Ignacio Arroyo-Fernández
Common Sense Knowledge Learning for Open Vocabulary Neural Reasoning: A First View into Chronic Disease Literature
Nov 30, 2021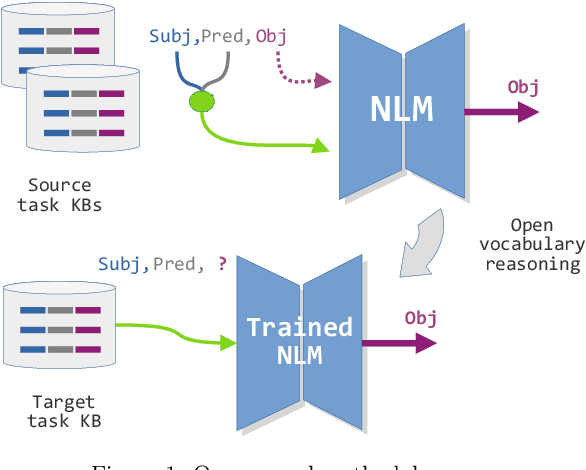
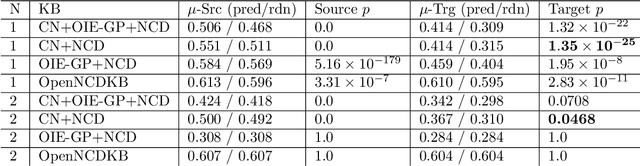
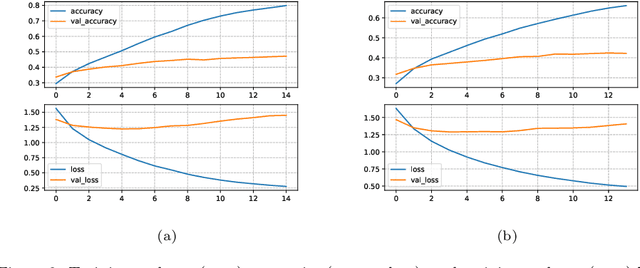
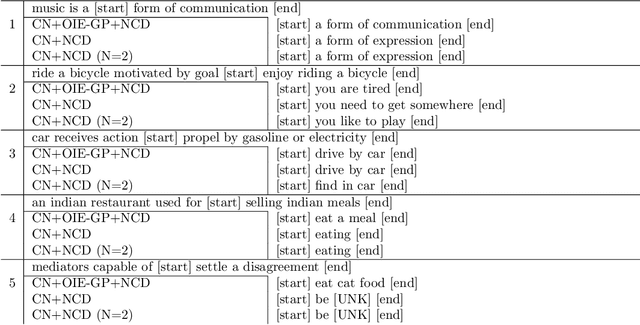
Abstract:In this paper, we address reasoning tasks from open vocabulary Knowledge Bases (openKBs) using state-of-the-art Neural Language Models (NLMs) with applications in scientific literature. For this purpose, self-attention based NLMs are trained using a common sense KB as a source task. The NLMs are then tested on a target KB for open vocabulary reasoning tasks involving scientific knowledge related to the most prevalent chronic diseases (also known as non-communicable diseases, NCDs). Our results identified NLMs that performed consistently and with significance in knowledge inference for both source and target tasks. Furthermore, in our analysis by inspection we discussed the semantic regularities and reasoning capabilities learned by the models, while showing a first insight into the potential benefits of our approach to aid NCD research.
On the Possibility of Rewarding Structure Learning Agents: Mutual Information on Linguistic Random Sets
Oct 09, 2019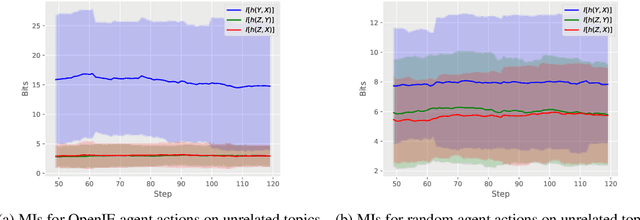

Abstract:We present a first attempt to elucidate an Information-Theoretic approach to design the reward provided by a natural language environment to some structure learning agent. To this end, we revisit the Information Theory of unsupervised induction of phrase-structure grammars to characterize the behavior of simulated agents whose actions are characterized in terms of random sets of linguistic samples. Our results showed empirical evidence of that semantic structures (built using Open Information Extraction methods) can be distinguished from randomly constructed structures by observing the Mutual Information among their constituent linguistic random sets. This suggests the possibility of rewarding structure learning agents without using pretrained structural analyzers (oracle actors or experts).
Unsupervised Sentence Representations as Word Information Series: Revisiting TF--IDF
Oct 20, 2017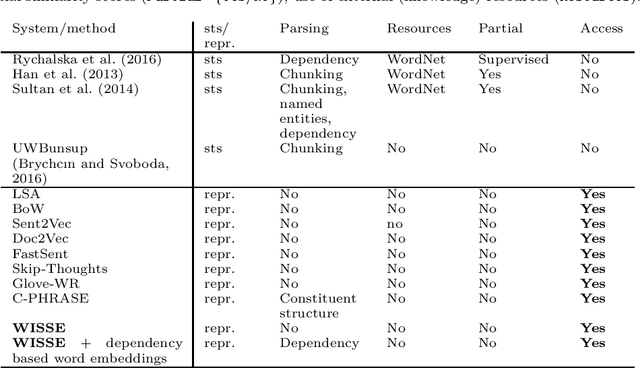


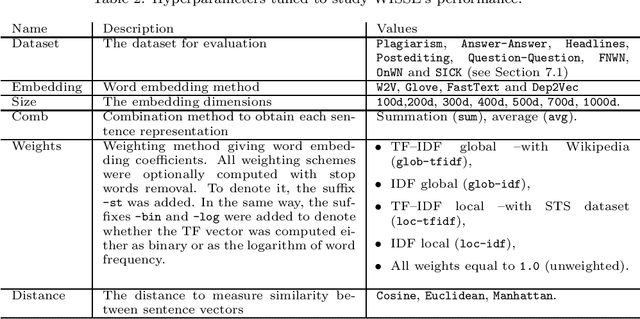
Abstract:Sentence representation at the semantic level is a challenging task for Natural Language Processing and Artificial Intelligence. Despite the advances in word embeddings (i.e. word vector representations), capturing sentence meaning is an open question due to complexities of semantic interactions among words. In this paper, we present an embedding method, which is aimed at learning unsupervised sentence representations from unlabeled text. We propose an unsupervised method that models a sentence as a weighted series of word embeddings. The weights of the word embeddings are fitted by using Shannon's word entropies provided by the Term Frequency--Inverse Document Frequency (TF--IDF) transform. The hyperparameters of the model can be selected according to the properties of data (e.g. sentence length and textual gender). Hyperparameter selection involves word embedding methods and dimensionalities, as well as weighting schemata. Our method offers advantages over existing methods: identifiable modules, short-term training, online inference of (unseen) sentence representations, as well as independence from domain, external knowledge and language resources. Results showed that our model outperformed the state of the art in well-known Semantic Textual Similarity (STS) benchmarks. Moreover, our model reached state-of-the-art performance when compared to supervised and knowledge-based STS systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge