Ian Benlolo
fintech-kMC: Agent based simulations of financial platforms for design and testing of machine learning systems
Jan 04, 2023



Abstract:We discuss our simulation tool, fintech-kMC, which is designed to generate synthetic data for machine learning model development and testing. fintech-kMC is an agent-based model driven by a kinetic Monte Carlo (a.k.a. continuous time Monte Carlo) engine which simulates the behaviour of customers using an online digital financial platform. The tool provides an interpretable, reproducible, and realistic way of generating synthetic data which can be used to validate and test AI/ML models and pipelines to be used in real-world customer-facing financial applications.
Training neural networks using Metropolis Monte Carlo and an adaptive variant
May 16, 2022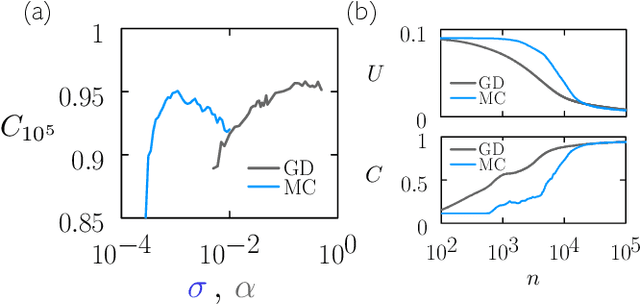
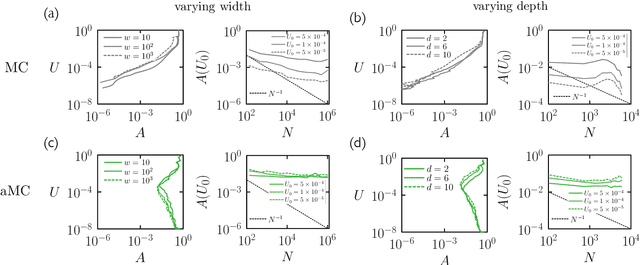
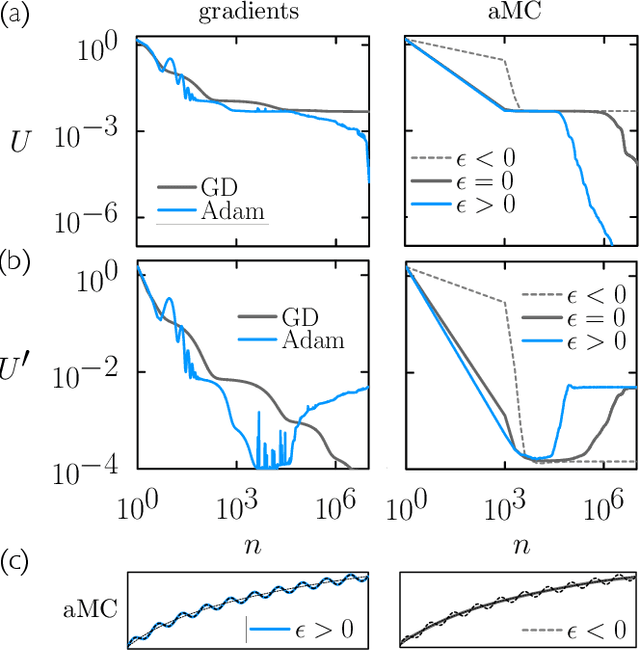
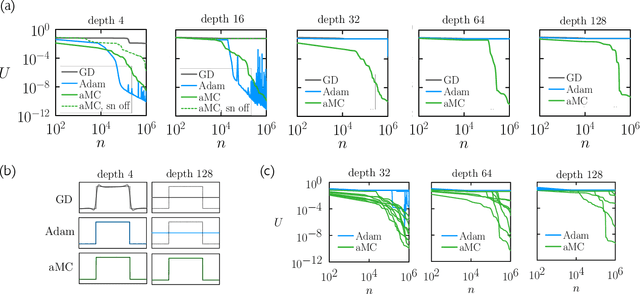
Abstract:We examine the zero-temperature Metropolis Monte Carlo algorithm as a tool for training a neural network by minimizing a loss function. We find that, as expected on theoretical grounds and shown empirically by other authors, Metropolis Monte Carlo can train a neural net with an accuracy comparable to that of gradient descent, if not necessarily as quickly. The Metropolis algorithm does not fail automatically when the number of parameters of a neural network is large. It can fail when a neural network's structure or neuron activations are strongly heterogenous, and we introduce an adaptive Monte Carlo algorithm, aMC, to overcome these limitations. The intrinsic stochasticity of the Monte Carlo method allows aMC to train neural networks in which the gradient is too small to allow training by gradient descent. We suggest that, as for molecular simulation, Monte Carlo methods offer a complement to gradient-based methods for training neural networks, allowing access to a distinct set of network architectures and principles.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge