Huaiyu Li
Incremental Concept Learning via Online Generative Memory Recall
Jul 05, 2019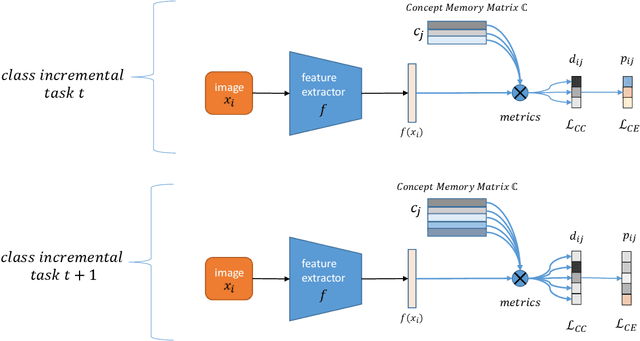
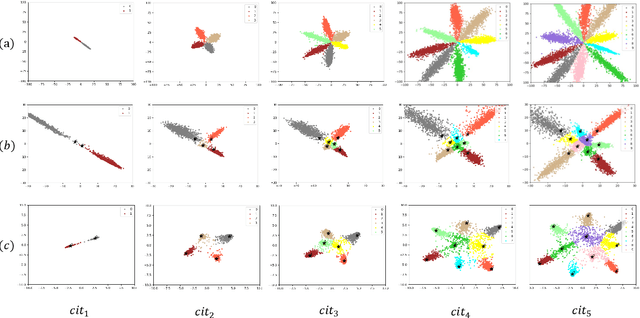
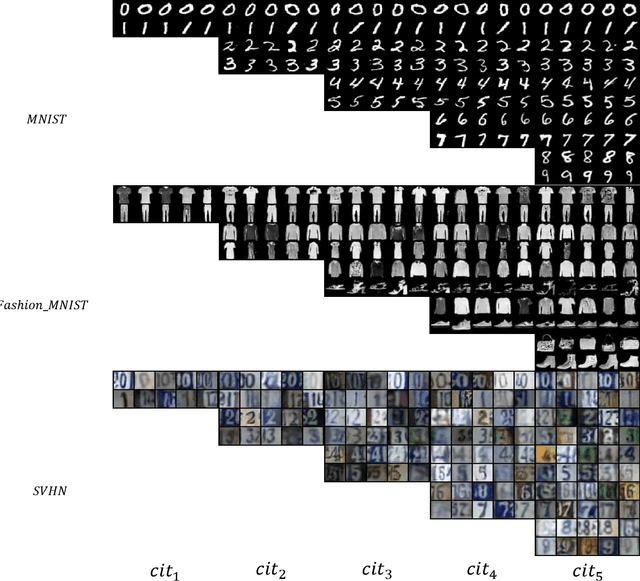
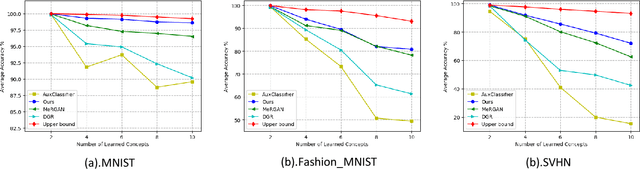
Abstract:The ability to learn more and more concepts over time from incrementally arriving data is essential for the development of a life-long learning system. However, deep neural networks often suffer from forgetting previously learned concepts when continually learning new concepts, which is known as catastrophic forgetting problem. The main reason for catastrophic forgetting is that the past concept data is not available and neural weights are changed during incrementally learning new concepts. In this paper, we propose a pseudo-rehearsal based class incremental learning approach to make neural networks capable of continually learning new concepts. We use a conditional generative adversarial network to consolidate old concepts memory and recall pseudo samples during learning new concepts and a balanced online memory recall strategy is to maximally maintain old memories. And we design a comprehensible incremental concept learning network as well as a concept contrastive loss to alleviate the magnitude of neural weights change. We evaluate the proposed approach on MNIST, Fashion-MNIST and SVHN datasets and compare with other rehearsal based approaches. The extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach.
LGM-Net: Learning to Generate Matching Networks for Few-Shot Learning
May 15, 2019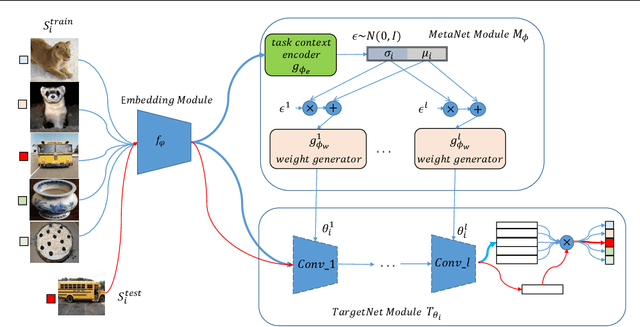
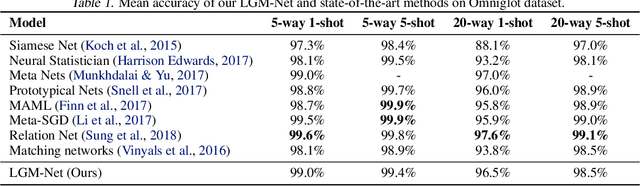
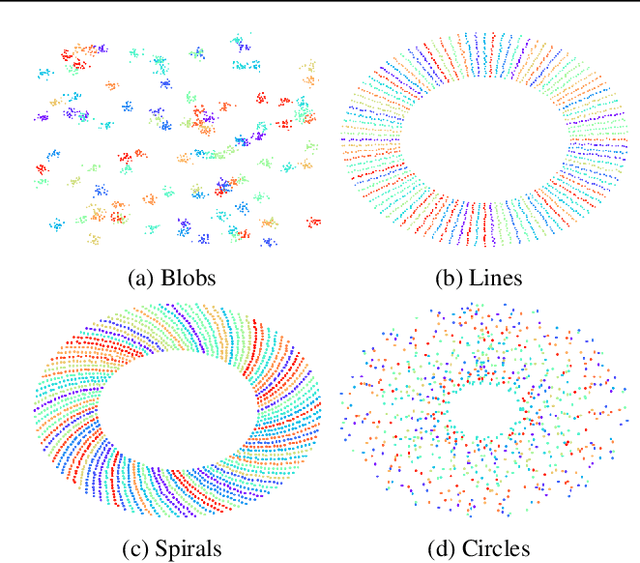
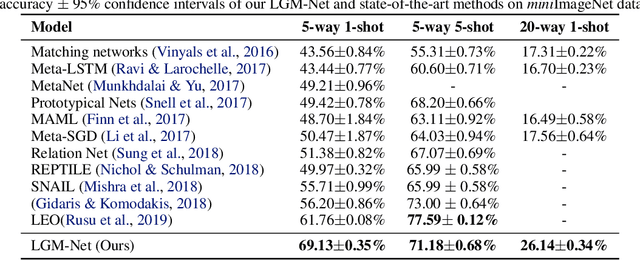
Abstract:In this work, we propose a novel meta-learning approach for few-shot classification, which learns transferable prior knowledge across tasks and directly produces network parameters for similar unseen tasks with training samples. Our approach, called LGM-Net, includes two key modules, namely, TargetNet and MetaNet. The TargetNet module is a neural network for solving a specific task and the MetaNet module aims at learning to generate functional weights for TargetNet by observing training samples. We also present an intertask normalization strategy for the training process to leverage common information shared across different tasks. The experimental results on Omniglot and miniImageNet datasets demonstrate that LGM-Net can effectively adapt to similar unseen tasks and achieve competitive performance, and the results on synthetic datasets show that transferable prior knowledge is learned by the MetaNet module via mapping training data to functional weights. LGM-Net enables fast learning and adaptation since no further tuning steps are required compared to other meta-learning approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge