J. Zhao
Self Generated Wargame AI: Double Layer Agent Task Planning Based on Large Language Model
Dec 02, 2023Abstract:The big language model represented by ChatGPT has had a disruptive impact on the field of artificial intelligence. But it mainly focuses on Natural language processing, speech recognition, machine learning and natural-language understanding. This paper innovatively applies the big language model to the field of intelligent decision-making, places the big language model in the decision-making center, and constructs an agent architecture with the big language model as the core. Based on this, it further proposes a two-layer agent task planning, issues and executes decision commands through the interaction of natural language, and carries out simulation verification through the wargame simulation environment. Through the game confrontation simulation experiment, it is found that the intelligent decision-making ability of the big language model is significantly stronger than the commonly used reinforcement learning AI and rule AI, and the intelligence, understandability and generalization are all better. And through experiments, it was found that the intelligence of the large language model is closely related to prompt. This work also extends the large language model from previous human-computer interaction to the field of intelligent decision-making, which has important reference value and significance for the development of intelligent decision-making.
Enhancing Functional Data Analysis with Sequential Neural Networks: Advantages and Comparative Study
Nov 03, 2023Abstract:Functional Data Analysis (FDA) is a statistical domain developed to handle functional data characterized by high dimensionality and complex data structures. Sequential Neural Networks (SNNs) are specialized neural networks capable of processing sequence data, a fundamental aspect of functional data. Despite their great flexibility in modeling functional data, SNNs have been inadequately employed in the FDA community. One notable advantage of SNNs is the ease of implementation, making them accessible to a broad audience beyond academia. Conversely, FDA-based methodologies present challenges, particularly for practitioners outside the field, due to their intricate complexity. In light of this, we propose utilizing SNNs in FDA applications and demonstrate their effectiveness through comparative analyses against popular FDA regression models based on numerical experiments and real-world data analysis. SNN architectures allow us to surpass the limitations of traditional FDA methods, offering scalability, flexibility, and improved analytical performance. Our findings highlight the potential of SNN-based methodologies as powerful tools for data applications involving functional data.
Rolling control and dynamics model of two section articulated-wing ornithopter
Jun 15, 2023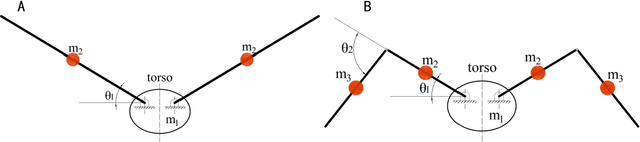

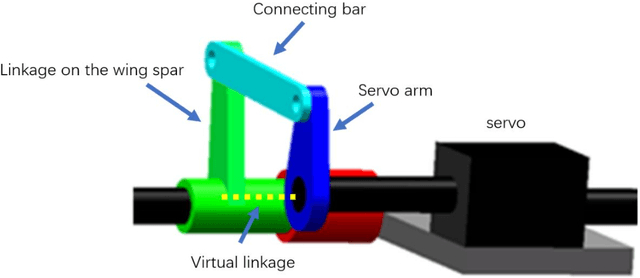
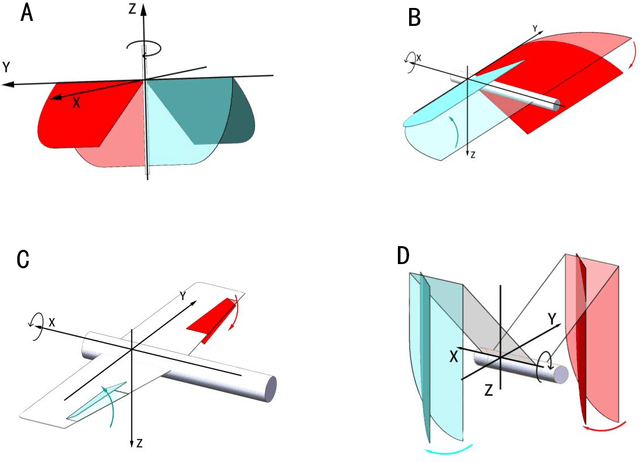
Abstract:This paper invented a new rolling control mechanism of two section articulated-wing ornithopter, which is analogues to aileron control in plane, however, similar control mechanism leads to opposite result, indicating the ornithopter supposed to go left now go right instead. This research gives a qualitative dynamics model which explains this new phenomenon. Because of wing folding, the differential rotation of outer-section wing (analogues to aileron in plane, left aileron up and right aileron down make left turn) around pitch axis becomes common mode rotation around yaw axis,leading its rotating torque changing from left-handed rotation (using left-handed as example, right-handed is the same) around roll axis to a common mode force pointing to front-right (northeast, NE) direction from first player's view of the ornithopter.Because most of the flapping movement is in the upper hemisphere from ornithopter's view, the NE force is above on the center of mass of the orthopter, generating a right-handed moment around roll axis. Therefore, the ornithopter supposed to go left now goes right. This phenomenon is a unique and only observed in two section articulated-wing ornithopter by far. Many field tests conducted by authors confirm it is highly repetitive.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge