Imed Riadh Farah
Sustainable Palm Tree Farming: Leveraging IoT and Multi-Modal Data for Early Detection and Mapping of Red Palm Weevil
Jun 29, 2023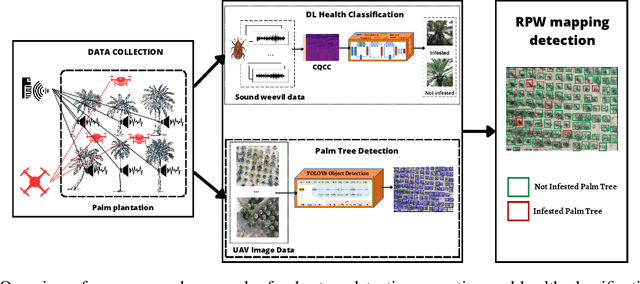
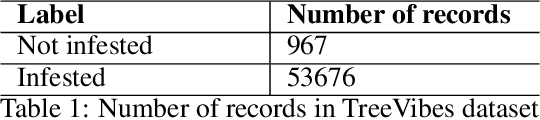
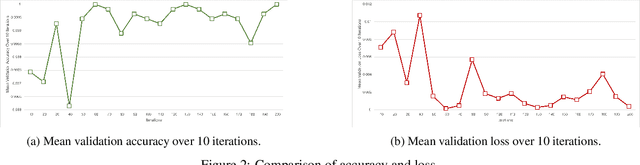
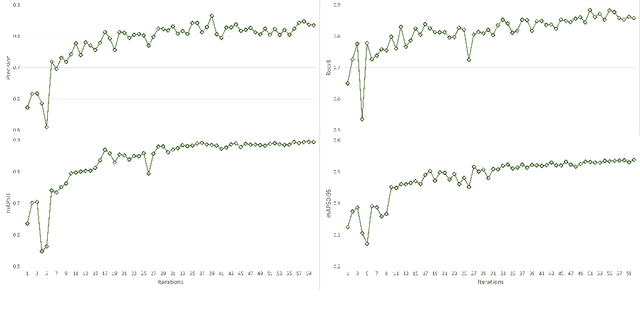
Abstract:The Red Palm Weevil (RPW) is a highly destructive insect causing economic losses and impacting palm tree farming worldwide. This paper proposes an innovative approach for sustainable palm tree farming by utilizing advanced technologies for the early detection and management of RPW. Our approach combines computer vision, deep learning (DL), the Internet of Things (IoT), and geospatial data to detect and classify RPW-infested palm trees effectively. The main phases include; (1) DL classification using sound data from IoT devices, (2) palm tree detection using YOLOv8 on UAV images, and (3) RPW mapping using geospatial data. Our custom DL model achieves 100% precision and recall in detecting and localizing infested palm trees. Integrating geospatial data enables the creation of a comprehensive RPW distribution map for efficient monitoring and targeted management strategies. This technology-driven approach benefits agricultural authorities, farmers, and researchers in managing RPW infestations and safeguarding palm tree plantations' productivity.
Modeling Complex Object Changes in Satellite Image Time-Series: Approach based on CSP and Spatiotemporal Graph
May 24, 2023Abstract:This paper proposes a method for automatically monitoring and analyzing the evolution of complex geographic objects. The objects are modeled as a spatiotemporal graph, which separates filiation relations, spatial relations, and spatiotemporal relations, and is analyzed by detecting frequent sub-graphs using constraint satisfaction problems (CSP). The process is divided into four steps: first, the identification of complex objects in each satellite image; second, the construction of a spatiotemporal graph to model the spatiotemporal changes of the complex objects; third, the creation of sub-graphs to be detected in the base spatiotemporal graph; and fourth, the analysis of the spatiotemporal graph by detecting the sub-graphs and solving a constraint network to determine relevant sub-graphs. The final step is further broken down into two sub-steps: (i) the modeling of the constraint network with defined variables and constraints, and (ii) the solving of the constraint network to find relevant sub-graphs in the spatiotemporal graph. Experiments were conducted using real-world satellite images representing several cities in Saudi Arabia, and the results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
Leveraging Artificial Intelligence Techniques for Smart Palm Tree Detection: A Decade Systematic Review
Sep 12, 2022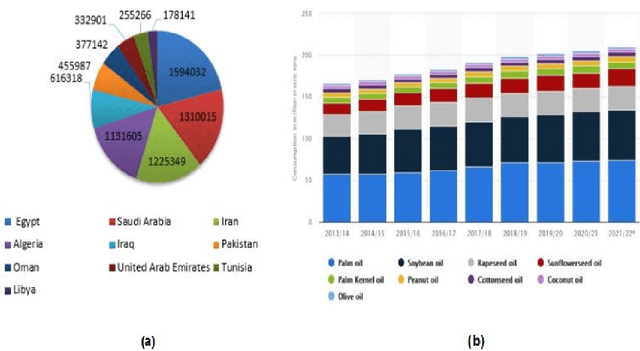
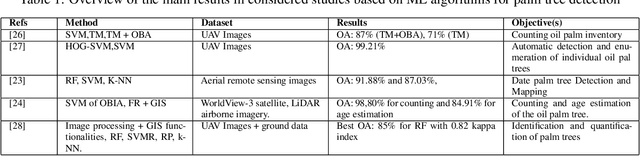
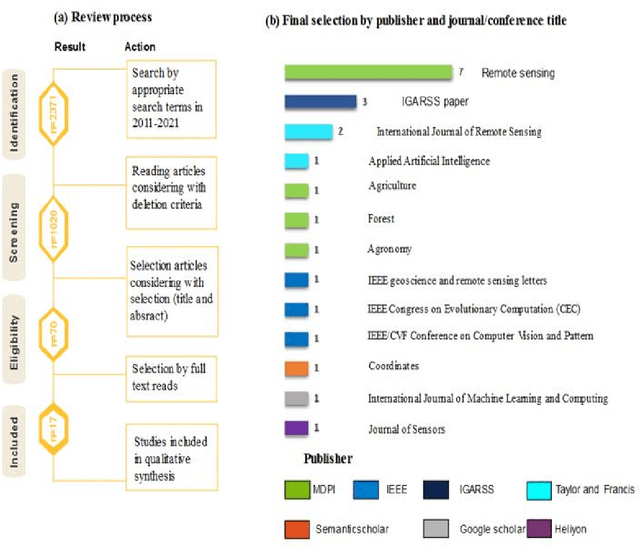
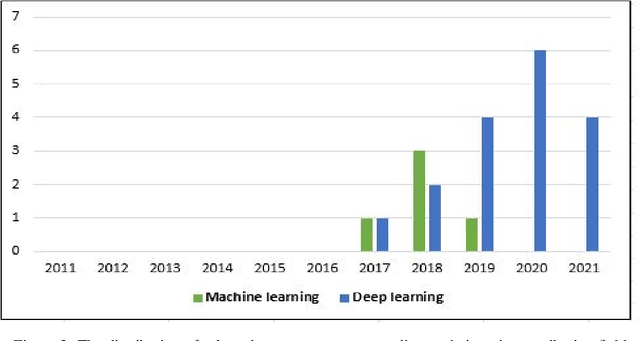
Abstract:Over the past few years, total financial investment in the agricultural sector has increased substantially. Palm tree is important for many countries' economies, particularly in northern Africa and the Middle East. Monitoring in terms of detection and counting palm trees provides useful information for various stakeholders; it helps in yield estimation and examination to ensure better crop quality and prevent pests, diseases, better irrigation, and other potential threats. Despite their importance, this information is still challenging to obtain. This study systematically reviews research articles between 2011 and 2021 on artificial intelligence (AI) technology for smart palm tree detection. A systematic review (SR) was performed using the PRISMA approach based on a four-stage selection process. Twenty-two articles were included for the synthesis activity reached from the search strategy alongside the inclusion criteria in order to answer to two main research questions. The study's findings reveal patterns, relationships, networks, and trends in applying artificial intelligence in palm tree detection over the last decade. Despite the good results in most of the studies, the effective and efficient management of large-scale palm plantations is still a challenge. In addition, countries whose economies strongly related to intelligent palm services, especially in North Africa, should give more attention to this kind of study. The results of this research could benefit both the research community and stakeholders.
A Hybrid APM-CPGSO Approach for Constraint Satisfaction Problem Solving: Application to Remote Sensing
Jun 06, 2021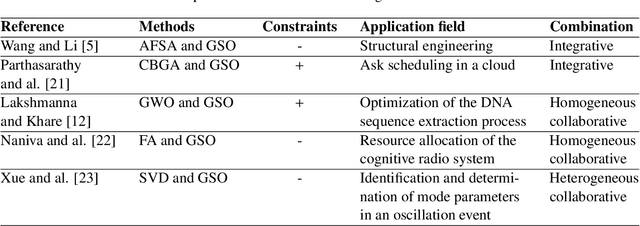
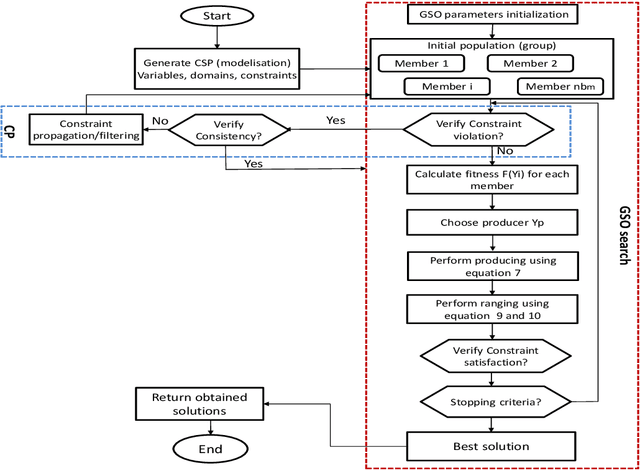
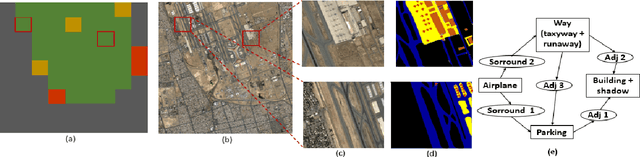
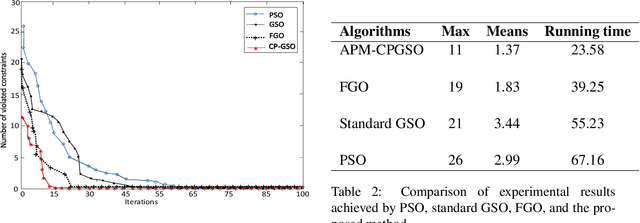
Abstract:Constraint satisfaction problem (CSP) has been actively used for modeling and solving a wide range of complex real-world problems. However, it has been proven that developing efficient methods for solving CSP, especially for large problems, is very difficult and challenging. Existing complete methods for problem-solving are in most cases unsuitable. Therefore, proposing hybrid CSP-based methods for problem-solving has been of increasing interest in the last decades. This paper aims at proposing a novel approach that combines incomplete and complete CSP methods for problem-solving. The proposed approach takes advantage of the group search algorithm (GSO) and the constraint propagation (CP) methods to solve problems related to the remote sensing field. To the best of our knowledge, this paper represents the first study that proposes a hybridization between an improved version of GSO and CP in the resolution of complex constraint-based problems. Experiments have been conducted for the resolution of object recognition problems in satellite images. Results show good performances in terms of convergence and running time of the proposed CSP-based method compared to existing state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge