Jason McEwen
How can spherical CNNs benefit ML-based diffusion MRI parameter estimation?
Jul 01, 2022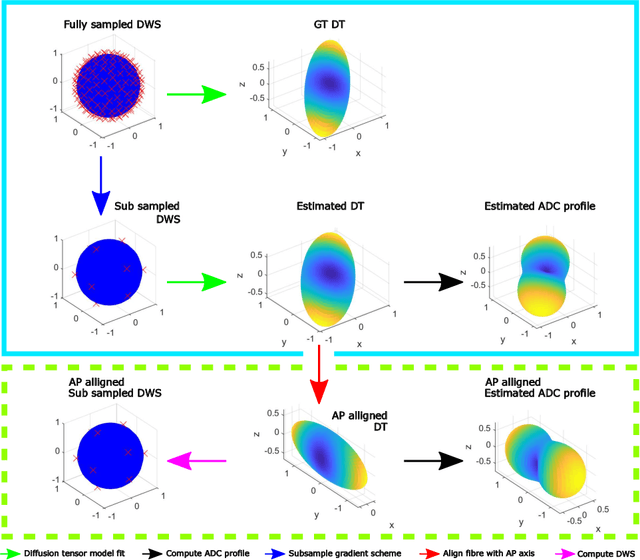
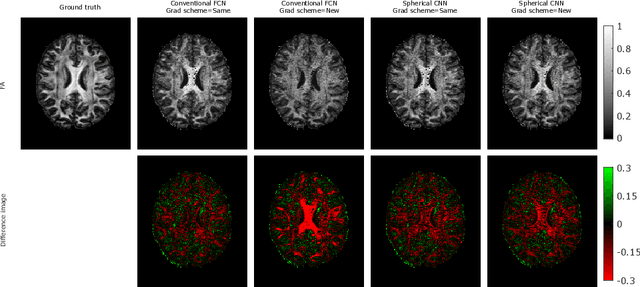
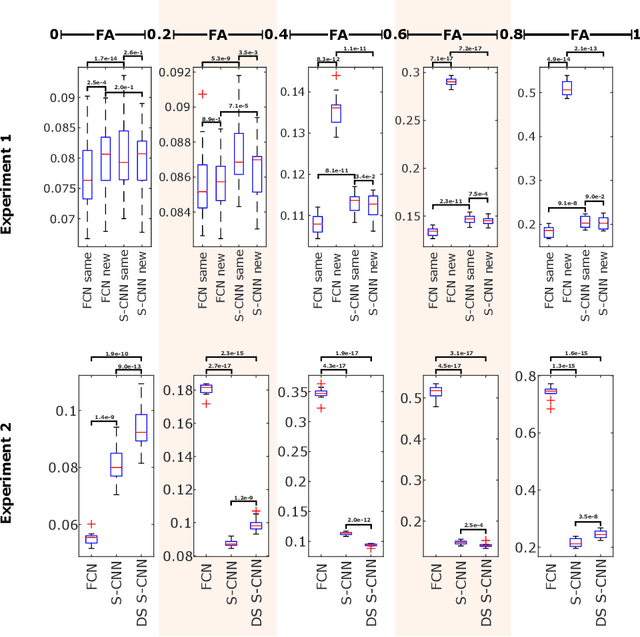
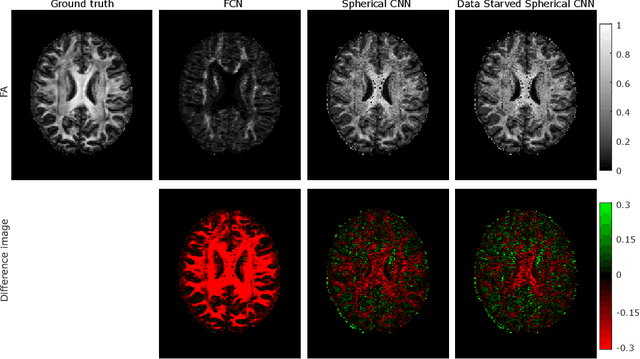
Abstract:This paper demonstrates spherical convolutional neural networks (S-CNN) offer distinct advantages over conventional fully-connected networks (FCN) at estimating scalar parameters of tissue microstructure from diffusion MRI (dMRI). Such microstructure parameters are valuable for identifying pathology and quantifying its extent. However, current clinical practice commonly acquires dMRI data consisting of only 6 diffusion weighted images (DWIs), limiting the accuracy and precision of estimated microstructure indices. Machine learning (ML) has been proposed to address this challenge. However, existing ML-based methods are not robust to differing dMRI gradient sampling schemes, nor are they rotation equivariant. Lack of robustness to sampling schemes requires a new network to be trained for each scheme, complicating the analysis of data from multiple sources. A possible consequence of the lack of rotational equivariance is that the training dataset must contain a diverse range of microstucture orientations. Here, we show spherical CNNs represent a compelling alternative that is robust to new sampling schemes as well as offering rotational equivariance. We show the latter can be leveraged to decrease the number of training datapoints required.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge