Huseyin Tuna Erdinc
Power-scaled Bayesian Inference with Score-based Generative mModels
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:We propose a score-based generative algorithm for sampling from power-scaled priors and likelihoods within the Bayesian inference framework. Our algorithm enables flexible control over prior-likelihood influence without requiring retraining for different power-scaling configurations. Specifically, we focus on synthesizing seismic velocity models conditioned on imaged seismic. Our method enables sensitivity analysis by sampling from intermediate power posteriors, allowing us to assess the relative influence of the prior and likelihood on samples of the posterior distribution. Through a comprehensive set of experiments, we evaluate the effects of varying the power parameter in different settings: applying it solely to the prior, to the likelihood of a Bayesian formulation, and to both simultaneously. The results show that increasing the power of the likelihood up to a certain threshold improves the fidelity of posterior samples to the conditioning data (e.g., seismic images), while decreasing the prior power promotes greater structural diversity among samples. Moreover, we find that moderate scaling of the likelihood leads to a reduced shot data residual, confirming its utility in posterior refinement.
Machine learning-enabled velocity model building with uncertainty quantification
Nov 14, 2024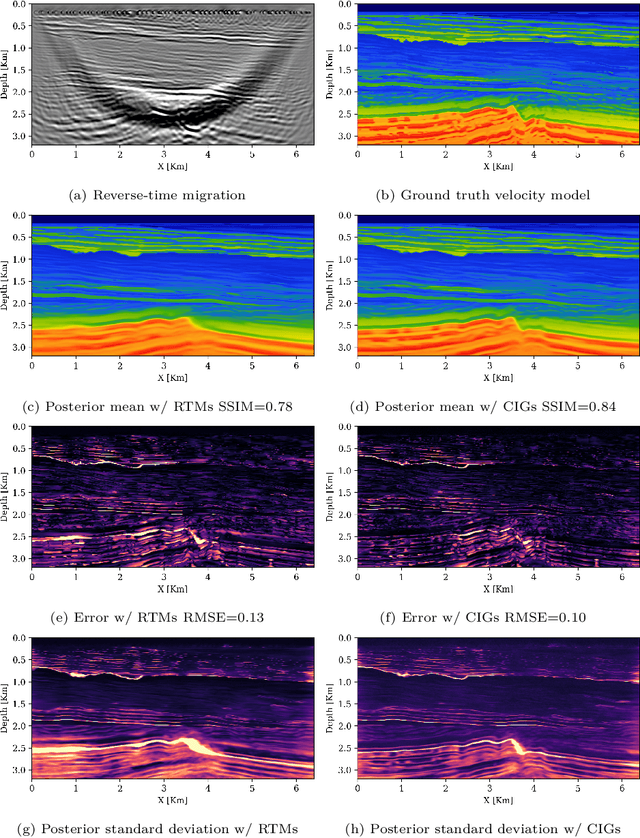
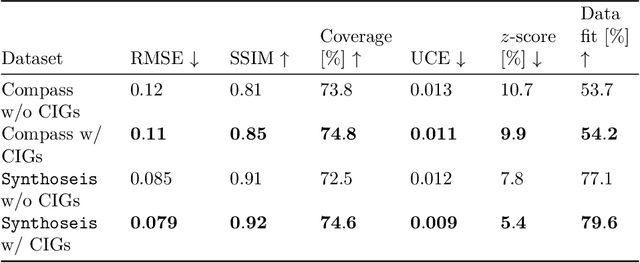
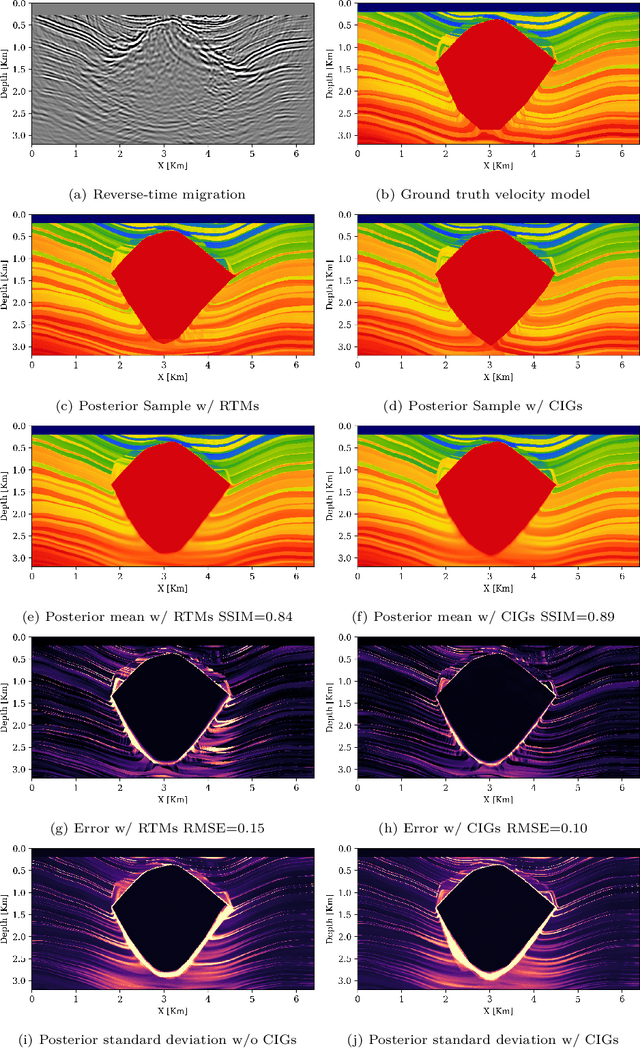
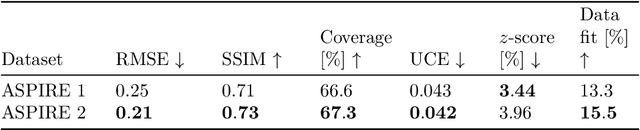
Abstract:Accurately characterizing migration velocity models is crucial for a wide range of geophysical applications, from hydrocarbon exploration to monitoring of CO2 sequestration projects. Traditional velocity model building methods such as Full-Waveform Inversion (FWI) are powerful but often struggle with the inherent complexities of the inverse problem, including noise, limited bandwidth, receiver aperture and computational constraints. To address these challenges, we propose a scalable methodology that integrates generative modeling, in the form of Diffusion networks, with physics-informed summary statistics, making it suitable for complicated imaging problems including field datasets. By defining these summary statistics in terms of subsurface-offset image volumes for poor initial velocity models, our approach allows for computationally efficient generation of Bayesian posterior samples for migration velocity models that offer a useful assessment of uncertainty. To validate our approach, we introduce a battery of tests that measure the quality of the inferred velocity models, as well as the quality of the inferred uncertainties. With modern synthetic datasets, we reconfirm gains from using subsurface-image gathers as the conditioning observable. For complex velocity model building involving salt, we propose a new iterative workflow that refines amortized posterior approximations with salt flooding and demonstrate how the uncertainty in the velocity model can be propagated to the final product reverse time migrated images. Finally, we present a proof of concept on field datasets to show that our method can scale to industry-sized problems.
Inference of CO2 flow patterns -- a feasibility study
Nov 01, 2023Abstract:As the global deployment of carbon capture and sequestration (CCS) technology intensifies in the fight against climate change, it becomes increasingly imperative to establish robust monitoring and detection mechanisms for potential underground CO2 leakage, particularly through pre-existing or induced faults in the storage reservoir's seals. While techniques such as history matching and time-lapse seismic monitoring of CO2 storage have been used successfully in tracking the evolution of CO2 plumes in the subsurface, these methods lack principled approaches to characterize uncertainties related to the CO2 plumes' behavior. Inclusion of systematic assessment of uncertainties is essential for risk mitigation for the following reasons: (i) CO2 plume-induced changes are small and seismic data is noisy; (ii) changes between regular and irregular (e.g., caused by leakage) flow patterns are small; and (iii) the reservoir properties that control the flow are strongly heterogeneous and typically only available as distributions. To arrive at a formulation capable of inferring flow patterns for regular and irregular flow from well and seismic data, the performance of conditional normalizing flow will be analyzed on a series of carefully designed numerical experiments. While the inferences presented are preliminary in the context of an early CO2 leakage detection system, the results do indicate that inferences with conditional normalizing flows can produce high-fidelity estimates for CO2 plumes with or without leakage. We are also confident that the inferred uncertainty is reasonable because it correlates well with the observed errors. This uncertainty stems from noise in the seismic data and from the lack of precise knowledge of the reservoir's fluid flow properties.
De-risking Carbon Capture and Sequestration with Explainable CO2 Leakage Detection in Time-lapse Seismic Monitoring Images
Dec 16, 2022Abstract:With the growing global deployment of carbon capture and sequestration technology to combat climate change, monitoring and detection of potential CO2 leakage through existing or storage induced faults are critical to the safe and long-term viability of the technology. Recent work on time-lapse seismic monitoring of CO2 storage has shown promising results in its ability to monitor the growth of the CO2 plume from surface recorded seismic data. However, due to the low sensitivity of seismic imaging to CO2 concentration, additional developments are required to efficiently interpret the seismic images for leakage. In this work, we introduce a binary classification of time-lapse seismic images to delineate CO2 plumes (leakage) using state-of-the-art deep learning models. Additionally, we localize the leakage region of CO2 plumes by leveraging Class Activation Mapping methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge