Irina Rabkina
A Knowledge Driven Approach to Adaptive Assistance Using Preference Reasoning and Explanation
Dec 05, 2020
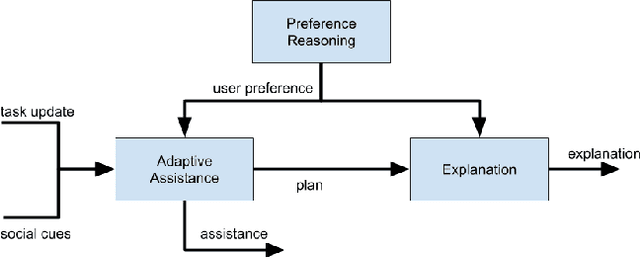
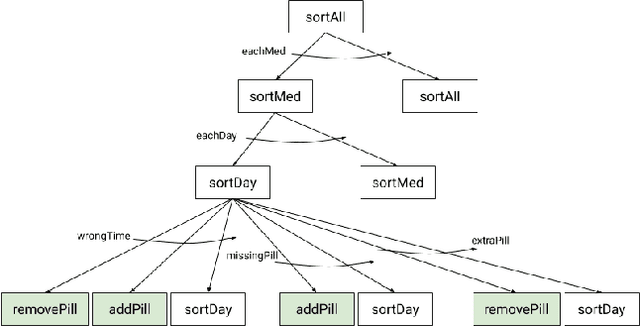
Abstract:There is a need for socially assistive robots (SARs) to provide transparency in their behavior by explaining their reasoning. Additionally, the reasoning and explanation should represent the user's preferences and goals. To work towards satisfying this need for interpretable reasoning and representations, we propose the robot uses Analogical Theory of Mind to infer what the user is trying to do and uses the Hint Engine to find an appropriate assistance based on what the user is trying to do. If the user is unsure or confused, the robot provides the user with an explanation, generated by the Explanation Synthesizer. The explanation helps the user understand what the robot inferred about the user's preferences and why the robot decided to provide the assistance it gave. A knowledge-driven approach provides transparency to reasoning about preferences, assistance, and explanations, thereby facilitating the incorporation of user feedback and allowing the robot to learn and adapt to the user.
Creative Captioning: An AI Grand Challenge Based on the Dixit Board Game
Sep 30, 2020


Abstract:We propose a new class of "grand challenge" AI problems that we call creative captioning---generating clever, interesting, or abstract captions for images, as well as understanding such captions. Creative captioning draws on core AI research areas of vision, natural language processing, narrative reasoning, and social reasoning, and across all these areas, it requires sophisticated uses of common sense and cultural knowledge. In this paper, we analyze several specific research problems that fall under creative captioning, using the popular board game Dixit as both inspiration and proposed testing ground. We expect that Dixit could serve as an engaging and motivating benchmark for creative captioning across numerous AI research communities for the coming 1-2 decades.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge