Javier J. Sanchez-Medina
Sentiment analysis and random forest to classify LLM versus human source applied to Scientific Texts
Apr 05, 2024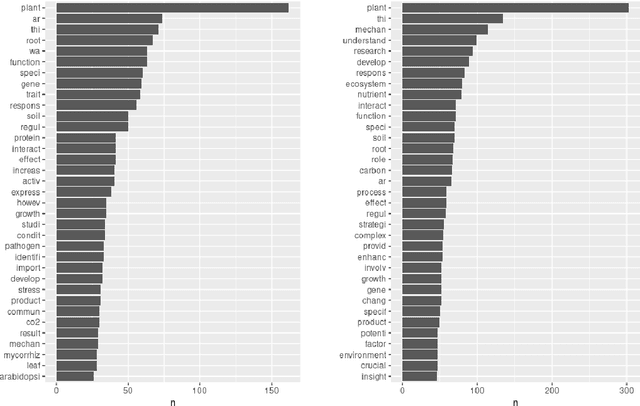
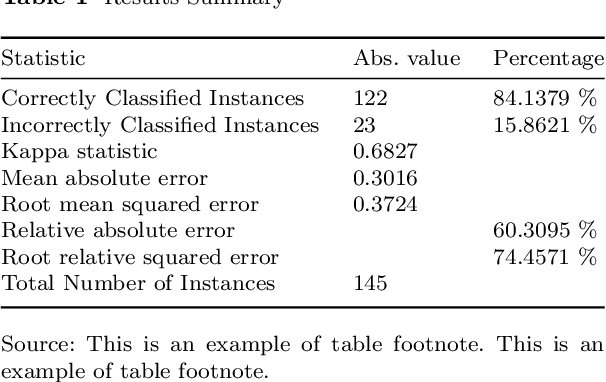
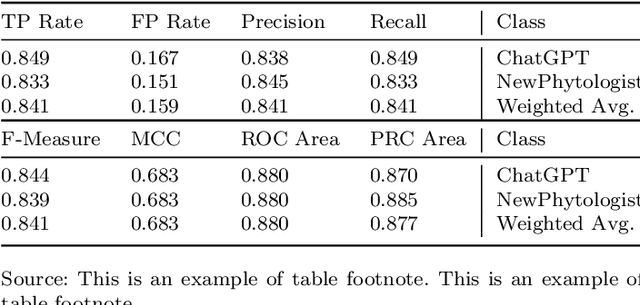
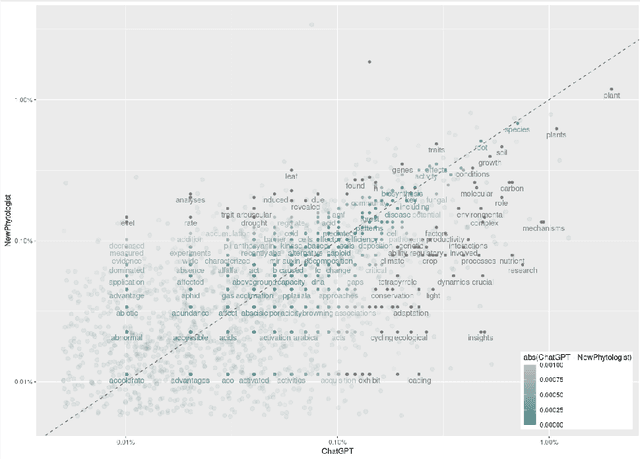
Abstract:After the launch of ChatGPT v.4 there has been a global vivid discussion on the ability of this artificial intelligence powered platform and some other similar ones for the automatic production of all kinds of texts, including scientific and technical texts. This has triggered a reflection in many institutions on whether education and academic procedures should be adapted to the fact that in future many texts we read will not be written by humans (students, scholars, etc.), at least, not entirely. In this work it is proposed a new methodology to classify texts coming from an automatic text production engine or a human, based on Sentiment Analysis as a source for feature engineering independent variables and then train with them a Random Forest classification algorithm. Using four different sentiment lexicons, a number of new features where produced, and then fed to a machine learning random forest methodology, to train such a model. Results seem very convincing that this may be a promising research line to detect fraud, in such environments where human are supposed to be the source of texts.
From Data to Actions in Intelligent Transportation Systems: a Prescription of Functional Requirements for Model Actionability
Feb 06, 2020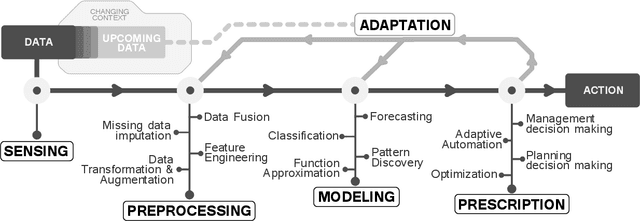
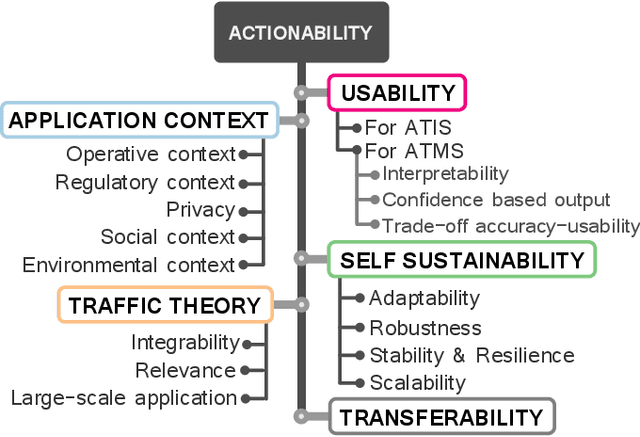
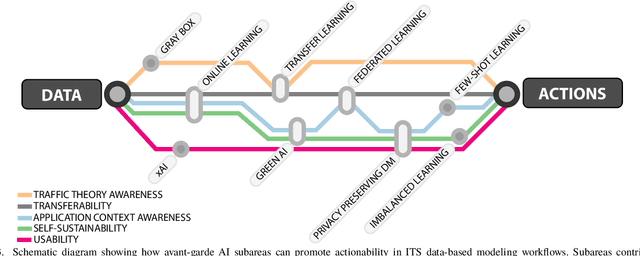
Abstract:Advances in Data Science are lately permeating every field of Transportation Science and Engineering, making it straightforward to imagine that developments in the transportation sector will be data-driven. Nowadays, Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) could be arguably approached as a "story" intensively producing and consuming large amounts of data. A diversity of sensing devices densely spread over the infrastructure, vehicles or the travelers' personal devices act as sources of data flows that are eventually fed to software running on automatic devices, actuators or control systems producing, in turn, complex information flows between users, traffic managers, data analysts, traffic modeling scientists, etc. These information flows provide enormous opportunities to improve model development and decision-making. The present work aims to describe how data, coming from diverse ITS sources, can be used to learn and adapt data-driven models for efficiently operating ITS assets, systems and processes; in other words, for data-based models to fully become actionable. Grounded on this described data modeling pipeline for ITS, we define the characteristics, engineering requisites and challenges intrinsic to its three compounding stages, namely, data fusion, adaptive learning and model evaluation. We deliberately generalize model learning to be adaptive, since, in the core of our paper is the firm conviction that most learners will have to adapt to the everchanging phenomenon scenario underlying the majority of ITS applications. Finally, we provide a prospect of current research lines within the Data Science realm that can bring notable advances to data-based ITS modeling, which will eventually bridge the gap towards the practicality and actionability of such models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge