Inavamsi Enaganti
Indian Institute of Science
An innovative Deep Learning Based Approach for Accurate Agricultural Crop Price Prediction
Apr 15, 2023Abstract:Accurate prediction of agricultural crop prices is a crucial input for decision-making by various stakeholders in agriculture: farmers, consumers, retailers, wholesalers, and the Government. These decisions have significant implications including, most importantly, the economic well-being of the farmers. In this paper, our objective is to accurately predict crop prices using historical price information, climate conditions, soil type, location, and other key determinants of crop prices. This is a technically challenging problem, which has been attempted before. In this paper, we propose an innovative deep learning based approach to achieve increased accuracy in price prediction. The proposed approach uses graph neural networks (GNNs) in conjunction with a standard convolutional neural network (CNN) model to exploit geospatial dependencies in prices. Our approach works well with noisy legacy data and produces a performance that is at least 20% better than the results available in the literature. We are able to predict prices up to 30 days ahead. We choose two vegetables, potato (stable price behavior) and tomato (volatile price behavior) and work with noisy public data available from Indian agricultural markets.
To mock a Mocking bird : Studies in Biomimicry
Apr 26, 2021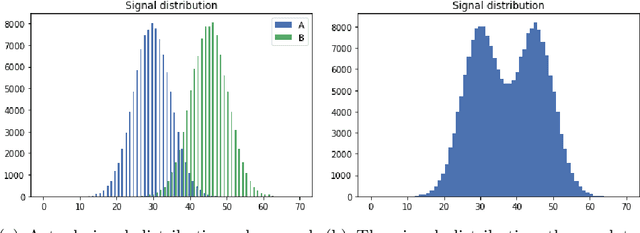
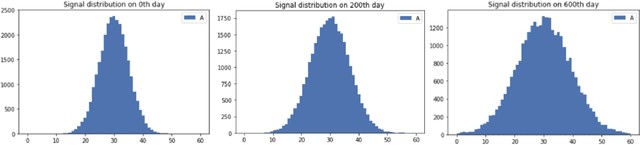
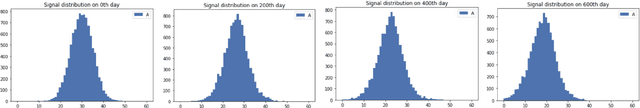
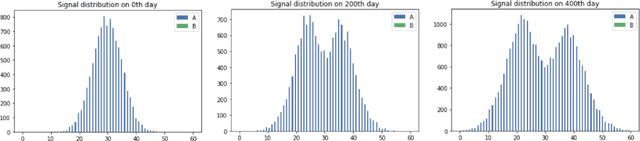
Abstract:This paper dwells on certain novel game-theoretic investigations in bio-mimicry, discussed from the perspectives of information asymmetry, individual utility and its optimization via strategic interactions involving co-evolving preys (e.g., insects) and predators (e.g., reptiles) who learn. Formally, we consider a panmictic ecosystem, occupied by species of prey with relatively short lifespan, which evolve mimicry signals over generations as they interact with predators with relatively longer lifespans, thus endowing predators with the ability to learn prey signals. Every prey sends a signal and provides utility to the predator. The prey can be either nutritious or toxic to the predator, but the prey may signal (possibly) deceptively without revealing its true "type." The model is used to study the situation where multi-armed bandit predators with zero prior information are introduced into the ecosystem. As a result of exploration and exploitation the predators naturally select the prey that result in the evolution of those signals. This co-evolution of strategies produces a variety of interesting phenomena which are subjects of this paper.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge