Jaeyong Park
Hybrid Beamforming for Intelligent Reflecting Surface Aided Millimeter Wave MIMO Systems
May 28, 2021



Abstract:While communication systems that employ millimeter wave (mmWave) frequency bands can support extremely high data rates, they must use large antenna arrays in order to overcome the severe propagation loss of mmWave signals. As the cost of traditional fully-digital beamforming at baseband increases rapidly with the number of antennas, hybrid beamforming that requires only a small number of radio frequency (RF) chains has been considered as a key enabling technology for mmWave communications. Intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) is another innovative technology that has been proposed as an integral element of future communication systems, establishing the favorable propagation environment in a timely manner through the use of low-cost passive reflecting elements. In this paper, we study IRS-aided mmWave multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems with hybrid beamforming architectures. We first propose the joint design of IRS reflection pattern and hybrid beamformer for narrowband MIMO systems. Then, by exploiting the sparsity of frequency-selective mmWave channels in the angular domain, we generalize the proposed joint design to broadband MIMO systems with orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) modulation. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed joint designs can significantly enhance the spectral efficiency of the systems of interest and achieve superior performance over the existing designs.
Practical Channel Estimation and Phase Shift Design for Intelligent Reflecting Surface Empowered MIMO Systems
Apr 29, 2021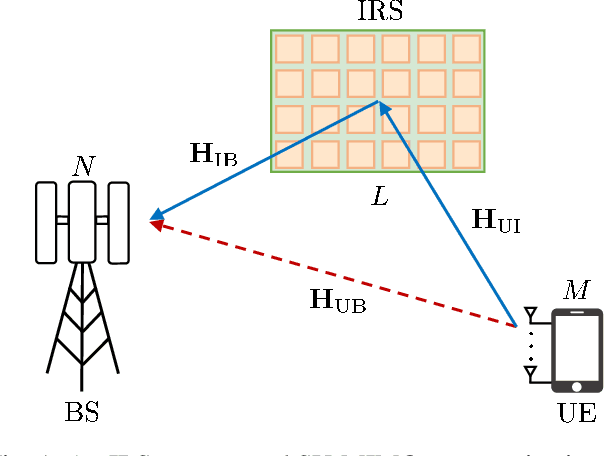
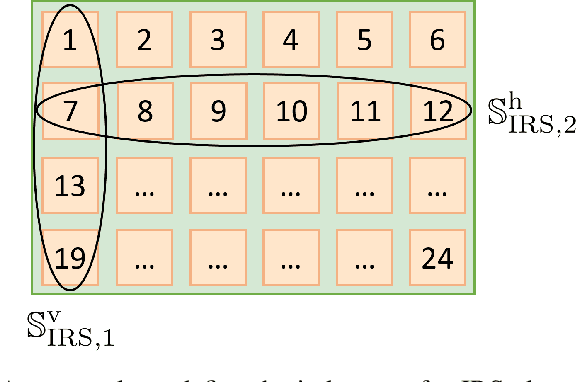
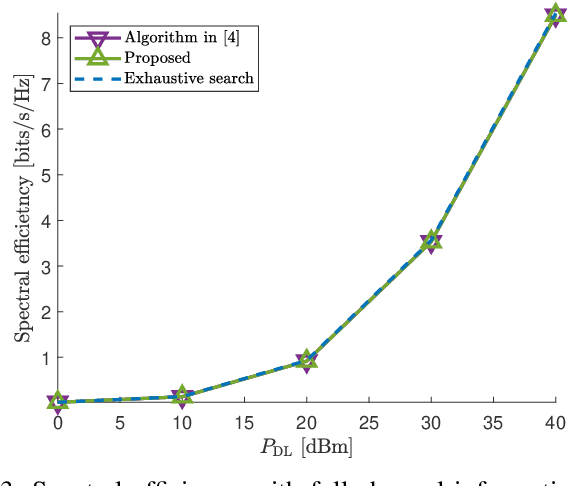
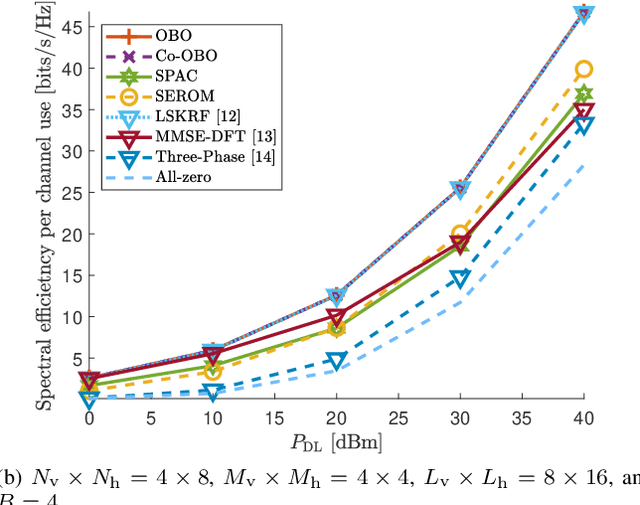
Abstract:In this paper, channel estimation techniques and phase shift design for intelligent reflecting surface (IRS)-empowered single-user multiple-input multiple-output (SU-MIMO) systems are proposed. Among four channel estimation techniques developed in the paper, the two novel ones, single-path approximated channel (SPAC) and selective emphasis on rank-one matrices (SEROM), have low training overhead to enable practical IRS-empowered SU-MIMO systems. SPAC is mainly based on parameter estimation by approximating IRS-related channels as dominant single-path channels. SEROM exploits IRS phase shifts as well as training signals for channel estimation and easily adjusts its training overhead. A closed-form solution for IRS phase shift design is also developed to maximize spectral efficiency where the solution only requires basic linear operations. Numerical results show that SPAC and SEROM combined with the proposed IRS phase shift design achieve high spectral efficiency even with low training overhead compared to existing methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge