James Pitton
Deep Recurrent NMF for Speech Separation by Unfolding Iterative Thresholding
Sep 21, 2017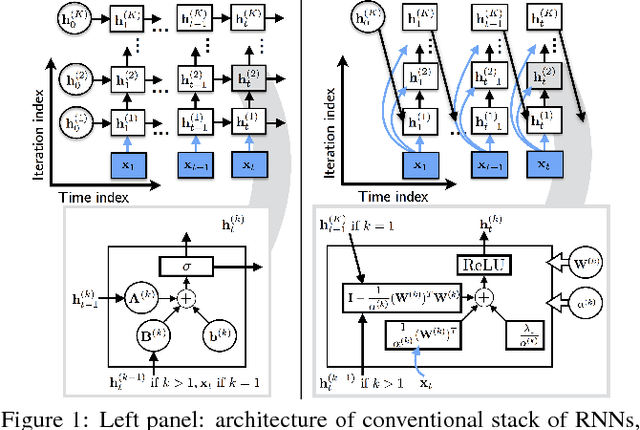
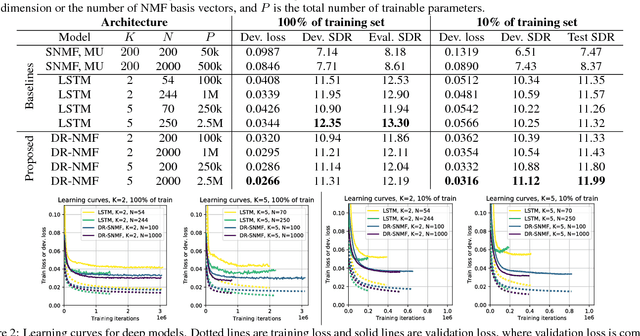
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel recurrent neural network architecture for speech separation. This architecture is constructed by unfolding the iterations of a sequential iterative soft-thresholding algorithm (ISTA) that solves the optimization problem for sparse nonnegative matrix factorization (NMF) of spectrograms. We name this network architecture deep recurrent NMF (DR-NMF). The proposed DR-NMF network has three distinct advantages. First, DR-NMF provides better interpretability than other deep architectures, since the weights correspond to NMF model parameters, even after training. This interpretability also provides principled initializations that enable faster training and convergence to better solutions compared to conventional random initialization. Second, like many deep networks, DR-NMF is an order of magnitude faster at test time than NMF, since computation of the network output only requires evaluating a few layers at each time step. Third, when a limited amount of training data is available, DR-NMF exhibits stronger generalization and separation performance compared to sparse NMF and state-of-the-art long-short term memory (LSTM) networks. When a large amount of training data is available, DR-NMF achieves lower yet competitive separation performance compared to LSTM networks.
Interpretable Recurrent Neural Networks Using Sequential Sparse Recovery
Nov 22, 2016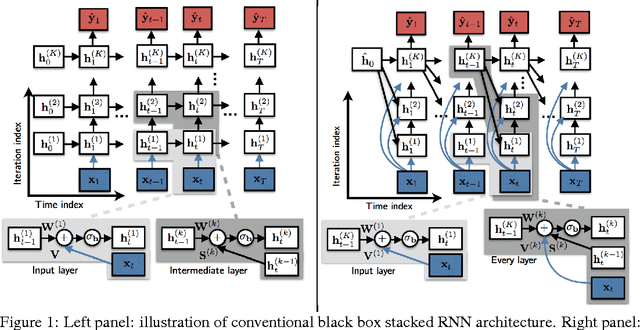
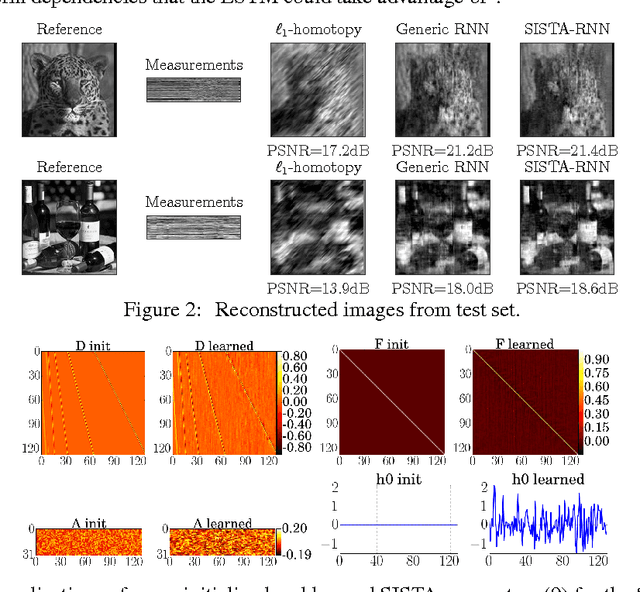
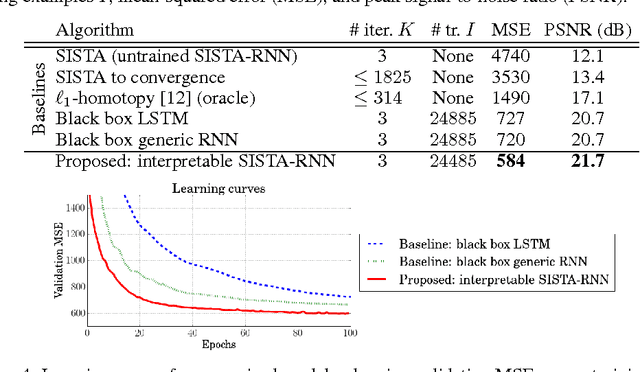
Abstract:Recurrent neural networks (RNNs) are powerful and effective for processing sequential data. However, RNNs are usually considered "black box" models whose internal structure and learned parameters are not interpretable. In this paper, we propose an interpretable RNN based on the sequential iterative soft-thresholding algorithm (SISTA) for solving the sequential sparse recovery problem, which models a sequence of correlated observations with a sequence of sparse latent vectors. The architecture of the resulting SISTA-RNN is implicitly defined by the computational structure of SISTA, which results in a novel stacked RNN architecture. Furthermore, the weights of the SISTA-RNN are perfectly interpretable as the parameters of a principled statistical model, which in this case include a sparsifying dictionary, iterative step size, and regularization parameters. In addition, on a particular sequential compressive sensing task, the SISTA-RNN trains faster and achieves better performance than conventional state-of-the-art black box RNNs, including long-short term memory (LSTM) RNNs.
Enhancement and Recognition of Reverberant and Noisy Speech by Extending Its Coherence
Sep 02, 2015
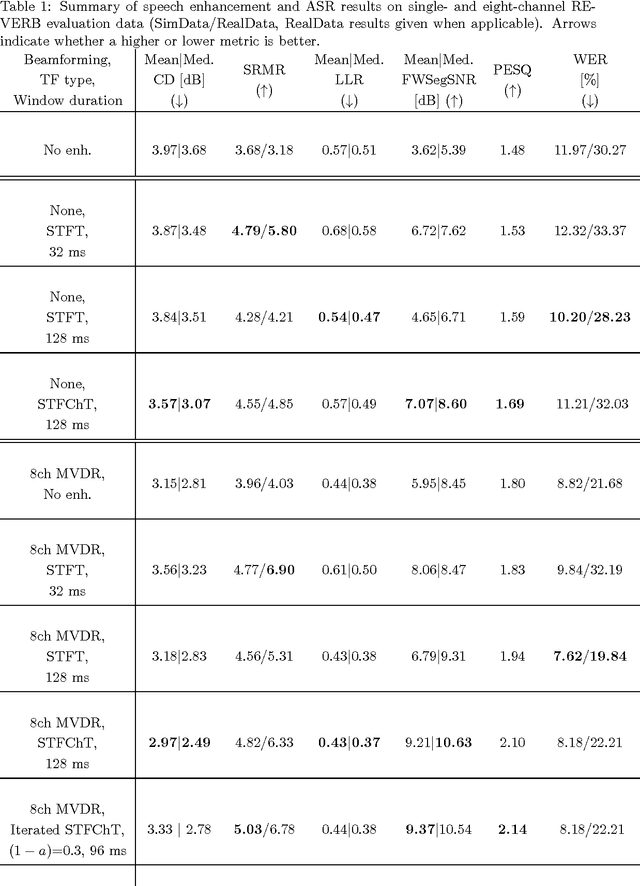
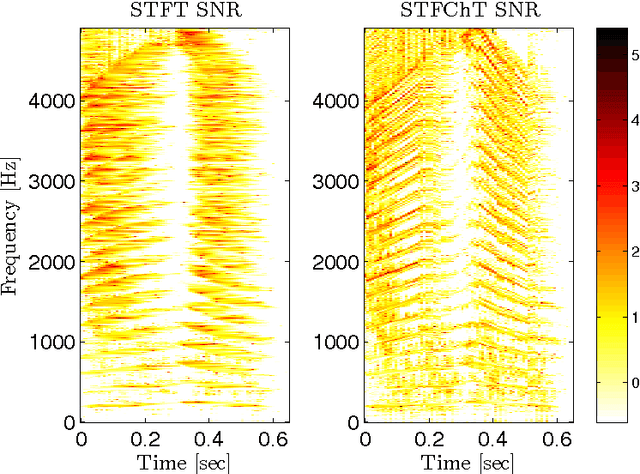
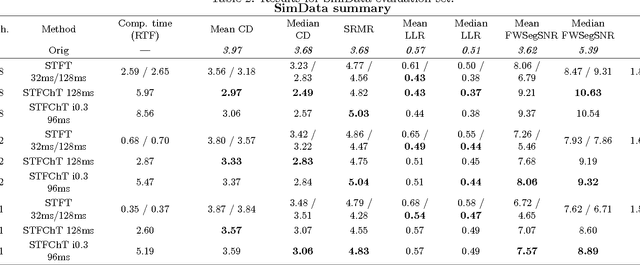
Abstract:Most speech enhancement algorithms make use of the short-time Fourier transform (STFT), which is a simple and flexible time-frequency decomposition that estimates the short-time spectrum of a signal. However, the duration of short STFT frames are inherently limited by the nonstationarity of speech signals. The main contribution of this paper is a demonstration of speech enhancement and automatic speech recognition in the presence of reverberation and noise by extending the length of analysis windows. We accomplish this extension by performing enhancement in the short-time fan-chirp transform (STFChT) domain, an overcomplete time-frequency representation that is coherent with speech signals over longer analysis window durations than the STFT. This extended coherence is gained by using a linear model of fundamental frequency variation of voiced speech signals. Our approach centers around using a single-channel minimum mean-square error log-spectral amplitude (MMSE-LSA) estimator proposed by Habets, which scales coefficients in a time-frequency domain to suppress noise and reverberation. In the case of multiple microphones, we preprocess the data with either a minimum variance distortionless response (MVDR) beamformer, or a delay-and-sum beamformer (DSB). We evaluate our algorithm on both speech enhancement and recognition tasks for the REVERB challenge dataset. Compared to the same processing done in the STFT domain, our approach achieves significant improvement in terms of objective enhancement metrics (including PESQ---the ITU-T standard measurement for speech quality). In terms of automatic speech recognition (ASR) performance as measured by word error rate (WER), our experiments indicate that the STFT with a long window is more effective for ASR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge