Inge Rasmus Groote
Segmenting white matter hyperintensities on isotropic three-dimensional Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery magnetic resonance images: A comparison of Deep learning tools on a Norwegian national imaging database
Jul 19, 2022



Abstract:Automated segmentation of white matter hyperintensities (WMHs) is an essential step in neuroimaging analysis of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery (FLAIR-weighted) is an MRI contrast that is particularly useful to visualize and quantify WMHs, a hallmark of cerebral small vessel disease and Alzheimer's disease (AD). Clinical MRI protocols migrate to a three-dimensional (3D) FLAIR-weighted acquisition to enable high spatial resolution in all three voxel dimensions. The current study details the deployment of deep learning tools to enable automated WMH segmentation and characterization from 3D FLAIR-weighted images acquired as part of a national AD imaging initiative. Among 642 participants (283 male, mean age: (65.18 +/- 9.33) years) from the DDI study, two in-house networks were trained and validated across five national collection sites. Three models were tested on a held-out subset of the internal data from the 642 participants and an external dataset with 29 cases from an international collaborator. These test sets were evaluated independently. Five established WMH performance metrics were used for comparison against ground truth human-in-the-loop segmentation. Results of the three networks tested, the 3D nnU-Net had the best performance with an average dice similarity coefficient score of 0.78 +/- 0.10, performing better than both the in-house developed 2.5D model and the SOTA Deep Bayesian network. With the increasing use of 3D FLAIR-weighted images in MRI protocols, our results suggest that WMH segmentation models can be trained on 3D data and yield WMH segmentation performance that is comparable to or better than state-of-the-art without the need for including T1-weighted image series.
A Densely Interconnected Network for Deep Learning Accelerated MRI
Jul 05, 2022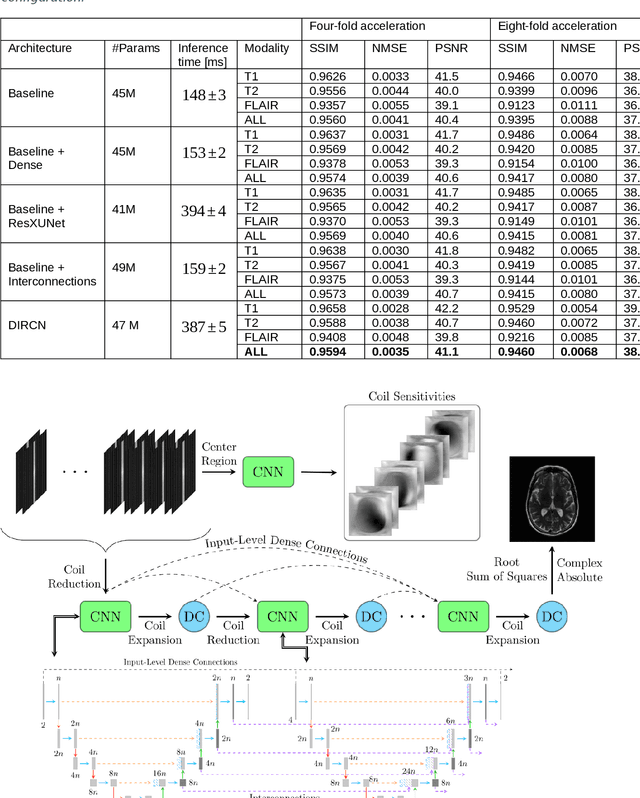
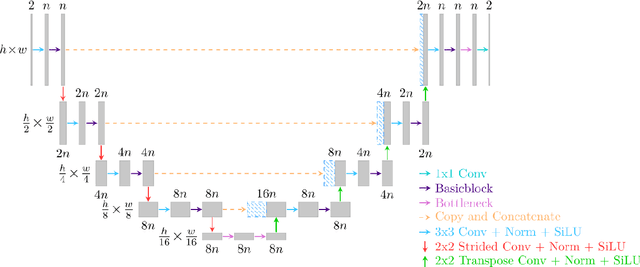
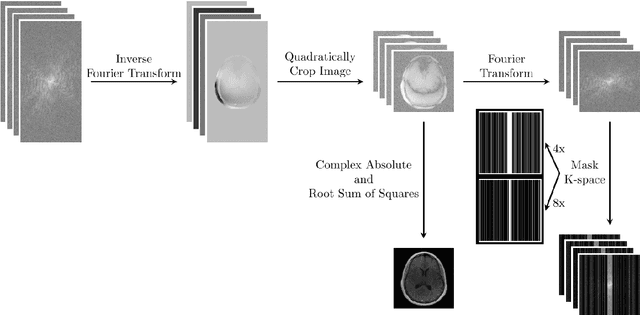
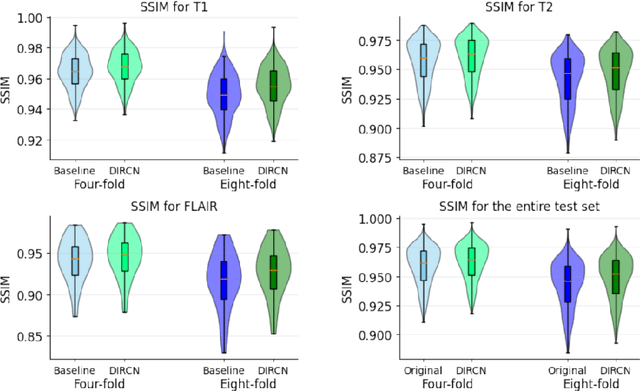
Abstract:Objective: To improve accelerated MRI reconstruction through a densely connected cascading deep learning reconstruction framework. Materials and Methods: A cascading deep learning reconstruction framework (baseline model) was modified by applying three architectural modifications: Input-level dense connections between cascade inputs and outputs, an improved deep learning sub-network, and long-range skip-connections between subsequent deep learning networks. An ablation study was performed, where five model configurations were trained on the NYU fastMRI neuro dataset with an end-to-end scheme conjunct on four- and eight-fold acceleration. The trained models were evaluated by comparing their respective structural similarity index measure (SSIM), normalized mean square error (NMSE) and peak signal to noise ratio (PSNR). Results: The proposed densely interconnected residual cascading network (DIRCN), utilizing all three suggested modifications, achieved a SSIM improvement of 8% and 11% for four- and eight-fold acceleration, respectively. For eight-fold acceleration, the model achieved a 23% decrease in the NMSE when compared to the baseline model. In an ablation study, the individual architectural modifications all contributed to this improvement, by reducing the SSIM and NMSE with approximately 3% and 5% for four-fold acceleration, respectively. Conclusion: The proposed architectural modifications allow for simple adjustments on an already existing cascading framework to further improve the resulting reconstructions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge