James E. Warner
Generative Modeling of Random Fields from Limited Data via Constrained Latent Flow Matching
May 19, 2025Abstract:Deep generative models are promising tools for science and engineering, but their reliance on abundant, high-quality data limits applicability. We present a novel framework for generative modeling of random fields (probability distributions over continuous functions) that incorporates domain knowledge to supplement limited, sparse, and indirect data. The foundation of the approach is latent flow matching, where generative modeling occurs on compressed function representations in the latent space of a pre-trained variational autoencoder (VAE). Innovations include the adoption of a function decoder within the VAE and integration of physical/statistical constraints into the VAE training process. In this way, a latent function representation is learned that yields continuous random field samples satisfying domain-specific constraints when decoded, even in data-limited regimes. Efficacy is demonstrated on two challenging applications: wind velocity field reconstruction from sparse sensors and material property inference from a limited number of indirect measurements. Results show that the proposed framework achieves significant improvements in reconstruction accuracy compared to unconstrained methods and enables effective inference with relatively small training datasets that is intractable without constraints.
Generative Modeling of Microweather Wind Velocities for Urban Air Mobility
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:Motivated by the pursuit of safe, reliable, and weather-tolerant urban air mobility (UAM) solutions, this work proposes a generative modeling approach for characterizing microweather wind velocities. Microweather, or the weather conditions in highly localized areas, is particularly complex in urban environments owing to the chaotic and turbulent nature of wind flows. Furthermore, traditional means of assessing local wind fields are not generally viable solutions for UAM applications: 1) field measurements that would rely on permanent wind profiling systems in operational air space are not practical, 2) physics-based models that simulate fluid dynamics at a sufficiently high resolution are not computationally tractable, and 3) data-driven modeling approaches that are largely deterministic ignore the inherent variability in turbulent flows that dictates UAM reliability. Thus, advancements in predictive capabilities are needed to help mitigate the unique operational safety risks that microweather winds pose for smaller, lighter weight UAM aircraft. This work aims to model microweather wind velocities in a manner that is computationally-efficient, captures random variability, and would only require a temporary, rather than permanent, field measurement campaign. Inspired by recent breakthroughs in conditional generative AI such as text-to-image generation, the proposed approach learns a probabilistic macro-to-microweather mapping between regional weather forecasts and measured local wind velocities using generative modeling (denoising diffusion probabilistic models, flow matching, and Gaussian mixture models). A simple proof of concept was implemented using a dataset comprised of local (micro) measurements from a Sonic Detection and Ranging (SoDAR) wind profiler along with (macro) forecast data from a nearby weather station over the same time period.
Entropy-based adaptive design for contour finding and estimating reliability
May 24, 2021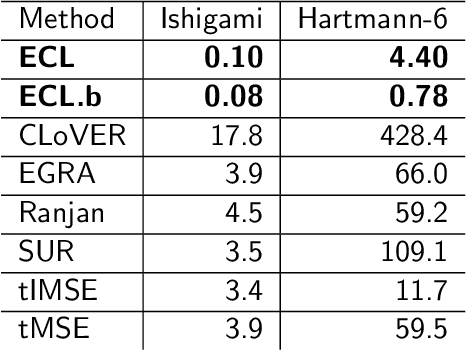
Abstract:In reliability analysis, methods used to estimate failure probability are often limited by the costs associated with model evaluations. Many of these methods, such as multifidelity importance sampling (MFIS), rely upon a computationally efficient, surrogate model like a Gaussian process (GP) to quickly generate predictions. The quality of the GP fit, particularly in the vicinity of the failure region(s), is instrumental in supplying accurately predicted failures for such strategies. We introduce an entropy-based GP adaptive design that, when paired with MFIS, provides more accurate failure probability estimates and with higher confidence. We show that our greedy data acquisition strategy better identifies multiple failure regions compared to existing contour-finding schemes. We then extend the method to batch selection, without sacrificing accuracy. Illustrative examples are provided on benchmark data as well as an application to an impact damage simulator for National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) spacesuits.
Inverse Estimation of Elastic Modulus Using Physics-Informed Generative Adversarial Networks
May 20, 2020



Abstract:While standard generative adversarial networks (GANs) rely solely on training data to learn unknown probability distributions, physics-informed GANs (PI-GANs) encode physical laws in the form of stochastic partial differential equations (PDEs) using auto differentiation. By relating observed data to unobserved quantities of interest through PDEs, PI-GANs allow for the estimation of underlying probability distributions without their direct measurement (i.e. inverse problems). The scalable nature of GANs allows high-dimensional, spatially-dependent probability distributions (i.e., random fields) to be inferred, while incorporating prior information through PDEs allows the training datasets to be relatively small. In this work, PI-GANs are demonstrated for the application of elastic modulus estimation in mechanical testing. Given measured deformation data, the underlying probability distribution of spatially-varying elastic modulus (stiffness) is learned. Two feed-forward deep neural network generators are used to model the deformation and material stiffness across a two dimensional domain. Wasserstein GANs with gradient penalty are employed for enhanced stability. In the absence of explicit training data, it is demonstrated that the PI-GAN learns to generate realistic, physically-admissible realizations of material stiffness by incorporating the PDE that relates it to the measured deformation. It is shown that the statistics (mean, standard deviation, point-wise distributions, correlation length) of these generated stiffness samples have good agreement with the true distribution.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge