Huafeng Yang
CAEN: A Hierarchically Attentive Evolution Network for Item-Attribute-Change-Aware Recommendation in the Growing E-commerce Environment
Aug 29, 2022


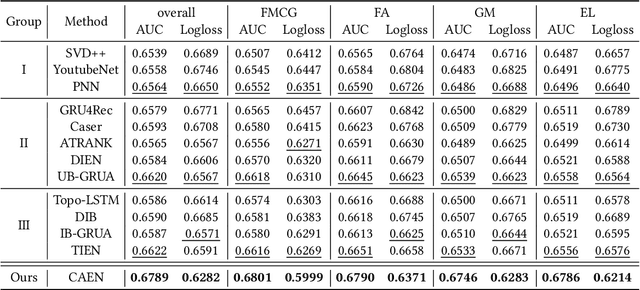
Abstract:Traditional recommendation systems mainly focus on modeling user interests. However, the dynamics of recommended items caused by attribute modifications (e.g. changes in prices) are also of great importance in real systems, especially in the fast-growing e-commerce environment, which may cause the users' demands to emerge, shift and disappear. Recent studies that make efforts on dynamic item representations treat the item attributes as side information but ignore its temporal dependency, or model the item evolution with a sequence of related users but do not consider item attributes. In this paper, we propose Core Attribute Evolution Network (CAEN), which partitions the user sequence according to the attribute value and thus models the item evolution over attribute dynamics with these users. Under this framework, we further devise a hierarchical attention mechanism that applies attribute-aware attention for user aggregation under each attribute, as well as personalized attention for activating similar users in assessing the matching degree between target user and item. Results from the extensive experiments over actual e-commerce datasets show that our approach outperforms the state-of-art methods and achieves significant improvements on the items with rapid changes over attributes, therefore helping the item recommendation to adapt to the growth of the e-commerce platform.
GCN-Based Linkage Prediction for Face Clustering on Imbalanced Datasets: An Empirical Study
Jul 07, 2021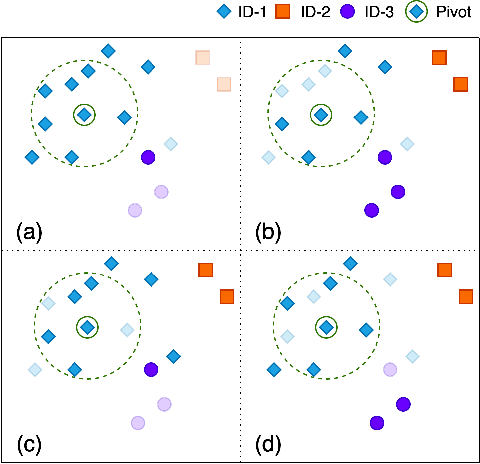
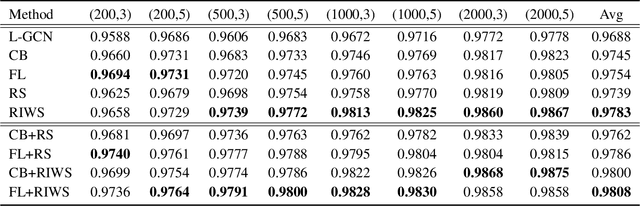
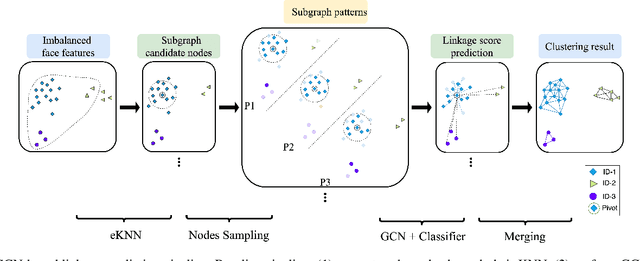
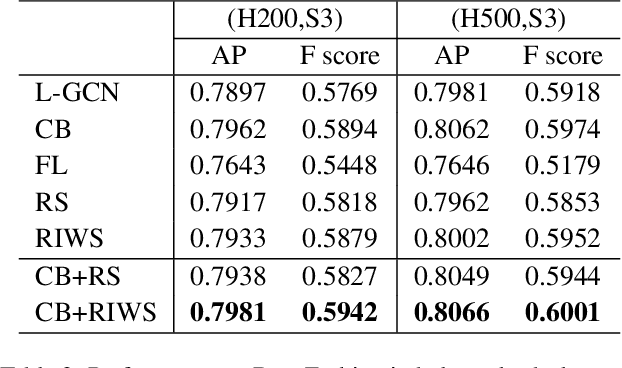
Abstract:In recent years, benefiting from the expressive power of Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs), significant breakthroughs have been made in face clustering. However, rare attention has been paid to GCN-based clustering on imbalanced data. Although imbalance problem has been extensively studied, the impact of imbalanced data on GCN-based linkage prediction task is quite different, which would cause problems in two aspects: imbalanced linkage labels and biased graph representations. The problem of imbalanced linkage labels is similar to that in image classification task, but the latter is a particular problem in GCN-based clustering via linkage prediction. Significantly biased graph representations in training can cause catastrophic overfitting of a GCN model. To tackle these problems, we evaluate the feasibility of those existing methods for imbalanced image classification problem on graphs with extensive experiments, and present a new method to alleviate the imbalanced labels and also augment graph representations using a Reverse-Imbalance Weighted Sampling (RIWS) strategy, followed with insightful analyses and discussions. The code and a series of imbalanced benchmark datasets synthesized from MS-Celeb-1M and DeepFashion are available on https://github.com/espectre/GCNs_on_imbalanced_datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge