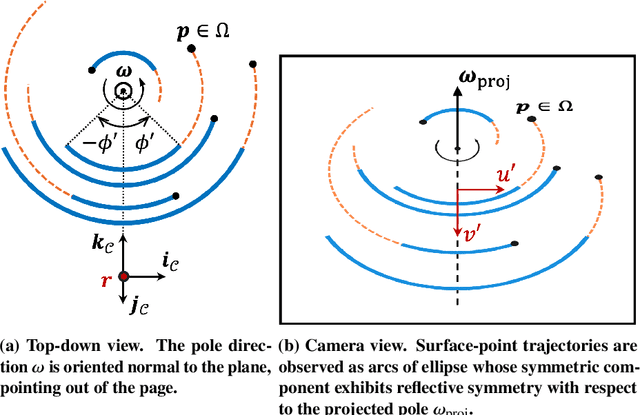
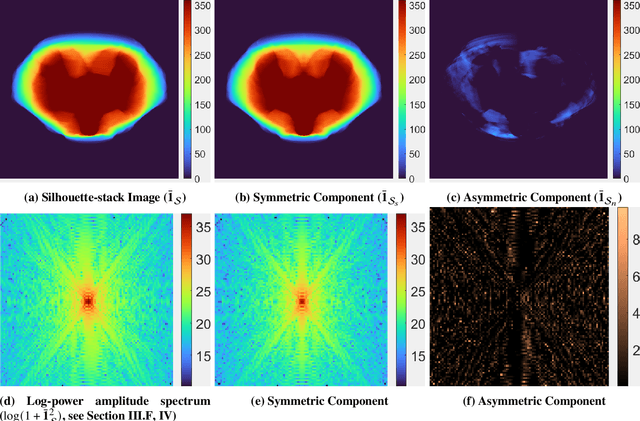
Abstract:We present an algorithm to estimate the rotation pole of a principal-axis rotator using silhouette images collected from multiple camera poses. First, a set of images is stacked to form a single silhouette-stack image, where the object's rotation introduces reflective symmetry about the imaged pole direction. We estimate this projected-pole direction by identifying maximum symmetry in the silhouette stack. To handle unknown center-of-mass image location, we apply the Discrete Fourier Transform to produce the silhouette-stack amplitude spectrum, achieving translation invariance and increased robustness to noise. Second, the 3D pole orientation is estimated by combining two or more projected-pole measurements collected from different camera orientations. We demonstrate degree-level pole estimation accuracy using low-resolution imagery, showing robustness to severe surface shadowing and centroid-based image-registration errors. The proposed approach could be suitable for pole estimation during both the approach phase toward a target object and while hovering.
Density Estimation for Entry Guidance Problems using Deep Learning
Oct 30, 2023



Abstract:This work presents a deep-learning approach to estimate atmospheric density profiles for use in planetary entry guidance problems. A long short-term memory (LSTM) neural network is trained to learn the mapping between measurements available onboard an entry vehicle and the density profile through which it is flying. Measurements include the spherical state representation, Cartesian sensed acceleration components, and a surface-pressure measurement. Training data for the network is initially generated by performing a Monte Carlo analysis of an entry mission at Mars using the fully numerical predictor-corrector guidance (FNPEG) algorithm that utilizes an exponential density model, while the truth density profiles are sampled from MarsGRAM. A curriculum learning procedure is developed to refine the LSTM network's predictions for integration within the FNPEG algorithm. The trained LSTM is capable of both predicting the density profile through which the vehicle will fly and reconstructing the density profile through which it has already flown. The performance of the FNPEG algorithm is assessed for three different density estimation techniques: an exponential model, an exponential model augmented with a first-order fading-memory filter, and the LSTM network. Results demonstrate that using the LSTM model results in superior terminal accuracy compared to the other two techniques when considering both noisy and noiseless measurements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge