PoleStack: Robust Pole Estimation of Irregular Objects from Silhouette Stacking
Paper and Code
Feb 05, 2025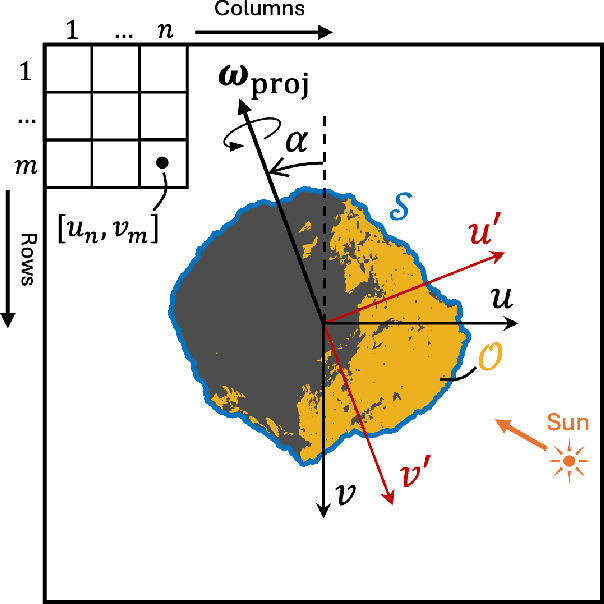
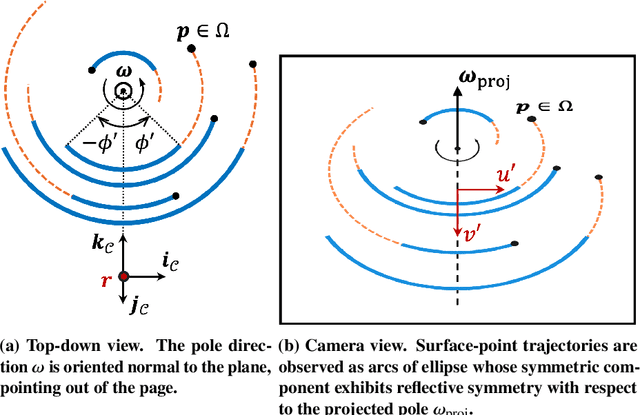
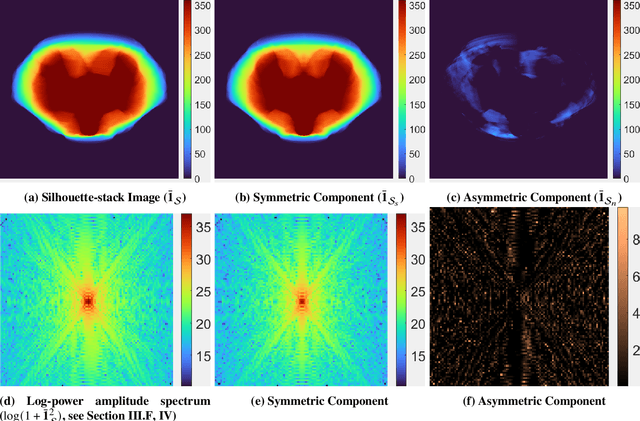
We present an algorithm to estimate the rotation pole of a principal-axis rotator using silhouette images collected from multiple camera poses. First, a set of images is stacked to form a single silhouette-stack image, where the object's rotation introduces reflective symmetry about the imaged pole direction. We estimate this projected-pole direction by identifying maximum symmetry in the silhouette stack. To handle unknown center-of-mass image location, we apply the Discrete Fourier Transform to produce the silhouette-stack amplitude spectrum, achieving translation invariance and increased robustness to noise. Second, the 3D pole orientation is estimated by combining two or more projected-pole measurements collected from different camera orientations. We demonstrate degree-level pole estimation accuracy using low-resolution imagery, showing robustness to severe surface shadowing and centroid-based image-registration errors. The proposed approach could be suitable for pole estimation during both the approach phase toward a target object and while hovering.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge