James Krogmeier
Constant Modulus Waveform Design with Interference Exploitation for DFRC Systems: A Block-Level Optimization Approach
Jun 27, 2024



Abstract:Dual-function radar-communication (DFRC) is a key enabler of location-based services for next-generation communication systems. In this paper, we investigate the problem of designing constant modulus waveforms for DFRC systems. For high-precision radar sensing, we consider joint optimization of the correlation properties and spatial beam pattern. For communication, we employ constructive interference-based block-level precoding (CI-BLP) to leverage distortion induced by multiuser multiple-input multiple-output (MU-MIMO) and radar transmission on a block level. We propose two solution algorithms based on the alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) and majorization-minimization (MM) principles, which are effective for small and large block sizes, respectively. The proposed ADMM-based solution decomposes the nonconvex formulated problem into multiple tractable subproblems, each of which admits a closed-form solution. To accelerate convergence of the MM-based solution, we propose an improved majorizing function that leverages a novel diagonal matrix structure. After majorization, we decompose the approximated problem into independent subproblems for parallelization, mitigating the complexity that increases with block size. We then evaluate the performance of the proposed algorithms through a series of numerical experiments. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed methods can substantially enhance spatial/temporal sidelobe suppression through block-level optimization.
Data Fusion-Based Predictive Beamforming for Downlink UAV-Assisted Massive MIMO Communication
Sep 10, 2023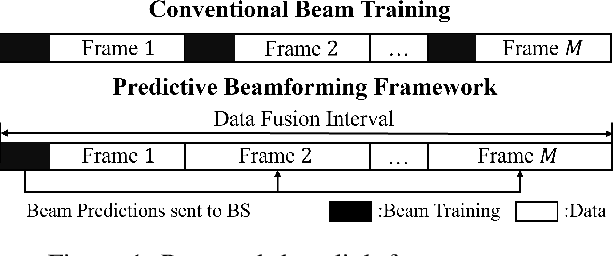
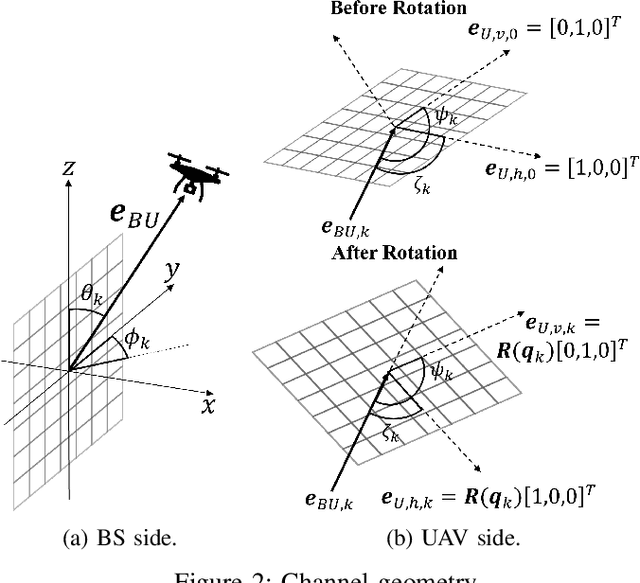
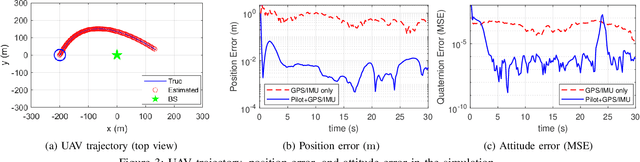
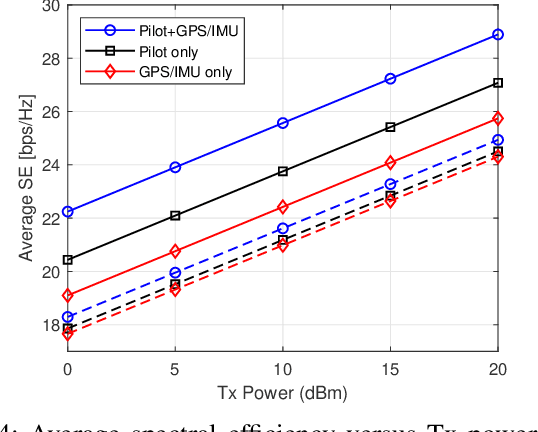
Abstract:In this letter, we propose a data fusion-based predictive beamforming scheme for unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-assisted massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) communication, which involves a base station and UAV, each equipped with a massive MIMO array. We consider aircraft dynamics to track and predict the trajectory and orientation of the UAV. To improve communication and tracking performance, we propose a novel fusion of the channel and motion data of the UAV using an extended Kalman filter (EKF). Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed scheme can improve overall spectral efficiency, particularly when the number of antennas is large.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge