Jaehun Song
Bitwidth-Adaptive Quantization-Aware Neural Network Training: A Meta-Learning Approach
Jul 20, 2022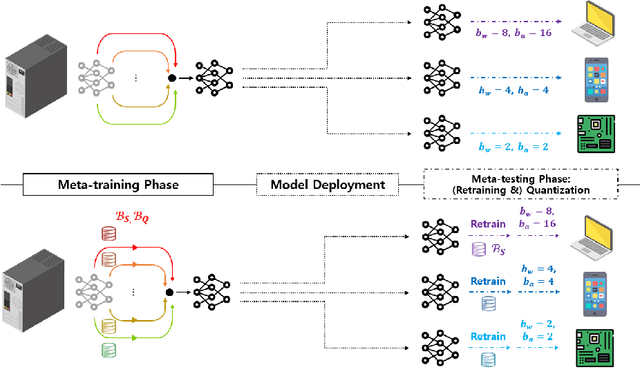


Abstract:Deep neural network quantization with adaptive bitwidths has gained increasing attention due to the ease of model deployment on various platforms with different resource budgets. In this paper, we propose a meta-learning approach to achieve this goal. Specifically, we propose MEBQAT, a simple yet effective way of bitwidth-adaptive quantization aware training (QAT) where meta-learning is effectively combined with QAT by redefining meta-learning tasks to incorporate bitwidths. After being deployed on a platform, MEBQAT allows the (meta-)trained model to be quantized to any candidate bitwidth then helps to conduct inference without much accuracy drop from quantization. Moreover, with a few-shot learning scenario, MEBQAT can also adapt a model to any bitwidth as well as any unseen target classes by adding conventional optimization or metric-based meta-learning. We design variants of MEBQAT to support both (1) a bitwidth-adaptive quantization scenario and (2) a new few-shot learning scenario where both quantization bitwidths and target classes are jointly adapted. We experimentally demonstrate their validity in multiple QAT schemes. By comparing their performance to (bitwidth-dedicated) QAT, existing bitwidth adaptive QAT and vanilla meta-learning, we find that merging bitwidths into meta-learning tasks achieves a higher level of robustness.
Personalized Federated Learning with Server-Side Information
May 23, 2022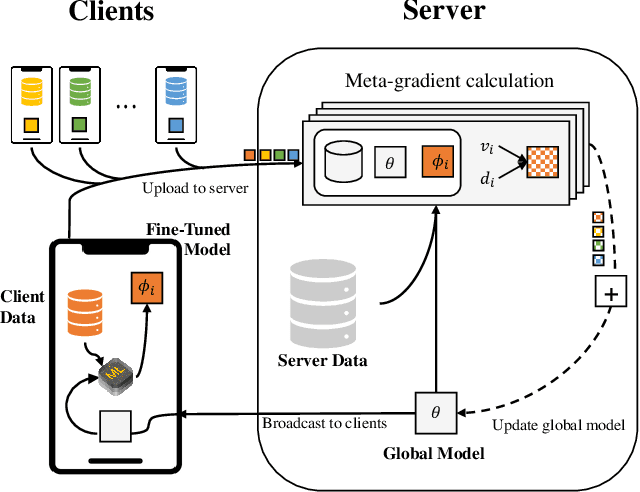
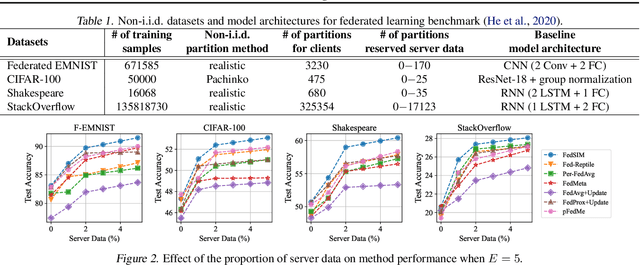
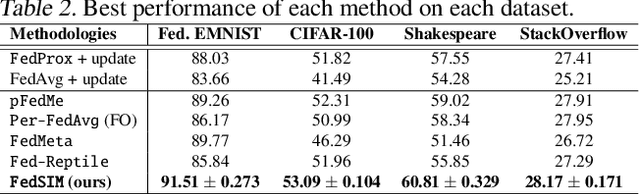
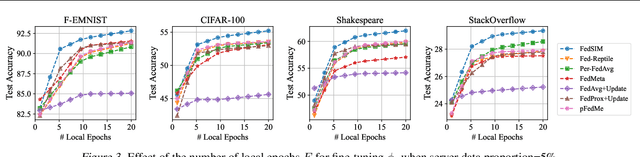
Abstract:Personalized Federated Learning (FL) is an emerging research field in FL that learns an easily adaptable global model in the presence of data heterogeneity among clients. However, one of the main challenges for personalized FL is the heavy reliance on clients' computing resources to calculate higher-order gradients since client data is segregated from the server to ensure privacy. To resolve this, we focus on a problem setting where the server may possess its own data independent of clients' data -- a prevalent problem setting in various applications, yet relatively unexplored in existing literature. Specifically, we propose FedSIM, a new method for personalized FL that actively utilizes such server data to improve meta-gradient calculation in the server for increased personalization performance. Experimentally, we demonstrate through various benchmarks and ablations that FedSIM is superior to existing methods in terms of accuracy, more computationally efficient by calculating the full meta-gradients in the server, and converges up to 34.2% faster.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge