Jan-Hendrik Niemann
Data-driven model reduction of agent-based systems using the Koopman generator
Dec 14, 2020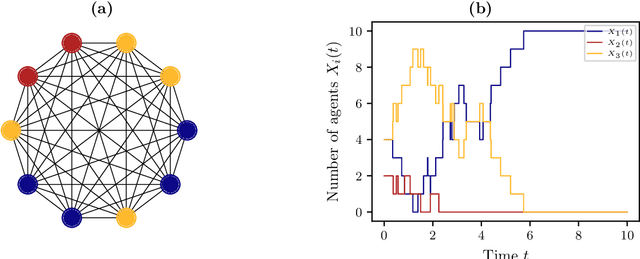

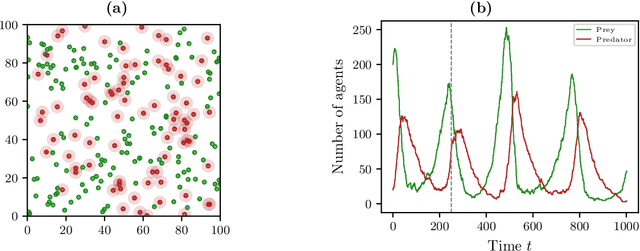

Abstract:The dynamical behavior of social systems can be described by agent-based models. Although single agents follow easily explainable rules, complex time-evolving patterns emerge due to their interaction. The simulation and analysis of such agent-based models, however, is often prohibitively time-consuming if the number of agents is large. In this paper, we show how Koopman operator theory can be used to derive reduced models of agent-based systems using only simulation or real-world data. Our goal is to learn coarse-grained models and to represent the reduced dynamics by ordinary or stochastic differential equations. The new variables are, for instance, aggregated state variables of the agent-based model, modeling the collective behavior of larger groups or the entire population. Using benchmark problems with known coarse-grained models, we demonstrate that the obtained reduced systems are in good agreement with the analytical results, provided that the numbers of agents is sufficiently large.
Data-driven approximation of the Koopman generator: Model reduction, system identification, and control
Sep 23, 2019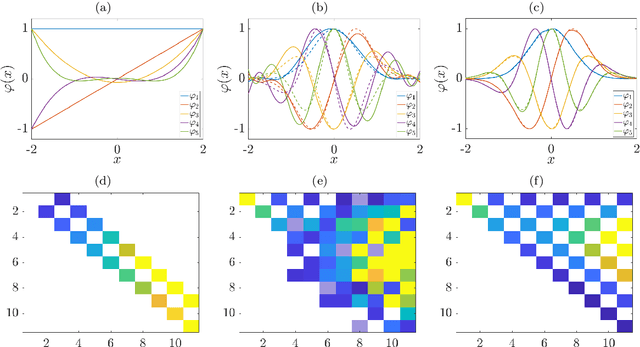
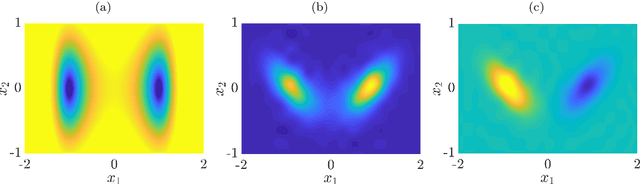
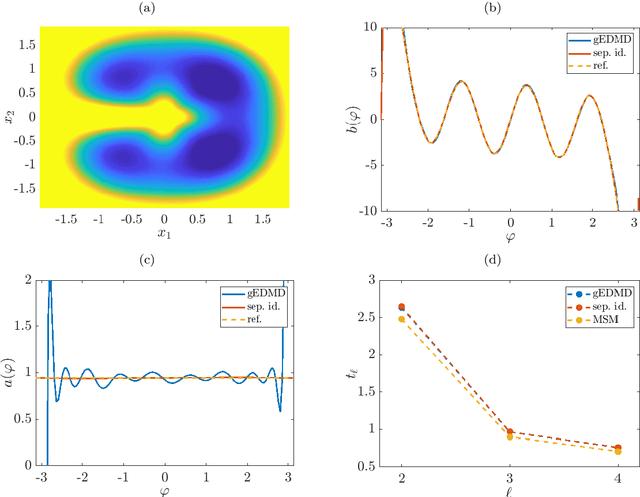
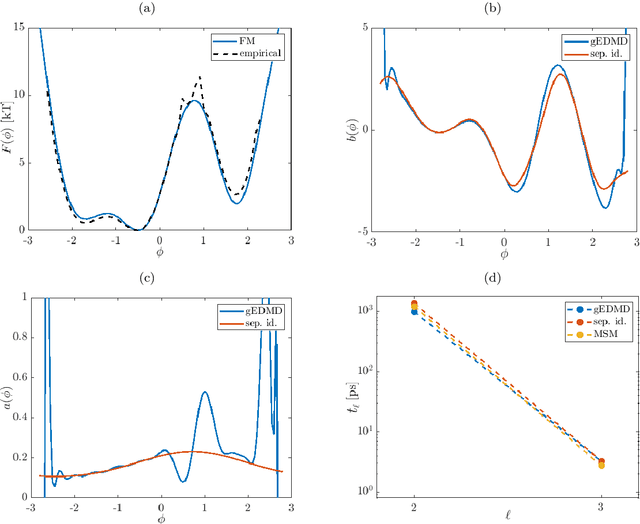
Abstract:We derive a data-driven method for the approximation of the Koopman generator called gEDMD, which can be regarded as a straightforward extension of EDMD (extended dynamic mode decomposition). This approach is applicable to deterministic and stochastic dynamical systems. It can be used for computing eigenvalues, eigenfunctions, and modes of the generator and for system identification. In addition to learning the governing equations of deterministic systems, which then reduces to SINDy (sparse identification of nonlinear dynamics), it is possible to identify the drift and diffusion terms of stochastic differential equations from data. Moreover, we apply gEDMD to derive coarse-grained models of high-dimensional systems, and also to determine efficient model predictive control strategies. We highlight relationships with other methods and demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed methods using several guiding examples and prototypical molecular dynamics problems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge