Hsiang-Yun Huang
Domain-adaptive Fall Detection Using Deep Adversarial Training
Dec 20, 2020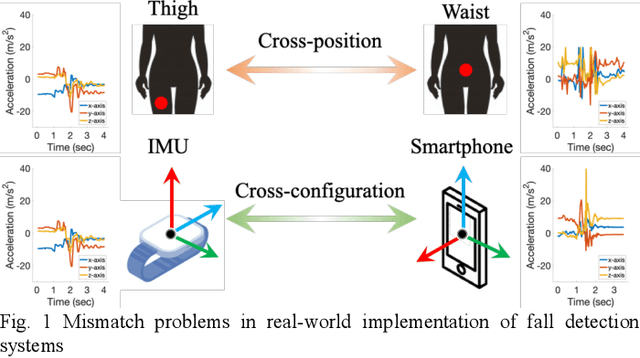

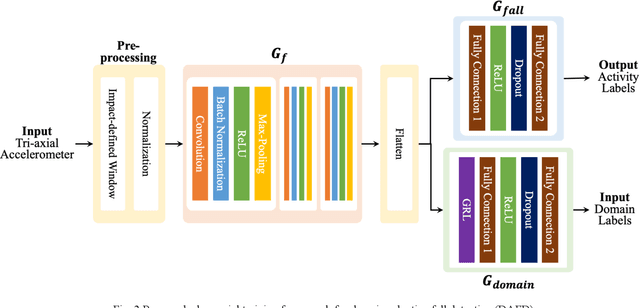
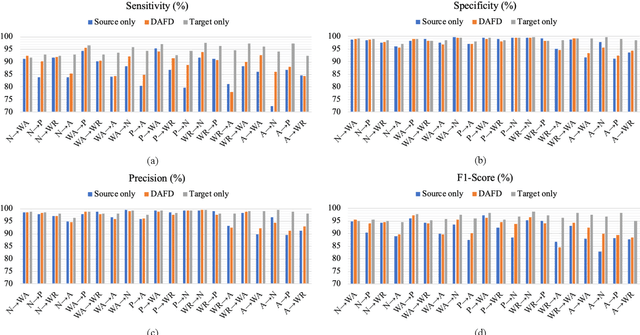
Abstract:Fall detection (FD) systems are important assistive technologies for healthcare that can detect emergency fall events and alert caregivers. However, it is not easy to obtain large-scale annotated fall events with various specifications of sensors or sensor positions, during the implementation of accurate FD systems. Moreover, the knowledge obtained through machine learning has been restricted to tasks in the same domain. The mismatch between different domains might hinder the performance of FD systems. Cross-domain knowledge transfer is very beneficial for machine-learning based FD systems to train a reliable FD model with well-labeled data in new environments. In this study, we propose domain-adaptive fall detection (DAFD) using deep adversarial training (DAT) to tackle cross-domain problems, such as cross-position and cross-configuration. The proposed DAFD can transfer knowledge from the source domain to the target domain by minimizing the domain discrepancy to avoid mismatch problems. The experimental results show that the average F1score improvement when using DAFD ranges from 1.5% to 7% in the cross-position scenario, and from 3.5% to 12% in the cross-configuration scenario, compared to using the conventional FD model without domain adaptation training. The results demonstrate that the proposed DAFD successfully helps to deal with cross-domain problems and to achieve better detection performance.
Deep Learning Based Signal Enhancement of Low-Resolution Accelerometer for Fall Detection Systems
Dec 07, 2020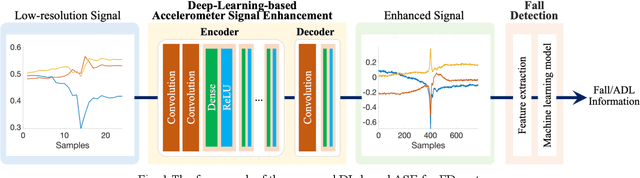
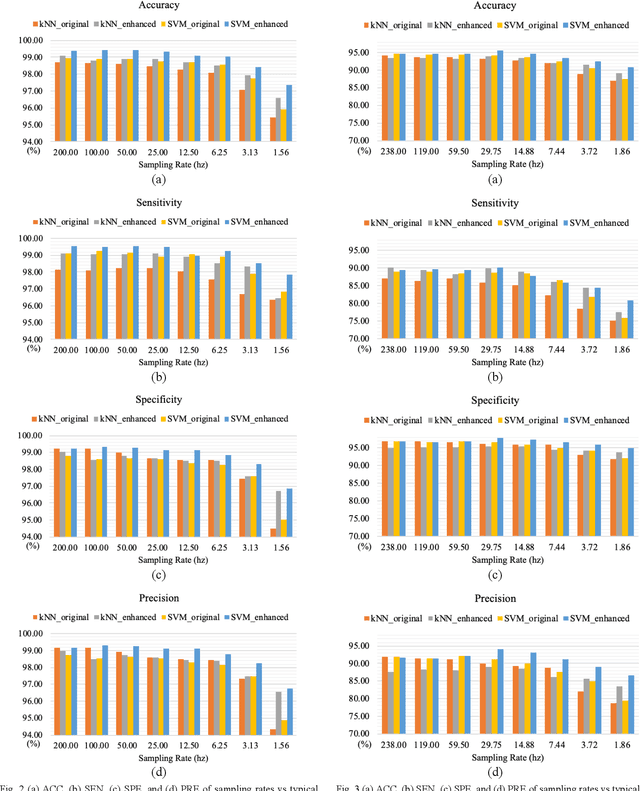
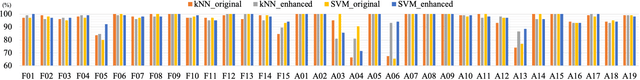
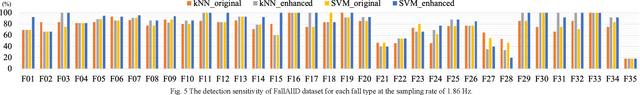
Abstract:In the last two decades, fall detection (FD) systems have been developed as a popular assistive technology. Such systems automatically detect critical fall events and immediately alert medical professionals or caregivers. To support long-term FD services, various power-saving strategies have been implemented. Among them, a reduced sampling rate is a common approach for an energy-efficient system in the real-world. However, the performance of FD systems is diminished owing to low-resolution (LR) accelerometer signals. To improve the detection accuracy with LR accelerometer signals, several technical challenges must be considered, including misalignment, mismatch of effective features, and the degradation effects. In this work, a deep-learning-based accelerometer signal enhancement (ASE) model is proposed to improve the detection performance of LR-FD systems. This proposed model reconstructs high-resolution (HR) signals from the LR signals by learning the relationship between the LR and HR signals. The results show that the FD system using support vector machine and the proposed ASE model at an extremely low sampling rate (sampling rate < 2 Hz) achieved 97.34% and 90.52% accuracies in the SisFall and FallAllD datasets, respectively, while those without ASE models only achieved 95.92% and 87.47% accuracies in the SisFall and FallAllD datasets, respectively. This study demonstrates that the ASE model helps the FD systems tackle the technical challenges of LR signals and achieve better detection performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge