Hoshin V. Gupta
KAN-Matrix: Visualizing Nonlinear Pairwise and Multivariate Contributions for Physical Insight
Dec 12, 2025



Abstract:Interpreting complex datasets remains a major challenge for scientists, particularly due to high dimensionality and collinearity among variables. We introduce a novel application of Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs) to enhance interpretability and parsimony beyond what traditional correlation analyses offer. We present two interpretable, color-coded visualization tools: the Pairwise KAN Matrix (PKAN) and the Multivariate KAN Contribution Matrix (MKAN). PKAN characterizes nonlinear associations between pairs of variables, while MKAN serves as a nonlinear feature-ranking tool that quantifies the relative contributions of inputs in predicting a target variable. These tools support pre-processing (e.g., feature selection, redundancy analysis) and post-processing (e.g., model explanation, physical insights) in model development workflows. Through experimental comparisons, we demonstrate that PKAN and MKAN yield more robust and informative results than Pearson Correlation and Mutual Information. By capturing the strength and functional forms of relationships, these matrices facilitate the discovery of hidden physical patterns and promote domain-informed model development.
Using Machine Learning to Discover Parsimonious and Physically-Interpretable Representations of Catchment-Scale Rainfall-Runoff Dynamics
Dec 06, 2024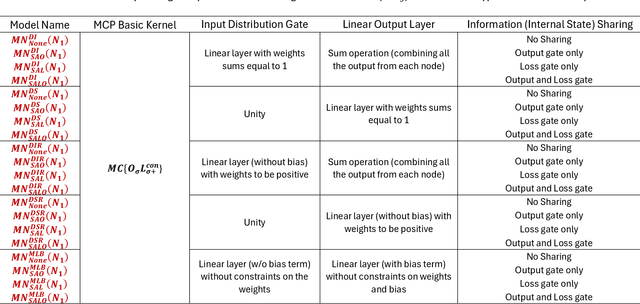
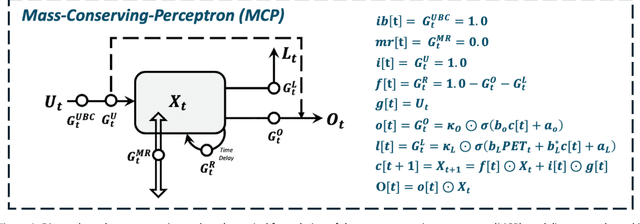
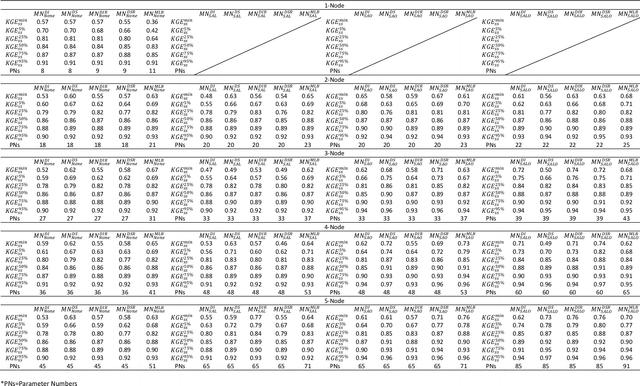
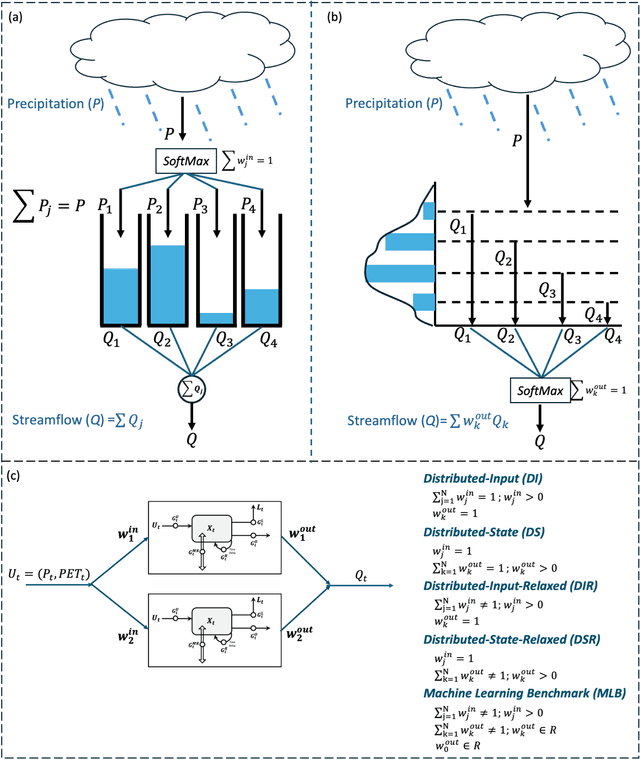
Abstract:Despite the excellent real-world predictive performance of modern machine learning (ML) methods, many scientists remain hesitant to discard traditional physical-conceptual (PC) approaches due mainly to their relative interpretability, which contributes to credibility during decision-making. In this context, a currently underexplored aspect of ML is how to develop minimally-optimal representations that can facilitate better insight regarding system functioning. Regardless of how this is achieved, it is arguably true that parsimonious representations better support the advancement of scientific understanding. Our own view is that ML-based modeling of geoscientific systems should be based in the use of computational units that are fundamentally interpretable by design. This paper continues our exploration of how the strengths of ML can be exploited in the service of better understanding via scientific investigation. Here, we use the Mass Conserving Perceptron (MCP) as the fundamental computational unit in a generic network architecture consisting of nodes arranged in series and parallel to explore several generic and important issues related to the use of observational data for constructing input-state-output models of dynamical systems. In the context of lumped catchment modeling, we show that physical interpretability and excellent predictive performance can both be achieved using a relatively parsimonious distributed-state multiple-flow-path network with context-dependent gating and information sharing across the nodes, suggesting that MCP-based modeling can play a significant role in application of ML to geoscientific investigation.
Towards Interpretable Physical-Conceptual Catchment-Scale Hydrological Modeling using the Mass-Conserving-Perceptron
Jan 29, 2024Abstract:We investigate the applicability of machine learning technologies to the development of parsimonious, interpretable, catchment-scale hydrologic models using directed-graph architectures based on the mass-conserving perceptron (MCP) as the fundamental computational unit. Here, we focus on architectural complexity (depth) at a single location, rather than universal applicability (breadth) across large samples of catchments. The goal is to discover a minimal representation (numbers of cell-states and flow paths) that represents the dominant processes that can explain the input-state-output behaviors of a given catchment, with particular emphasis given to simulating the full range (high, medium, and low) of flow dynamics. We find that a HyMod-like architecture with three cell-states and two major flow pathways achieves such a representation at our study location, but that the additional incorporation of an input-bypass mechanism significantly improves the timing and shape of the hydrograph, while the inclusion of bi-directional groundwater mass exchanges significantly enhances the simulation of baseflow. Overall, our results demonstrate the importance of using multiple diagnostic metrics for model evaluation, while highlighting the need for designing training metrics that are better suited to extracting information across the full range of flow dynamics. Further, they set the stage for interpretable regional-scale MCP-based hydrological modeling (using large sample data) by using neural architecture search to determine appropriate minimal representations for catchments in different hydroclimatic regimes.
A Mass-Conserving-Perceptron for Machine Learning-Based Modeling of Geoscientific Systems
Oct 24, 2023Abstract:Although decades of effort have been devoted to building Physical-Conceptual (PC) models for predicting the time-series evolution of geoscientific systems, recent work shows that Machine Learning (ML) based Gated Recurrent Neural Network technology can be used to develop models that are much more accurate. However, the difficulty of extracting physical understanding from ML-based models complicates their utility for enhancing scientific knowledge regarding system structure and function. Here, we propose a physically-interpretable Mass Conserving Perceptron (MCP) as a way to bridge the gap between PC-based and ML-based modeling approaches. The MCP exploits the inherent isomorphism between the directed graph structures underlying both PC models and GRNNs to explicitly represent the mass-conserving nature of physical processes while enabling the functional nature of such processes to be directly learned (in an interpretable manner) from available data using off-the-shelf ML technology. As a proof of concept, we investigate the functional expressivity (capacity) of the MCP, explore its ability to parsimoniously represent the rainfall-runoff (RR) dynamics of the Leaf River Basin, and demonstrate its utility for scientific hypothesis testing. To conclude, we discuss extensions of the concept to enable ML-based physical-conceptual representation of the coupled nature of mass-energy-information flows through geoscientific systems.
Nowcasting-Nets: Deep Neural Network Structures for Precipitation Nowcasting Using IMERG
Aug 16, 2021



Abstract:Accurate and timely estimation of precipitation is critical for issuing hazard warnings (e.g., for flash floods or landslides). Current remotely sensed precipitation products have a few hours of latency, associated with the acquisition and processing of satellite data. By applying a robust nowcasting system to these products, it is (in principle) possible to reduce this latency and improve their applicability, value, and impact. However, the development of such a system is complicated by the chaotic nature of the atmosphere, and the consequent rapid changes that can occur in the structures of precipitation systems In this work, we develop two approaches (hereafter referred to as Nowcasting-Nets) that use Recurrent and Convolutional deep neural network structures to address the challenge of precipitation nowcasting. A total of five models are trained using Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Integrated Multi-satellitE Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) precipitation data over the Eastern Contiguous United States (CONUS) and then tested against independent data for the Eastern and Western CONUS. The models were designed to provide forecasts with a lead time of up to 1.5 hours and, by using a feedback loop approach, the ability of the models to extend the forecast time to 4.5 hours was also investigated. Model performance was compared against the Random Forest (RF) and Linear Regression (LR) machine learning methods, and also against a persistence benchmark (BM) that used the most recent observation as the forecast. Independent IMERG observations were used as a reference, and experiments were conducted to examine both overall statistics and case studies involving specific precipitation events. Overall, the forecasts provided by the Nowcasting-Net models are superior, with the Convolutional Nowcasting Network with Residual Head (CNC-R) achieving 25%, 28%, and 46% improvement in the test ...
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge