Irina Espejo
Walrus: A Cross-Domain Foundation Model for Continuum Dynamics
Nov 19, 2025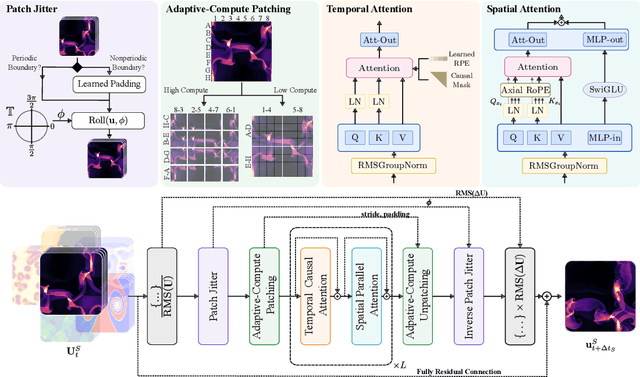


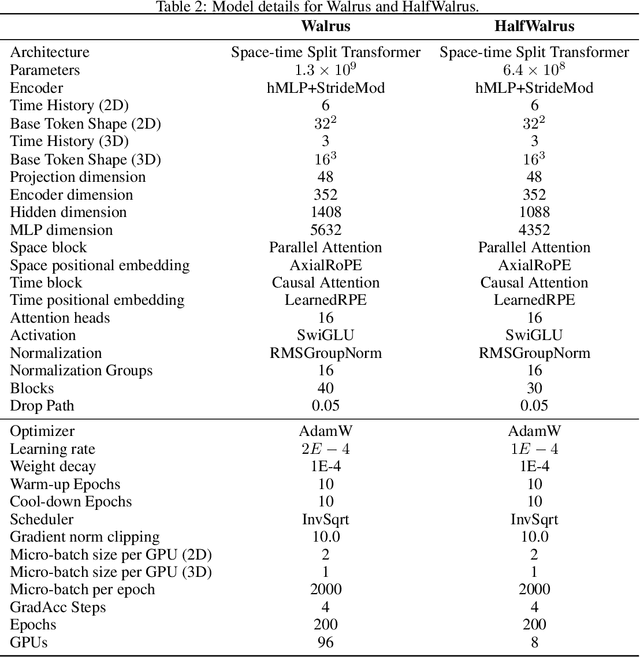
Abstract:Foundation models have transformed machine learning for language and vision, but achieving comparable impact in physical simulation remains a challenge. Data heterogeneity and unstable long-term dynamics inhibit learning from sufficiently diverse dynamics, while varying resolutions and dimensionalities challenge efficient training on modern hardware. Through empirical and theoretical analysis, we incorporate new approaches to mitigate these obstacles, including a harmonic-analysis-based stabilization method, load-balanced distributed 2D and 3D training strategies, and compute-adaptive tokenization. Using these tools, we develop Walrus, a transformer-based foundation model developed primarily for fluid-like continuum dynamics. Walrus is pretrained on nineteen diverse scenarios spanning astrophysics, geoscience, rheology, plasma physics, acoustics, and classical fluids. Experiments show that Walrus outperforms prior foundation models on both short and long term prediction horizons on downstream tasks and across the breadth of pretraining data, while ablation studies confirm the value of our contributions to forecast stability, training throughput, and transfer performance over conventional approaches. Code and weights are released for community use.
MadMiner: Machine learning-based inference for particle physics
Jul 24, 2019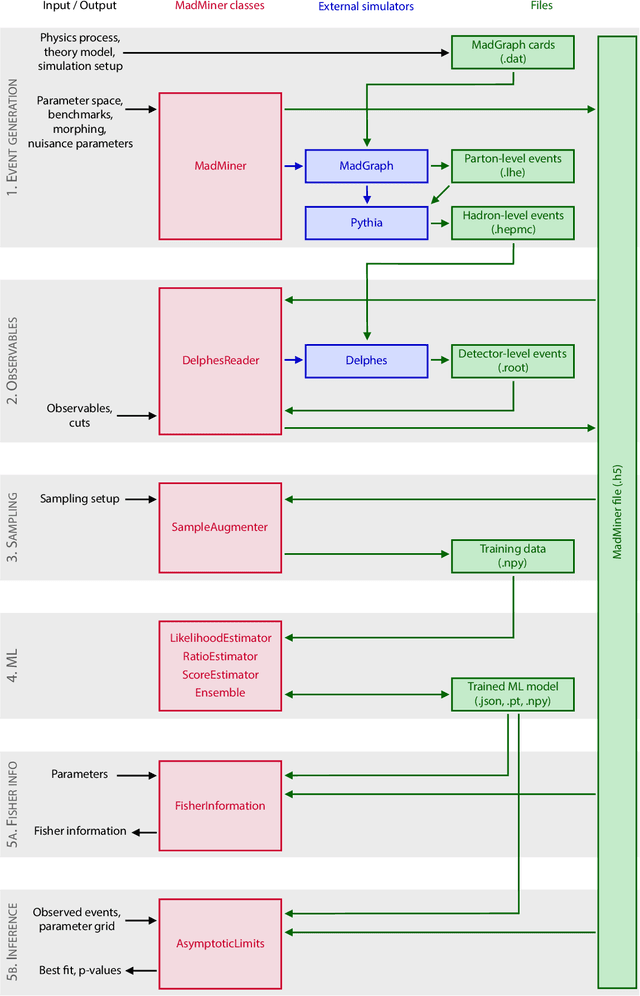
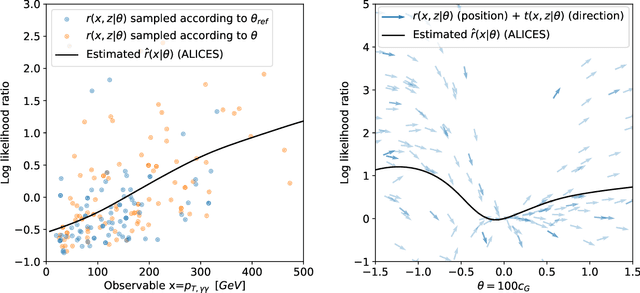
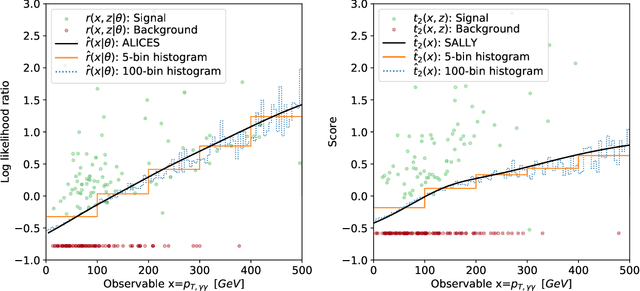
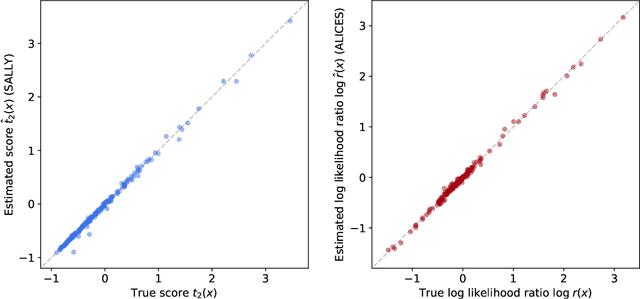
Abstract:The legacy measurements of the LHC will require analyzing high-dimensional event data for subtle kinematic signatures, which is challenging for established analysis methods. Recently, a powerful family of multivariate inference techniques that leverage both matrix element information and machine learning has been developed. This approach neither requires the reduction of high-dimensional data to summary statistics nor any simplifications to the underlying physics or detector response. In this paper we introduce MadMiner, a Python module that streamlines the steps involved in this procedure. Wrapping around MadGraph5_aMC and Pythia 8, it supports almost any physics process and model. To aid phenomenological studies, the tool also wraps around Delphes 3, though it is extendable to a full Geant4-based detector simulation. We demonstrate the use of MadMiner in an example analysis of dimension-six operators in ttH production, finding that the new techniques substantially increase the sensitivity to new physics.
Effective LHC measurements with matrix elements and machine learning
Jun 04, 2019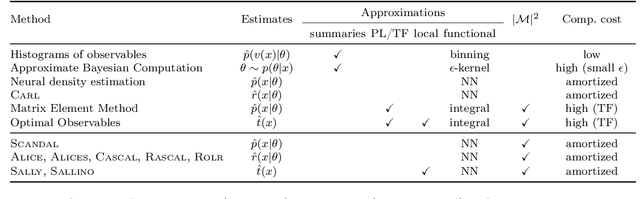
Abstract:One major challenge for the legacy measurements at the LHC is that the likelihood function is not tractable when the collected data is high-dimensional and the detector response has to be modeled. We review how different analysis strategies solve this issue, including the traditional histogram approach used in most particle physics analyses, the Matrix Element Method, Optimal Observables, and modern techniques based on neural density estimation. We then discuss powerful new inference methods that use a combination of matrix element information and machine learning to accurately estimate the likelihood function. The MadMiner package automates all necessary data-processing steps. In first studies we find that these new techniques have the potential to substantially improve the sensitivity of the LHC legacy measurements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge