J. Glenn Morris
Joint Application of the Target Trial Causal Framework and Machine Learning Modeling to Optimize Antibiotic Therapy: Use Case on Acute Bacterial Skin and Skin Structure Infections due to Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Jul 15, 2022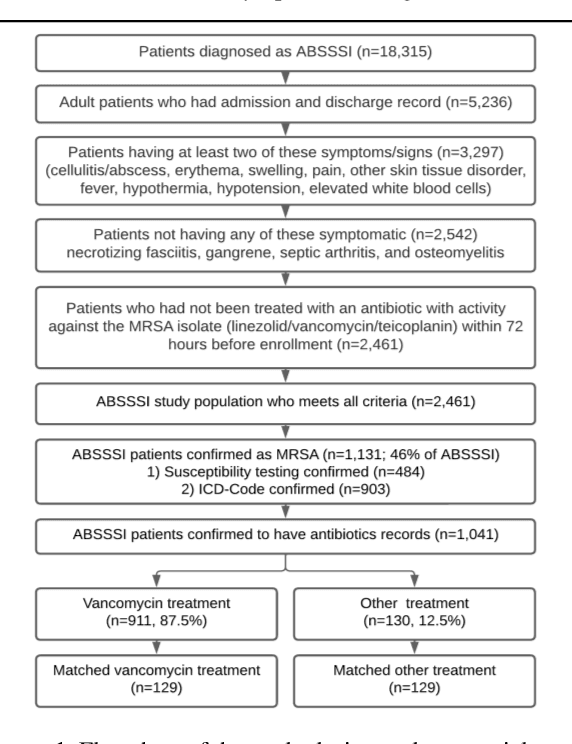
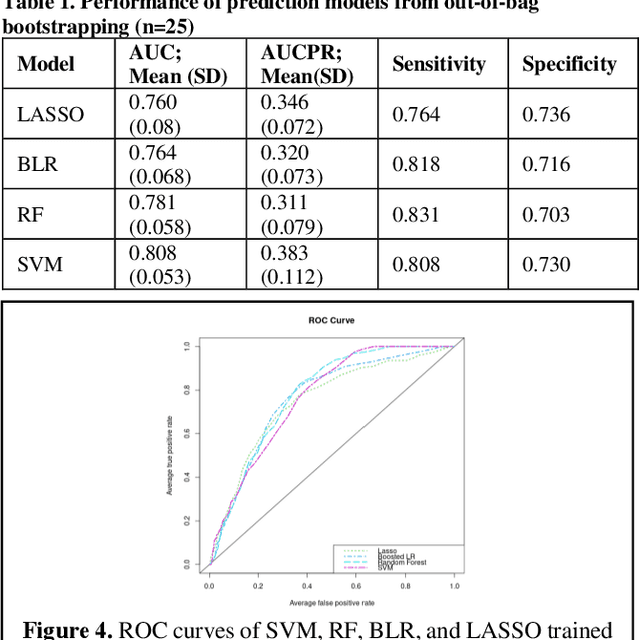
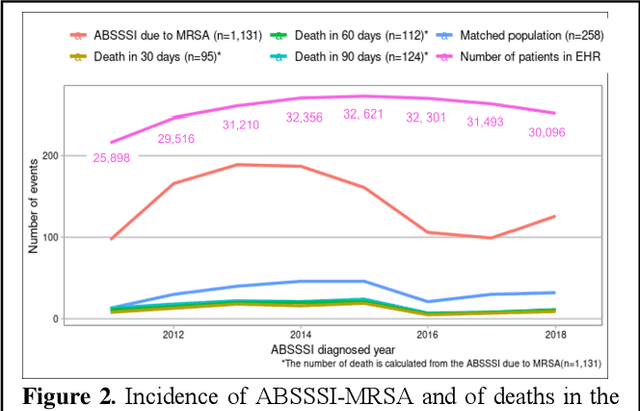
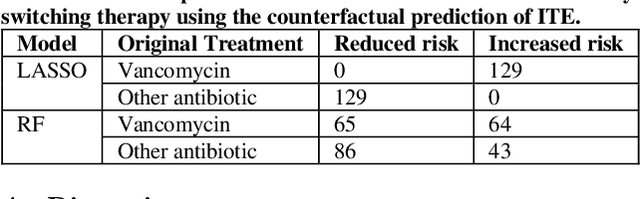
Abstract:Bacterial infections are responsible for high mortality worldwide. Antimicrobial resistance underlying the infection, and multifaceted patient's clinical status can hamper the correct choice of antibiotic treatment. Randomized clinical trials provide average treatment effect estimates but are not ideal for risk stratification and optimization of therapeutic choice, i.e., individualized treatment effects (ITE). Here, we leverage large-scale electronic health record data, collected from Southern US academic clinics, to emulate a clinical trial, i.e., 'target trial', and develop a machine learning model of mortality prediction and ITE estimation for patients diagnosed with acute bacterial skin and skin structure infection (ABSSSI) due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). ABSSSI-MRSA is a challenging condition with reduced treatment options - vancomycin is the preferred choice, but it has non-negligible side effects. First, we use propensity score matching to emulate the trial and create a treatment randomized (vancomycin vs. other antibiotics) dataset. Next, we use this data to train various machine learning methods (including boosted/LASSO logistic regression, support vector machines, and random forest) and choose the best model in terms of area under the receiver characteristic (AUC) through bootstrap validation. Lastly, we use the models to calculate ITE and identify possible averted deaths by therapy change. The out-of-bag tests indicate that SVM and RF are the most accurate, with AUC of 81% and 78%, respectively, but BLR/LASSO is not far behind (76%). By calculating the counterfactuals using the BLR/LASSO, vancomycin increases the risk of death, but it shows a large variation (odds ratio 1.2, 95% range 0.4-3.8) and the contribution to outcome probability is modest. Instead, the RF exhibits stronger changes in ITE, suggesting more complex treatment heterogeneity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge