Homa Fashandi
Weakly-Supervised Multi-Task Learning for Audio-Visual Speaker Verification
Sep 13, 2023



Abstract:In this paper, we present a methodology for achieving robust multimodal person representations optimized for open-set audio-visual speaker verification. Distance Metric Learning (DML) approaches have typically dominated this problem space, owing to strong performance on new and unseen classes. In our work, we explored multitask learning techniques to further boost performance of the DML approach and show that an auxiliary task with weak labels can increase the compactness of the learned speaker representation. We also extend the Generalized end-to-end loss (GE2E) to multimodal inputs and demonstrate that it can achieve competitive performance in an audio-visual space. Finally, we introduce a non-synchronous audio-visual sampling random strategy during training time that has shown to improve generalization. Our network achieves state of the art performance for speaker verification, reporting 0.244%, 0.252%, 0.441% Equal Error Rate (EER) on the three official trial lists of VoxCeleb1-O/E/H, which is to our knowledge, the best published results on VoxCeleb1-E and VoxCeleb1-H.
Stochastic Whitening Batch Normalization
Jun 03, 2021
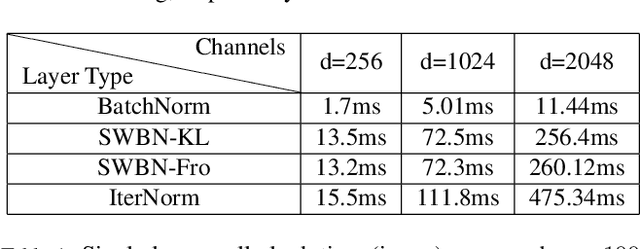

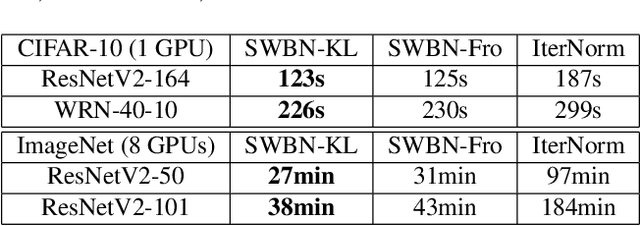
Abstract:Batch Normalization (BN) is a popular technique for training Deep Neural Networks (DNNs). BN uses scaling and shifting to normalize activations of mini-batches to accelerate convergence and improve generalization. The recently proposed Iterative Normalization (IterNorm) method improves these properties by whitening the activations iteratively using Newton's method. However, since Newton's method initializes the whitening matrix independently at each training step, no information is shared between consecutive steps. In this work, instead of exact computation of whitening matrix at each time step, we estimate it gradually during training in an online fashion, using our proposed Stochastic Whitening Batch Normalization (SWBN) algorithm. We show that while SWBN improves the convergence rate and generalization of DNNs, its computational overhead is less than that of IterNorm. Due to the high efficiency of the proposed method, it can be easily employed in most DNN architectures with a large number of layers. We provide comprehensive experiments and comparisons between BN, IterNorm, and SWBN layers to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed technique in conventional (many-shot) image classification and few-shot classification tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge