Igor Peterlik
IHU Strasbourg
Real-time visio-haptic interaction with static soft tissue model shaving geometric and material nonlinearity
Apr 09, 2021



Abstract:We propose a new approach allowing visio-haptic interaction with a FE model of a human liver having both non-linear geometric and material properties. The material properties used in the model are extracted from the experimental data of pig liver to make the simulations more realistic. Our computational approach consists of two main steps: a pre-computation of the configuration space of all possible deformation states of the model, followed by the interpolation of the precomputed data for the calculation of the reaction forces displayed to the user through a haptic device during the real-time interactions. No a priori assumptions or modeling simplifications about the mathematical complexity of the underlying soft tissue model, size and irregularity of the FE mesh are necessary. We show that deformation and force response of the liver in simulations are heavily influenced by the material model, boundary conditions, path of the loading and the type of function used for the interpolation of the pre-computed data.
Elastic registration based on compliance analysis and biomechanical graph matching
Dec 13, 2019

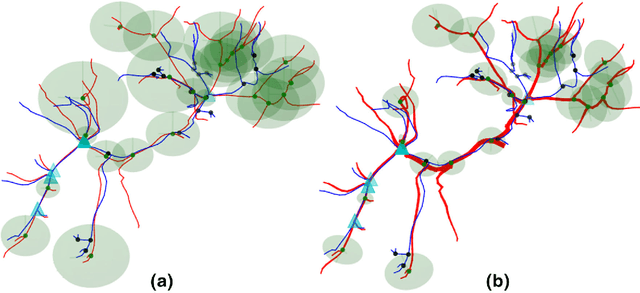
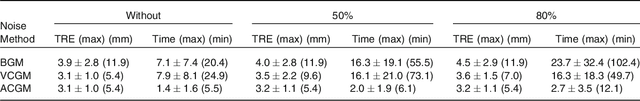
Abstract:An automatic elastic registration method suited for vascularized organs is proposed. The vasculature in both the preoperative and intra-operative images is represented as a graph. A typical application of this method is the fusion of pre-operative information onto the organ during surgery, to compensate for the limited details provided by the intra-operative imaging modality (e.g. CBCT) and to cope with changes in the shape of the organ. Due to image modalities differences and organ deformation, each graph has a different topology and shape. The Adaptive Compliance Graph Matching (ACGM) method presented does not require any manual initialization, handles intra-operative nonrigid deformations of up to 65 mm and computes a complete displacement field over the organ from only the matched vasculature. ACGM is better than the previous Biomechanical Graph Matching method 3 (BGM) because it uses an efficient biomechanical vascularized liver model to compute the organ's transformation and the vessels bifurcations compliance. This allows to efficiently find the best graph matches with a novel compliance-based adaptive search. These contributions are evaluated on ten realistic synthetic and two real porcine automatically segmented datasets. ACGM obtains better target registration error (TRE) than BGM, with an average TRE in the real datasets of 4.2 mm compared to 6.5 mm, respectively. It also is up to one order of magnitude faster, less dependent on the parameters used and more robust to noise.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge