Jaap Suermondt
Updating Probabilities in Multiply-Connected Belief Networks
Mar 27, 2013



Abstract:This paper focuses on probability updates in multiply-connected belief networks. Pearl has designed the method of conditioning, which enables us to apply his algorithm for belief updates in singly-connected networks to multiply-connected belief networks by selecting a loop-cutset for the network and instantiating these loop-cutset nodes. We discuss conditions that need to be satisfied by the selected nodes. We present a heuristic algorithm for finding a loop-cutset that satisfies these conditions.
Bounded Conditioning: Flexible Inference for Decisions under Scarce Resources
Mar 27, 2013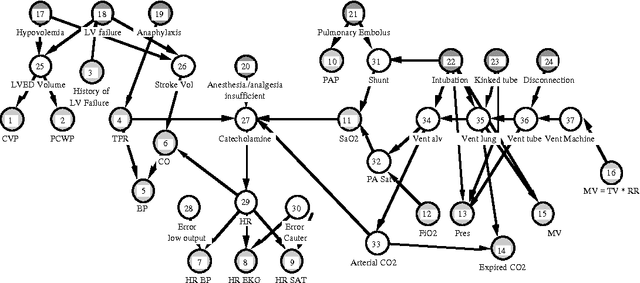
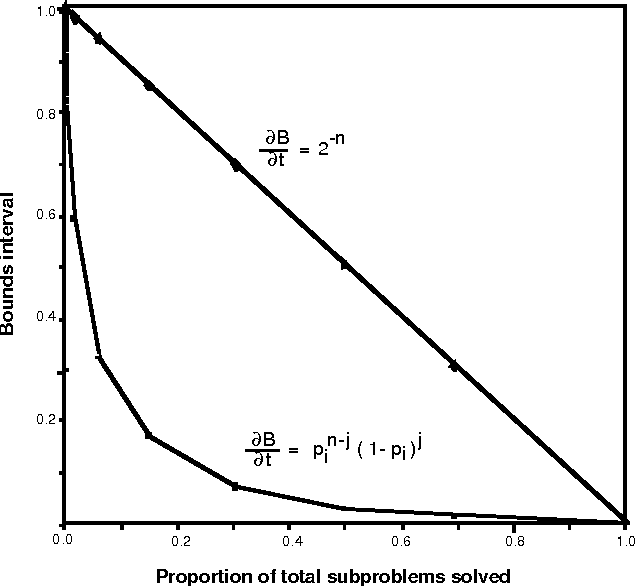
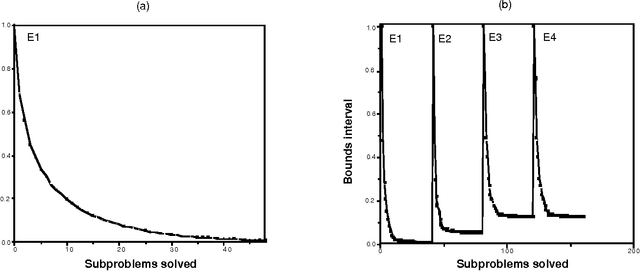
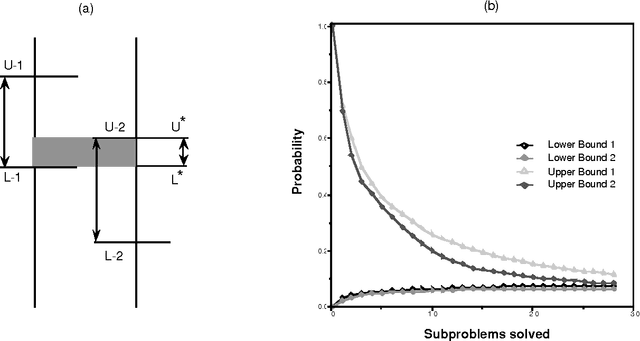
Abstract:We introduce a graceful approach to probabilistic inference called bounded conditioning. Bounded conditioning monotonically refines the bounds on posterior probabilities in a belief network with computation, and converges on final probabilities of interest with the allocation of a complete resource fraction. The approach allows a reasoner to exchange arbitrary quantities of computational resource for incremental gains in inference quality. As such, bounded conditioning holds promise as a useful inference technique for reasoning under the general conditions of uncertain and varying reasoning resources. The algorithm solves a probabilistic bounding problem in complex belief networks by breaking the problem into a set of mutually exclusive, tractable subproblems and ordering their solution by the expected effect that each subproblem will have on the final answer. We introduce the algorithm, discuss its characterization, and present its performance on several belief networks, including a complex model for reasoning about problems in intensive-care medicine.
A Combination of Cutset Conditioning with Clique-Tree Propagation in the Pathfinder System
Mar 27, 2013Abstract:Cutset conditioning and clique-tree propagation are two popular methods for performing exact probabilistic inference in Bayesian belief networks. Cutset conditioning is based on decomposition of a subset of network nodes, whereas clique-tree propagation depends on aggregation of nodes. We describe a means to combine cutset conditioning and clique- tree propagation in an approach called aggregation after decomposition (AD). We discuss the application of the AD method in the Pathfinder system, a medical expert system that offers assistance with diagnosis in hematopathology.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge