Stochastic Whitening Batch Normalization
Paper and Code
Jun 03, 2021
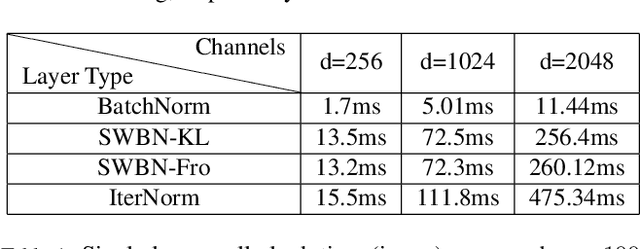

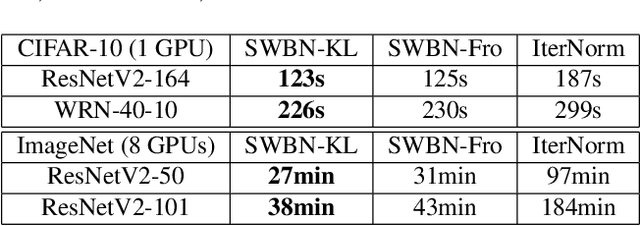
Batch Normalization (BN) is a popular technique for training Deep Neural Networks (DNNs). BN uses scaling and shifting to normalize activations of mini-batches to accelerate convergence and improve generalization. The recently proposed Iterative Normalization (IterNorm) method improves these properties by whitening the activations iteratively using Newton's method. However, since Newton's method initializes the whitening matrix independently at each training step, no information is shared between consecutive steps. In this work, instead of exact computation of whitening matrix at each time step, we estimate it gradually during training in an online fashion, using our proposed Stochastic Whitening Batch Normalization (SWBN) algorithm. We show that while SWBN improves the convergence rate and generalization of DNNs, its computational overhead is less than that of IterNorm. Due to the high efficiency of the proposed method, it can be easily employed in most DNN architectures with a large number of layers. We provide comprehensive experiments and comparisons between BN, IterNorm, and SWBN layers to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed technique in conventional (many-shot) image classification and few-shot classification tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge