Jahna Otterbacher
Crowdsourcing Lexical Diversity
Oct 30, 2024



Abstract:Lexical-semantic resources (LSRs), such as online lexicons or wordnets, are fundamental for natural language processing applications. In many languages, however, such resources suffer from quality issues: incorrect entries, incompleteness, but also, the rarely addressed issue of bias towards the English language and Anglo-Saxon culture. Such bias manifests itself in the absence of concepts specific to the language or culture at hand, the presence of foreign (Anglo-Saxon) concepts, as well as in the lack of an explicit indication of untranslatability, also known as cross-lingual \emph{lexical gaps}, when a term has no equivalent in another language. This paper proposes a novel crowdsourcing methodology for reducing bias in LSRs. Crowd workers compare lexemes from two languages, focusing on domains rich in lexical diversity, such as kinship or food. Our LingoGap crowdsourcing tool facilitates comparisons through microtasks identifying equivalent terms, language-specific terms, and lexical gaps across languages. We validated our method by applying it to two case studies focused on food-related terminology: (1) English and Arabic, and (2) Standard Indonesian and Banjarese. These experiments identified 2,140 lexical gaps in the first case study and 951 in the second. The success of these experiments confirmed the usability of our method and tool for future large-scale lexicon enrichment tasks.
Towards Algorithmic Transparency: A Diversity Perspective
Apr 12, 2021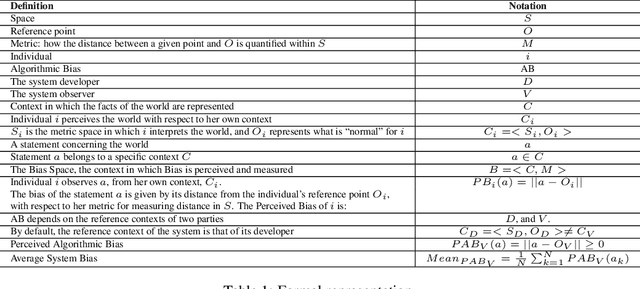
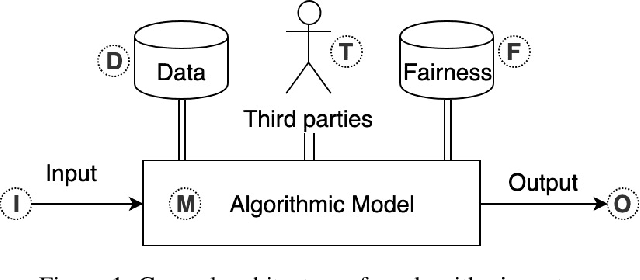
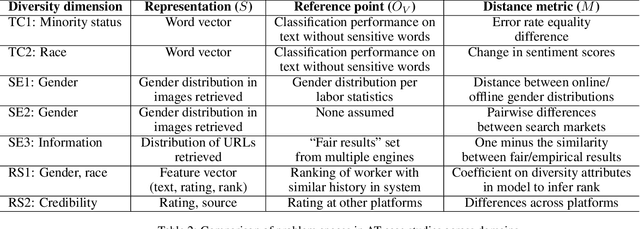
Abstract:As the role of algorithmic systems and processes increases in society, so does the risk of bias, which can result in discrimination against individuals and social groups. Research on algorithmic bias has exploded in recent years, highlighting both the problems of bias, and the potential solutions, in terms of algorithmic transparency (AT). Transparency is important for facilitating fairness management as well as explainability in algorithms; however, the concept of diversity, and its relationship to bias and transparency, has been largely left out of the discussion. We reflect on the relationship between diversity and bias, arguing that diversity drives the need for transparency. Using a perspective-taking lens, which takes diversity as a given, we propose a conceptual framework to characterize the problem and solution spaces of AT, to aid its application in algorithmic systems. Example cases from three research domains are described using our framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge