Jae Hyeon Yoo
Provably efficient variational generative modeling of quantum many-body systems via quantum-probabilistic information geometry
Jun 09, 2022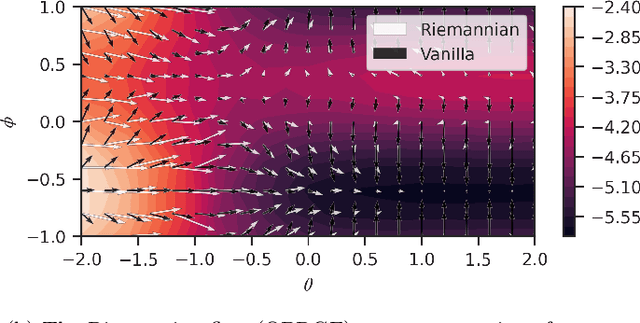
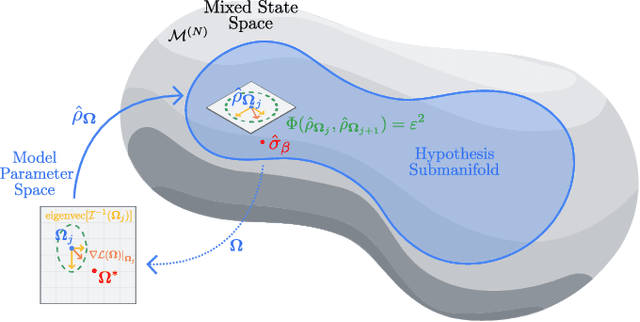
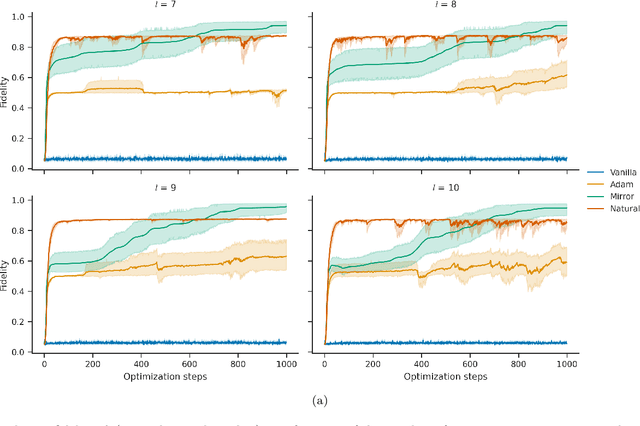
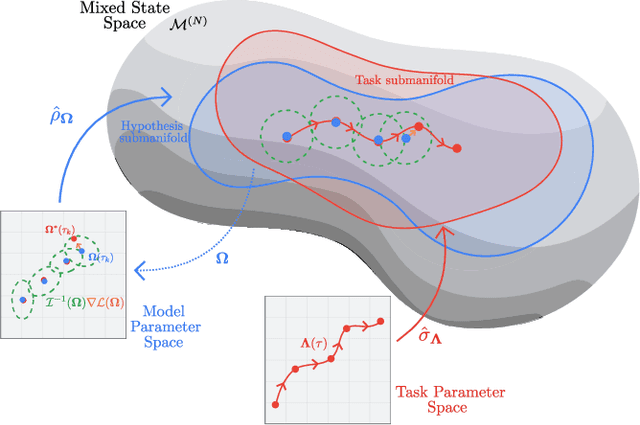
Abstract:The dual tasks of quantum Hamiltonian learning and quantum Gibbs sampling are relevant to many important problems in physics and chemistry. In the low temperature regime, algorithms for these tasks often suffer from intractabilities, for example from poor sample- or time-complexity. With the aim of addressing such intractabilities, we introduce a generalization of quantum natural gradient descent to parameterized mixed states, as well as provide a robust first-order approximating algorithm, Quantum-Probabilistic Mirror Descent. We prove data sample efficiency for the dual tasks using tools from information geometry and quantum metrology, thus generalizing the seminal result of classical Fisher efficiency to a variational quantum algorithm for the first time. Our approaches extend previously sample-efficient techniques to allow for flexibility in model choice, including to spectrally-decomposed models like Quantum Hamiltonian-Based Models, which may circumvent intractable time complexities. Our first-order algorithm is derived using a novel quantum generalization of the classical mirror descent duality. Both results require a special choice of metric, namely, the Bogoliubov-Kubo-Mori metric. To test our proposed algorithms numerically, we compare their performance to existing baselines on the task of quantum Gibbs sampling for the transverse field Ising model. Finally, we propose an initialization strategy leveraging geometric locality for the modelling of sequences of states such as those arising from quantum-stochastic processes. We demonstrate its effectiveness empirically for both real and imaginary time evolution while defining a broader class of potential applications.
TensorFlow Quantum: A Software Framework for Quantum Machine Learning
Mar 06, 2020
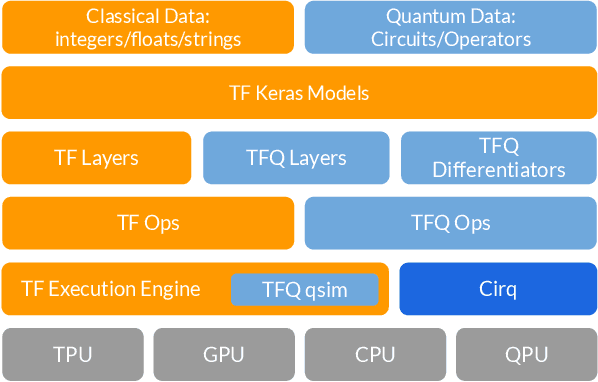
Abstract:We introduce TensorFlow Quantum (TFQ), an open source library for the rapid prototyping of hybrid quantum-classical models for classical or quantum data. This framework offers high-level abstractions for the design and training of both discriminative and generative quantum models under TensorFlow and supports high-performance quantum circuit simulators. We provide an overview of the software architecture and building blocks through several examples and review the theory of hybrid quantum-classical neural networks. We illustrate TFQ functionalities via several basic applications including supervised learning for quantum classification, quantum control, and quantum approximate optimization. Moreover, we demonstrate how one can apply TFQ to tackle advanced quantum learning tasks including meta-learning, Hamiltonian learning, and sampling thermal states. We hope this framework provides the necessary tools for the quantum computing and machine learning research communities to explore models of both natural and artificial quantum systems, and ultimately discover new quantum algorithms which could potentially yield a quantum advantage.
Large-scale Video Classification guided by Batch Normalized LSTM Translator
Jul 13, 2017


Abstract:Youtube-8M dataset enhances the development of large-scale video recognition technology as ImageNet dataset has encouraged image classification, recognition and detection of artificial intelligence fields. For this large video dataset, it is a challenging task to classify a huge amount of multi-labels. By change of perspective, we propose a novel method by regarding labels as words. In details, we describe online learning approaches to multi-label video classification that are guided by deep recurrent neural networks for video to sentence translator. We designed the translator based on LSTMs and found out that a stochastic gating before the input of each LSTM cell can help us to design the structural details. In addition, we adopted batch normalizations into our models to improve our LSTM models. Since our models are feature extractors, they can be used with other classifiers. Finally we report improved validation results of our models on large-scale Youtube-8M datasets and discussions for the further improvement.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge