Jacky Visser
Toward Reasonable Parrots: Why Large Language Models Should Argue with Us by Design
May 08, 2025

Abstract:In this position paper, we advocate for the development of conversational technology that is inherently designed to support and facilitate argumentative processes. We argue that, at present, large language models (LLMs) are inadequate for this purpose, and we propose an ideal technology design aimed at enhancing argumentative skills. This involves re-framing LLMs as tools to exercise our critical thinking rather than replacing them. We introduce the concept of 'reasonable parrots' that embody the fundamental principles of relevance, responsibility, and freedom, and that interact through argumentative dialogical moves. These principles and moves arise out of millennia of work in argumentation theory and should serve as the starting point for LLM-based technology that incorporates basic principles of argumentation.
Extracting Implicitly Asserted Propositions in Argumentation
Oct 06, 2020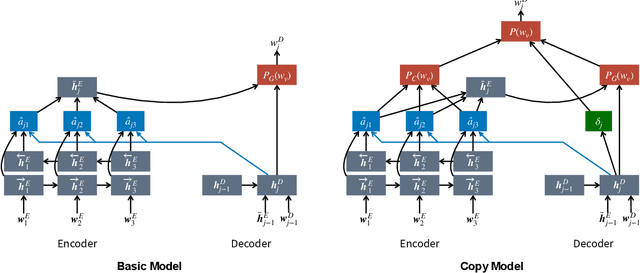
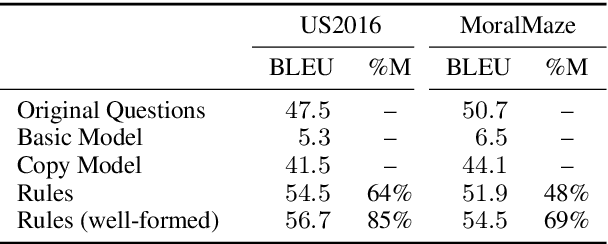

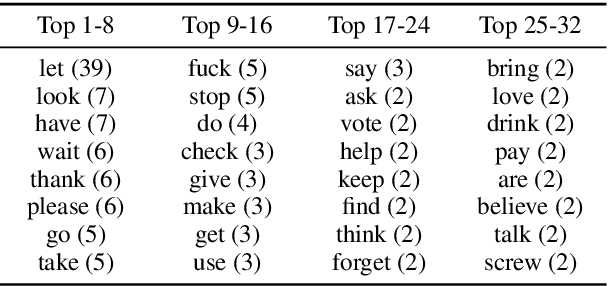
Abstract:Argumentation accommodates various rhetorical devices, such as questions, reported speech, and imperatives. These rhetorical tools usually assert argumentatively relevant propositions rather implicitly, so understanding their true meaning is key to understanding certain arguments properly. However, most argument mining systems and computational linguistics research have paid little attention to implicitly asserted propositions in argumentation. In this paper, we examine a wide range of computational methods for extracting propositions that are implicitly asserted in questions, reported speech, and imperatives in argumentation. By evaluating the models on a corpus of 2016 U.S. presidential debates and online commentary, we demonstrate the effectiveness and limitations of the computational models. Our study may inform future research on argument mining and the semantics of these rhetorical devices in argumentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge