Hunny Mehrotra
Stratified SIFT Matching for Human Iris Recognition
Jan 06, 2013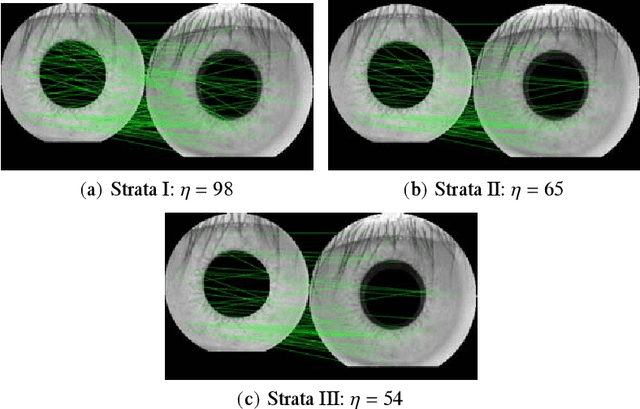
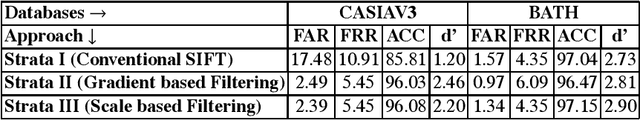
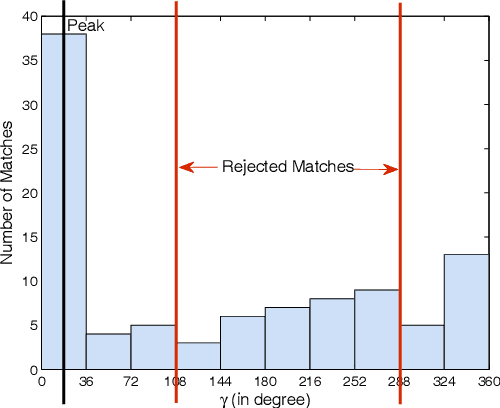
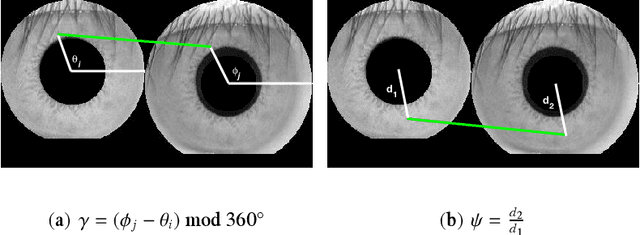
Abstract:This paper proposes an efficient three fold stratified SIFT matching for iris recognition. The objective is to filter wrongly paired conventional SIFT matches. In Strata I, the keypoints from gallery and probe iris images are paired using traditional SIFT approach. Due to high image similarity at different regions of iris there may be some impairments. These are detected and filtered by finding gradient of paired keypoints in Strata II. Further, the scaling factor of paired keypoints is used to remove impairments in Strata III. The pairs retained after Strata III are likely to be potential matches for iris recognition. The proposed system performs with an accuracy of 96.08% and 97.15% on publicly available CASIAV3 and BATH databases respectively. This marks significant improvement of accuracy and FAR over the existing SIFT matching for iris.
* 7 pages
Robust multi-camera view face recognition
Mar 30, 2010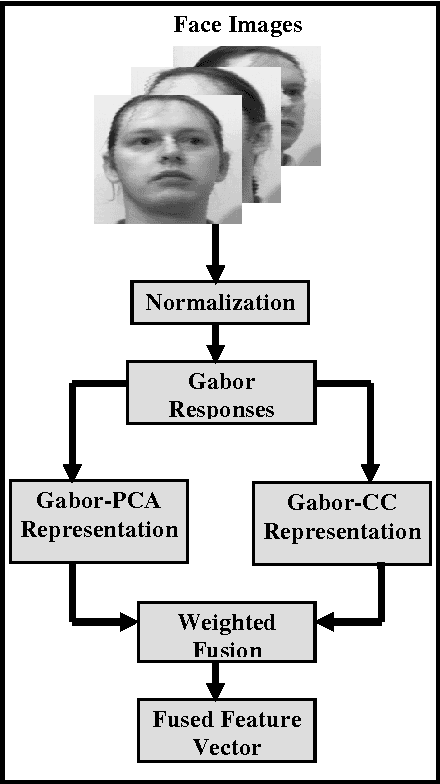
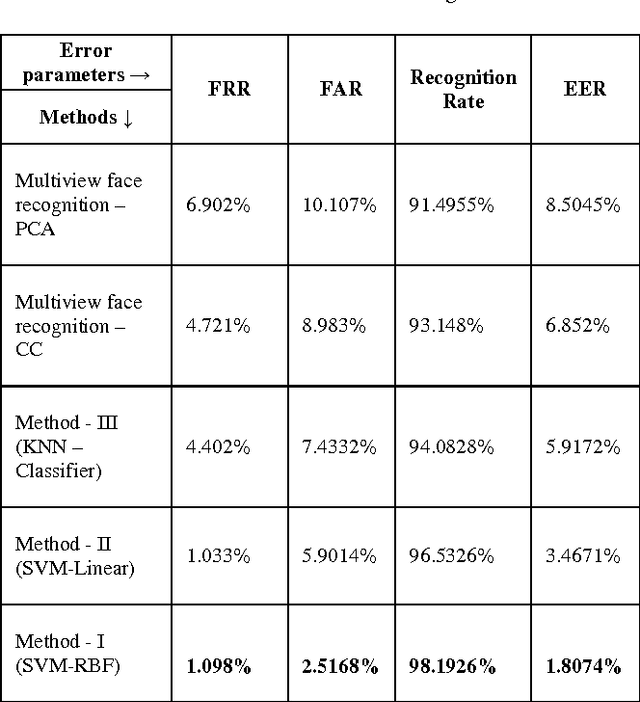
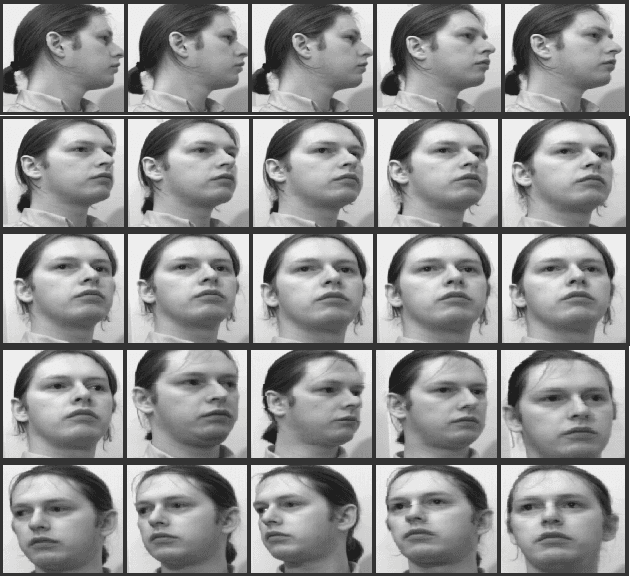
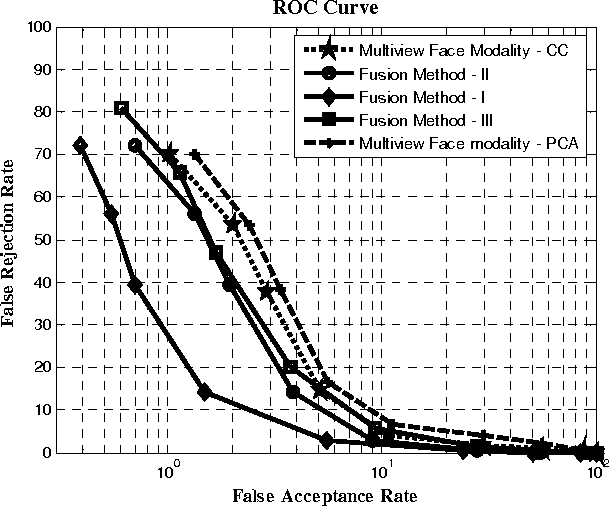
Abstract:This paper presents multi-appearance fusion of Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and generalization of Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) for multi-camera view offline face recognition (verification) system. The generalization of LDA has been extended to establish correlations between the face classes in the transformed representation and this is called canonical covariate. The proposed system uses Gabor filter banks for characterization of facial features by spatial frequency, spatial locality and orientation to make compensate to the variations of face instances occurred due to illumination, pose and facial expression changes. Convolution of Gabor filter bank to face images produces Gabor face representations with high dimensional feature vectors. PCA and canonical covariate are then applied on the Gabor face representations to reduce the high dimensional feature spaces into low dimensional Gabor eigenfaces and Gabor canonical faces. Reduced eigenface vector and canonical face vector are fused together using weighted mean fusion rule. Finally, support vector machines (SVM) have trained with augmented fused set of features and perform the recognition task. The system has been evaluated with UMIST face database consisting of multiview faces. The experimental results demonstrate the efficiency and robustness of the proposed system for multi-view face images with high recognition rates. Complexity analysis of the proposed system is also presented at the end of the experimental results.
SIFT-based Ear Recognition by Fusion of Detected Keypoints from Color Similarity Slice Regions
Feb 02, 2010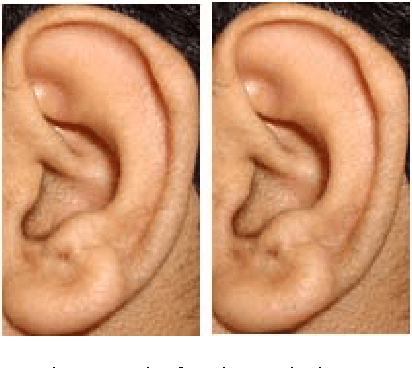
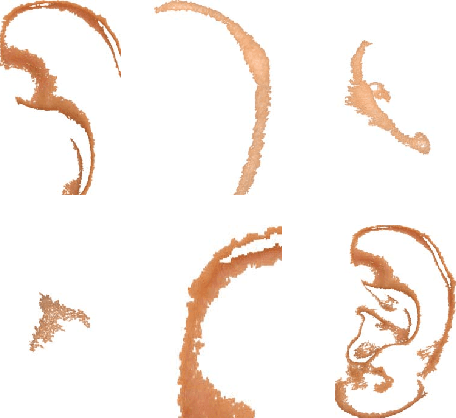
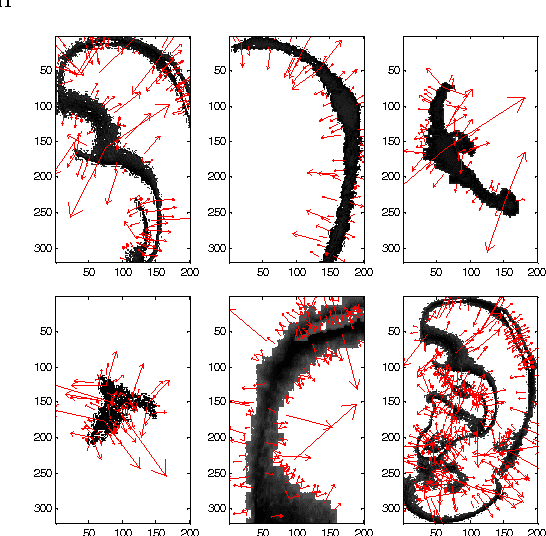
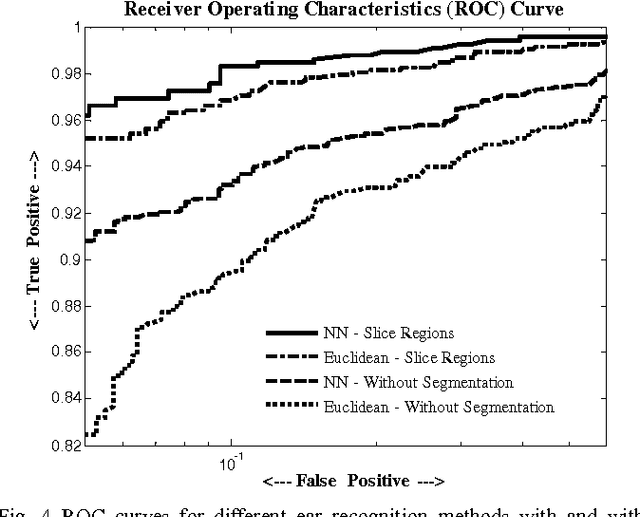
Abstract:Ear biometric is considered as one of the most reliable and invariant biometrics characteristics in line with iris and fingerprint characteristics. In many cases, ear biometrics can be compared with face biometrics regarding many physiological and texture characteristics. In this paper, a robust and efficient ear recognition system is presented, which uses Scale Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT) as feature descriptor for structural representation of ear images. In order to make it more robust to user authentication, only the regions having color probabilities in a certain ranges are considered for invariant SIFT feature extraction, where the K-L divergence is used for keeping color consistency. Ear skin color model is formed by Gaussian mixture model and clustering the ear color pattern using vector quantization. Finally, K-L divergence is applied to the GMM framework for recording the color similarity in the specified ranges by comparing color similarity between a pair of reference model and probe ear images. After segmentation of ear images in some color slice regions, SIFT keypoints are extracted and an augmented vector of extracted SIFT features are created for matching, which is accomplished between a pair of reference model and probe ear images. The proposed technique has been tested on the IITK Ear database and the experimental results show improvements in recognition accuracy while invariant features are extracted from color slice regions to maintain the robustness of the system.
Feature Level Clustering of Large Biometric Database
Feb 02, 2010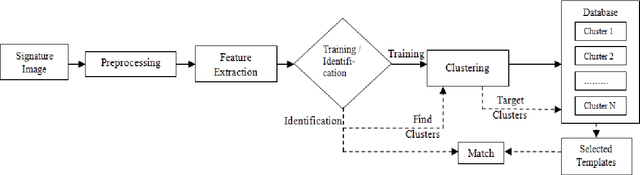
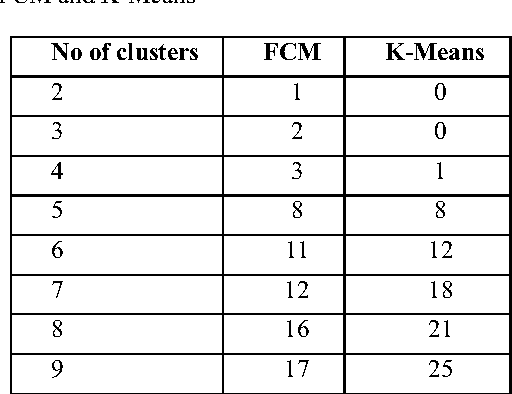
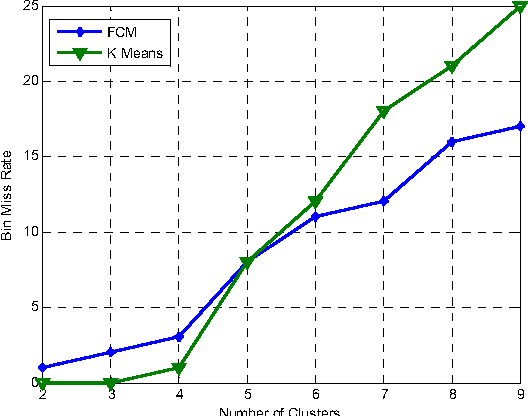
Abstract:This paper proposes an efficient technique for partitioning large biometric database during identification. In this technique feature vector which comprises of global and local descriptors extracted from offline signature are used by fuzzy clustering technique to partition the database. As biometric features posses no natural order of sorting, thus it is difficult to index them alphabetically or numerically. Hence, some supervised criteria is required to partition the search space. At the time of identification the fuzziness criterion is introduced to find the nearest clusters for declaring the identity of query sample. The system is tested using bin-miss rate and performs better in comparison to traditional k-means approach.
SVM-based Multiview Face Recognition by Generalization of Discriminant Analysis
Jan 23, 2010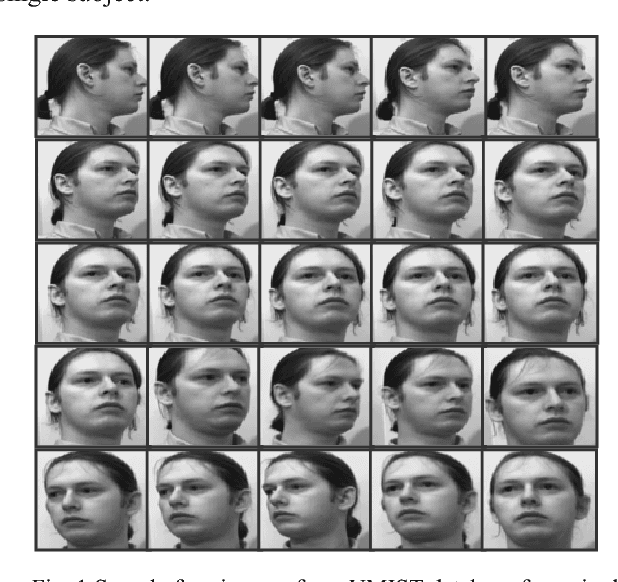
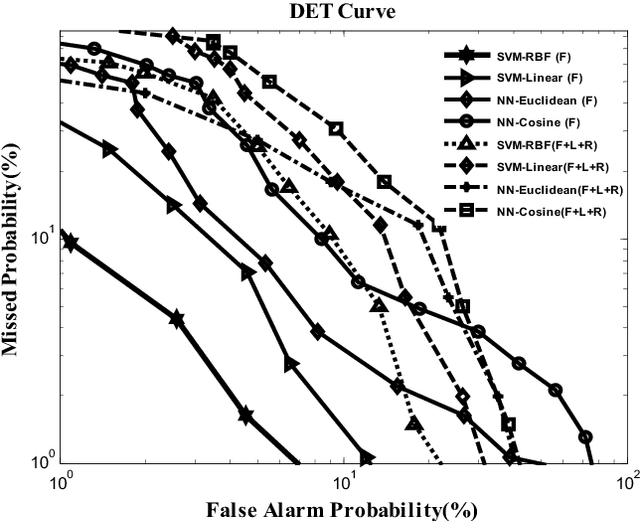

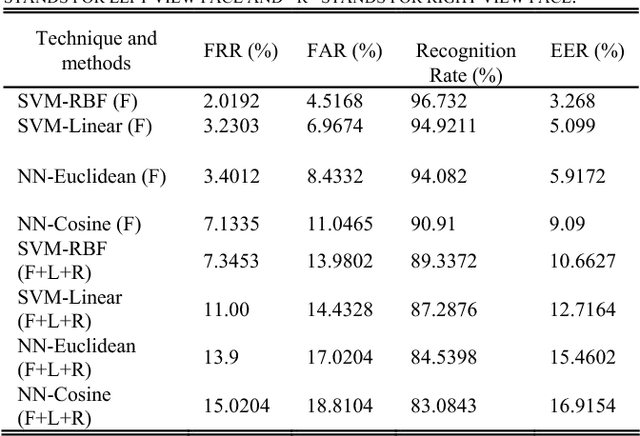
Abstract:Identity verification of authentic persons by their multiview faces is a real valued problem in machine vision. Multiview faces are having difficulties due to non-linear representation in the feature space. This paper illustrates the usability of the generalization of LDA in the form of canonical covariate for face recognition to multiview faces. In the proposed work, the Gabor filter bank is used to extract facial features that characterized by spatial frequency, spatial locality and orientation. Gabor face representation captures substantial amount of variations of the face instances that often occurs due to illumination, pose and facial expression changes. Convolution of Gabor filter bank to face images of rotated profile views produce Gabor faces with high dimensional features vectors. Canonical covariate is then used to Gabor faces to reduce the high dimensional feature spaces into low dimensional subspaces. Finally, support vector machines are trained with canonical sub-spaces that contain reduced set of features and perform recognition task. The proposed system is evaluated with UMIST face database. The experiment results demonstrate the efficiency and robustness of the proposed system with high recognition rates.
* 6 pages, 3 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge