Jacob A. George
Discrimination Among Multiple Cutaneous and Proprioceptive Hand Percepts Evoked by Nerve Stimulation with Utah Slanted Electrode Arrays in Human Amputees
Mar 07, 2020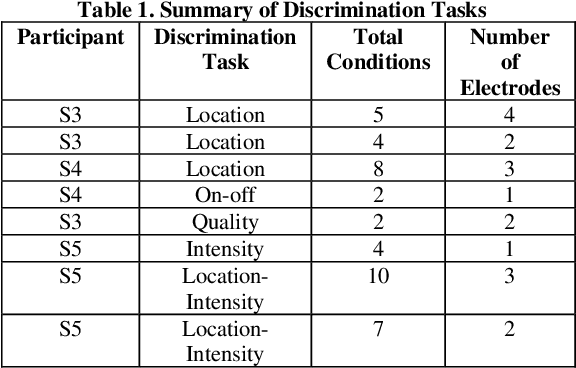
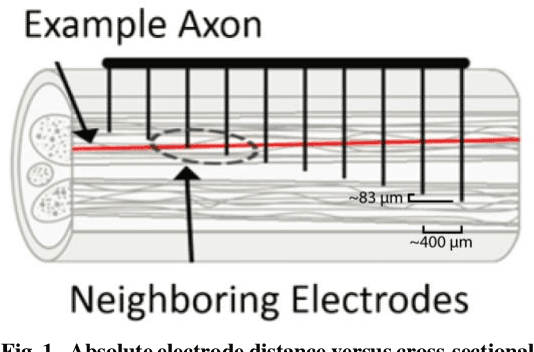
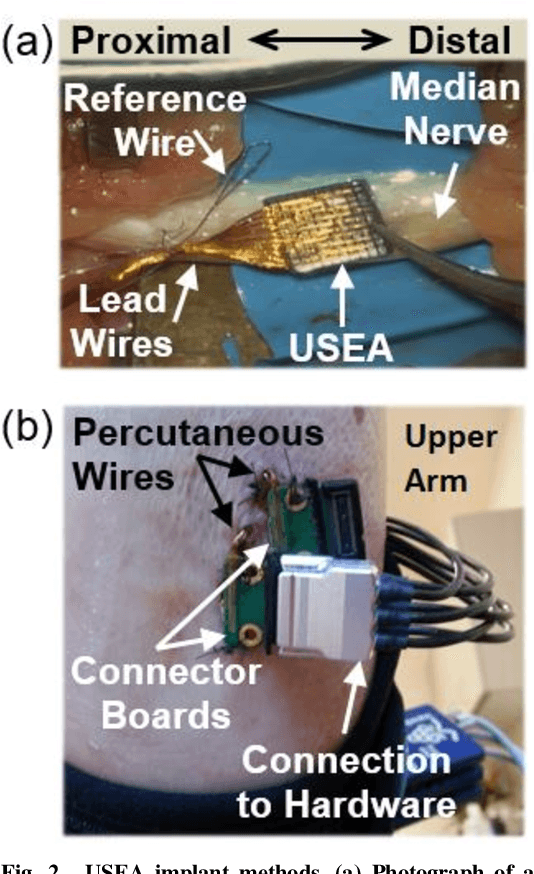
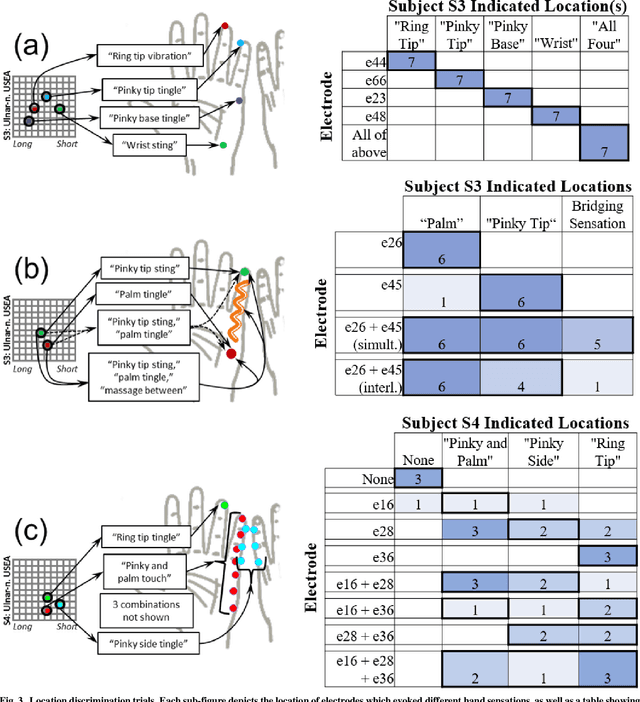
Abstract:Objective: This paper aims to demonstrate functional discriminability among restored hand sensations with different locations, qualities, and intensities that are evoked by microelectrode stimulation of residual afferent fibers in human amputees. Methods: We implanted a Utah Slanted Electrode Array (USEA) in the median and ulnar residual arm nerves of three transradial amputees and delivered stimulation via different electrodes and at different frequencies to produce various locations, qualities, and intensities of sensation on the missing hand. Blind discrimination trials were performed to determine how well subjects could discriminate among these restored sensations. Results: Subjects discriminated among restored sensory percepts with varying cutaneous and proprioceptive locations, qualities, and intensities in blind trials, including discrimination among up to 10 different location-intensity combinations (15/30 successes, p < 0.0005). Variations in the site of stimulation within the nerve, via electrode selection, enabled discrimination among up to 5 locations and qualities (35/35 successes, p < 0.0001). Variations in the stimulation frequency enabled discrimination among 4 different intensities at the same location (13/20 successes, p < 0.005). One subject discriminated among simultaneous, alternating, and isolated stimulation of two different USEA electrodes, as may be desired during multi-sensor closed-loop prosthesis use (20/25 successes, p < 0.001). Conclusion: USEA stimulation enables encoding of a diversity of functionally discriminable sensations with different locations, qualities, and intensities. Significance: These percepts provide a potentially rich source of sensory feedback that may enhance performance and embodiment during multi-sensor, closed-loop prosthesis use.
Inexpensive surface electromyography sleeve with consistent electrode placement enables dexterous and stable prosthetic control through deep learning
Feb 28, 2020



Abstract:The dexterity of conventional myoelectric prostheses is limited in part by the small datasets used to train the control algorithms. Variations in surface electrode positioning make it difficult to collect consistent data and to estimate motor intent reliably over time. To address these challenges, we developed an inexpensive, easy-to-don sleeve that can record robust and repeatable surface electromyography from 32 embedded monopolar electrodes. Embedded grommets are used to consistently align the sleeve with natural skin markings (e.g., moles, freckles, scars). The sleeve can be manufactured in a few hours for less than $60. Data from seven intact participants show the sleeve provides a signal-to-noise ratio of 14, a don-time under 11 seconds, and sub-centimeter precision for electrode placement. Furthermore, in a case study with one intact participant, we use the sleeve to demonstrate that neural networks can provide simultaneous and proportional control of six degrees of freedom, even 263 days after initial algorithm training. We also highlight that consistent recordings, accumulated over time to establish a large dataset, significantly improve dexterity. These results suggest that deep learning with a 74-layer neural network can substantially improve the dexterity and stability of myoelectric prosthetic control, and that deep-learning techniques can be readily instantiated and further validated through inexpensive sleeves/sockets with consistent recording locations.
Intensity Discriminability of Electrocutaneous and Intraneural Stimulation Pulse Frequency in Intact Individuals and Amputees
Jan 23, 2020



Abstract:Electrical stimulation of residual nerves can be used to provide amputees with intuitive sensory feedback. An important aspect of this artificial sensory feedback is the ability to convey the magnitude of tactile stimuli. Using classical psychophysical methods, we quantified the just-noticeable differences for electrocutaneous stimulation pulse frequency in both intact participants and one transradial amputee. For the transradial amputee, we also quantified the just-noticeable difference of intraneural microstimulation pulse frequency via chronically implanted Utah Slanted Electrode Arrays. We demonstrate that intensity discrimination is similar across conditions: intraneural microstimulation of the residual nerves, electrocutaneous stimulation of the reinnervated skin on the residual limb, and electrocutaneous stimulation of intact hands. We also show that intensity discrimination performance is significantly better at lower pulse frequencies than at higher ones - a finding that's unique to electrocutaneous and intraneural stimulation and suggests that supplemental sensory cues may be present at lower pulse frequencies. These results can help guide the implementation of artificial sensory feedback for sensorized bionic arms.
Bilaterally Mirrored Movements Improve the Accuracy and Precision of Training Data for Supervised Learning of Neural or Myoelectric Prosthetic Control
Jan 23, 2020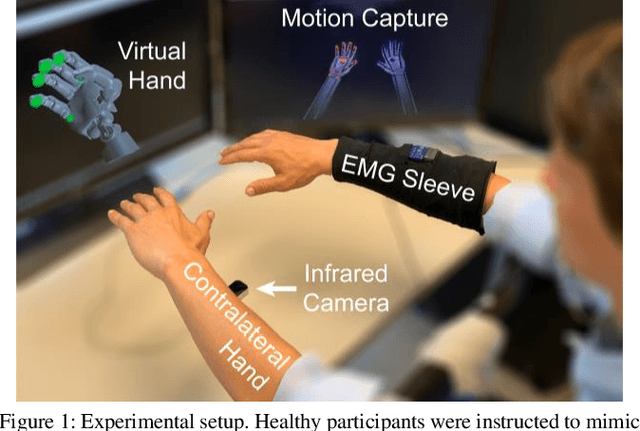
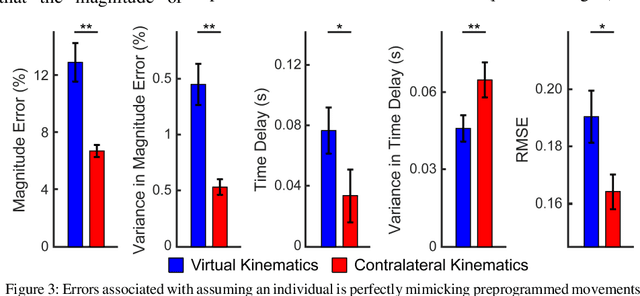
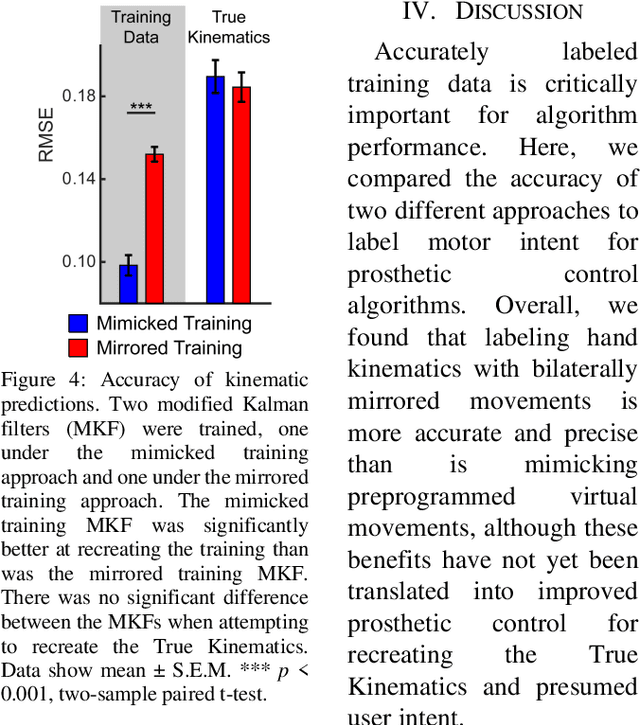
Abstract:Intuitive control of prostheses relies on training algorithms to correlate biological recordings to motor intent. The quality of the training dataset is critical to run-time performance, but it is difficult to label hand kinematics accurately after the hand has been amputated. We quantified the accuracy and precision of labeling hand kinematics for two different approaches: 1) assuming a participant is perfectly mimicking predetermined motions of a prosthesis (mimicked training), and 2) assuming a participant is perfectly mirroring their contralateral hand during identical bilateral movements (mirrored training). We compared these approaches in non-amputee individuals, using an infrared camera to track eight different joint angles of the hands in real-time. Aggregate data revealed that mimicked training does not account for biomechanical coupling or temporal changes in hand posture. Mirrored training was significantly more accurate and precise at labeling hand kinematics. However, when training a modified Kalman filter to estimate motor intent, the mimicked and mirrored training approaches were not significantly different. The results suggest that the mirrored training approach creates a more faithful but more complex dataset. Advanced algorithms, more capable of learning the complex mirrored training dataset, may yield better run-time prosthetic control.
Inexpensive and Portable System for Dexterous High-Density Myoelectric Control of Multiarticulate Prostheses
Jan 23, 2020



Abstract:Multiarticulate bionic arms are now capable of mimicking the endogenous movements of the human hand. 3D-printing has reduced the cost of prosthetic hands themselves, but there is currently no low-cost alternative to dexterous electromyographic (EMG) control systems. To address this need, we developed an inexpensive (~$675) and portable EMG control system by integrating low-cost microcontrollers with an EMG acquisition device. We validated signal acquisition by comparing the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of our system with that of a high-end research-grade system. We also demonstrate the ability to use the low-cost control system for proportional and independent control of various prosthetic hands in real-time. We found that the SNR of the low-cost control system was statistically no worse than 44% of the SNR of a research-grade control system. The RMSEs of predicted hand movements (from a modified Kalman filter) were typically a few percent better than, and not more than 6% worse than, RMSEs of a research-grade system for up to six degrees of freedom when only relatively few (six) EMG electrodes were used. However, RMSEs were generally higher than RMSEs of research-grade systems that utilize considerably more (32) EMG electrodes, guiding future work towards increasing electrode count. Successful instantiation of this low-cost control system constitutes an important step towards the commercialization and wide-spread availability of dexterous bionic hands.
Intuitive Neuromyoelectric Control of a Dexterous Bionic Arm Using a Modified Kalman Filter
Oct 10, 2019
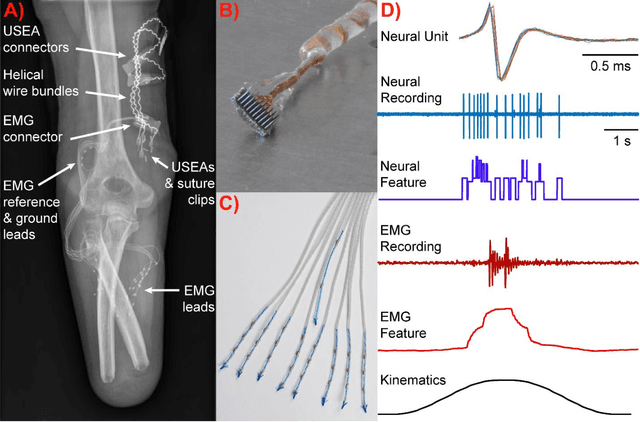
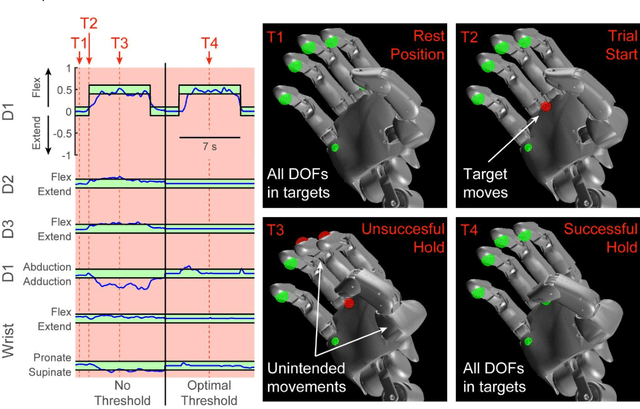
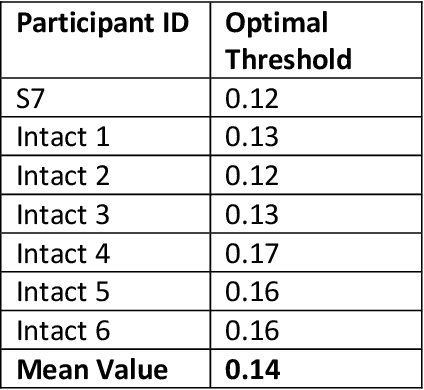
Abstract:Background: Multi-articulate prostheses are capable of performing dexterous hand movements. However, clinically available control strategies fail to provide users with intuitive, independent and proportional control over multiple degrees of freedom (DOFs) in real-time. New Method: We detail the use of a modified Kalman filter (MKF) to provide intuitive, independent and proportional control over six-DOF prostheses such as the DEKA "LUKE" Arm. Input features include neural firing rates recorded from Utah Slanted Electrode Arrays and mean absolute value of intramuscular electromyographic (EMG) recordings. Ad-hoc modifications include thresholds and non-unity gains on the output of a Kalman filter. Results: We demonstrate that both neural and EMG data can be combined effectively. We also highlight that modifications can be optimized to significantly improve performance relative to an unmodified Kalman filter. Thresholds significantly reduced unintended movement and promoted more independent control of the different DOFs. Gain were significantly greater than one and served to amplify participant effort. Optimal modifications can be determined quickly offline and translate to functional improvements online. Using a portable take-home system, participants performed various activities of daily living. Comparison with Existing Methods: In contrast to pattern recognition, the MKF allows users to continuously modulate their force output, which is critical for fine dexterity. The MKF is also computationally efficient and can be trained in less than five minutes. Conclusions: The MKF can be used to explore the functional and psychological benefits associated with long-term, at-home control of dexterous prosthetic hands.
A Modular Transradial Bypass Socket for Surface Myoelectric Prosthetic Control in Non-Amputees
Sep 26, 2019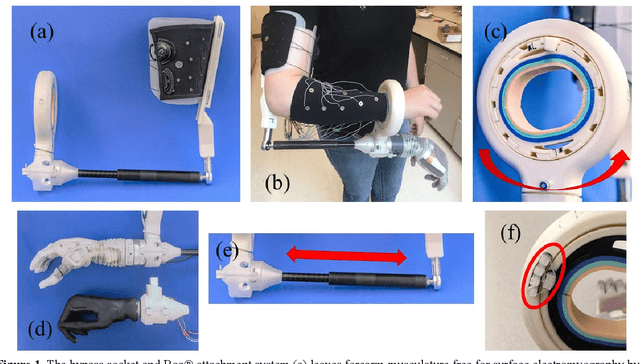
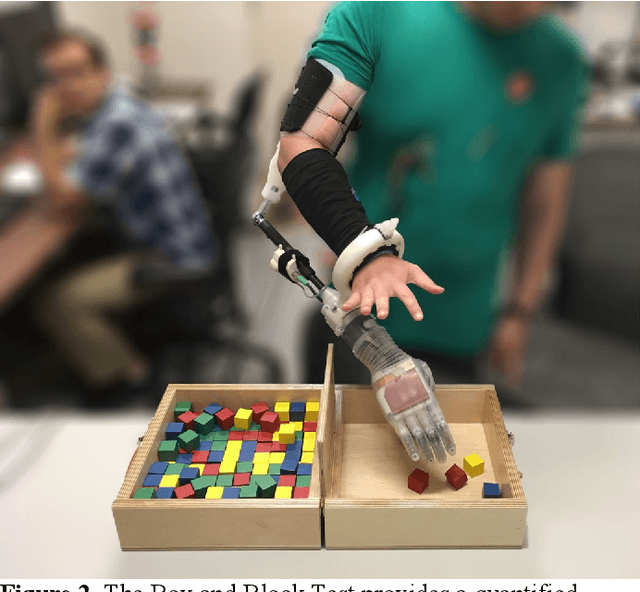
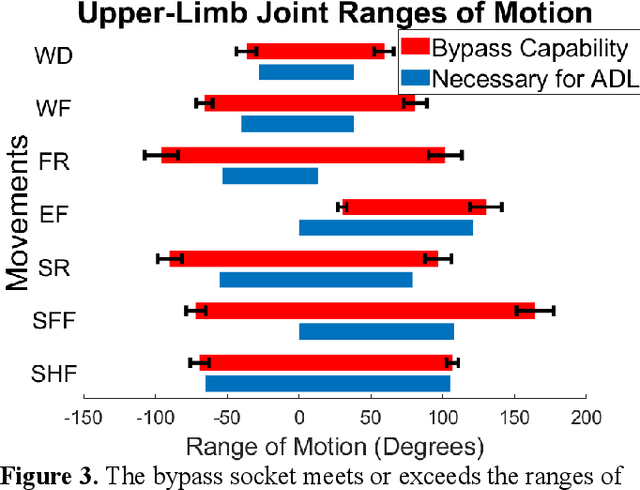
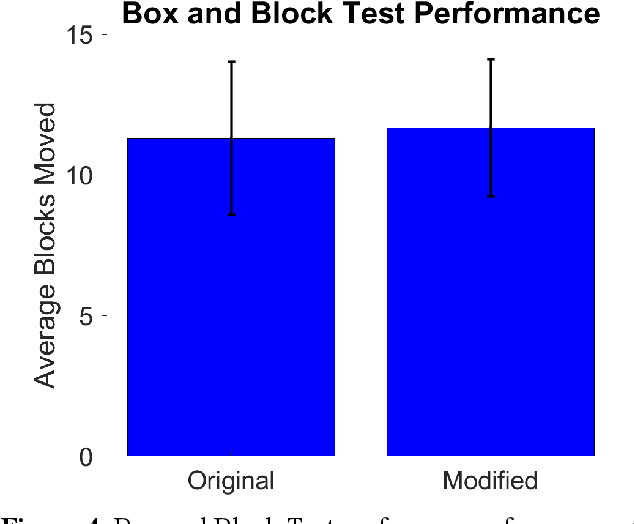
Abstract:Bypass sockets allow researchers to perform tests of prosthetic systems from the prosthetic user's perspective. We designed a modular upper-limb bypass socket with 3D-printed components that can be easily modified for use with a variety of terminal devices. Our bypass socket preserves access to forearm musculature and the hand, which are necessary for surface electromyography and to provide substituted sensory feedback. Our bypass socket allows a sufficient range of motion to complete tasks in the frontal working area, as measured on non-amputee participants. We examined the performance of non-amputee participants using the bypass socket on the original and modified Box and Block Tests. Participants moved 11.3 +/- 2.7 and 11.7 +/- 2.4 blocks in the original and modified Box and Block Tests (mean +/- SD), respectively, within the range of reported scores using amputee participants. Range-of-motion for users wearing the bypass socket meets or exceeds most reported range-of-motion requirements for activities of daily living. The bypass socket was originally designed with a freely rotating wrist; we found that adding elastic resistance to user wrist rotation while wearing the bypass socket had no significant effect on motor decode performance. We have open-sourced the design files and an assembly manual for the bypass socket. We anticipate that the bypass socket will be a useful tool to evaluate and develop sensorized myoelectric prosthesis technology.
* 8 pages, 5 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge