Hoang-Son Nguyen
Learning Graph from Smooth Signals under Partial Observation: A Robustness Analysis
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Learning the graph underlying a networked system from nodal signals is crucial to downstream tasks in graph signal processing and machine learning. The presence of hidden nodes whose signals are not observable might corrupt the estimated graph. While existing works proposed various robustifications of vanilla graph learning objectives by explicitly accounting for the presence of these hidden nodes, a robustness analysis of "naive", hidden-node agnostic approaches is still underexplored. This work demonstrates that vanilla graph topology learning methods are implicitly robust to partial observations of low-pass filtered graph signals. We achieve this theoretical result through extending the restricted isometry property (RIP) to the Dirichlet energy function used in graph learning objectives. We show that smoothness-based graph learning formulation (e.g., the GL-SigRep method) on partial observations can recover the ground truth graph topology corresponding to the observed nodes. Synthetic and real data experiments corroborate our findings.
On Detecting Low-pass Graph Signals under Partial Observations
May 16, 2024Abstract:The application of graph signal processing (GSP) on partially observed graph signals with missing nodes has gained attention recently. This is because processing data from large graphs are difficult, if not impossible due to the lack of availability of full observations. Many prior works have been developed using the assumption that the generated graph signals are smooth or low pass filtered. This paper treats a blind graph filter detection problem under this context. We propose a detector that certifies whether the partially observed graph signals are low pass filtered, without requiring the graph topology knowledge. As an example application, our detector leads to a pre-screening method to filter out non low pass signals and thus robustify the prior GSP algorithms. We also bound the sample complexity of our detector in terms of the class of filters, number of observed nodes, etc. Numerical experiments verify the efficacy of our method.
On the Stability of Low Pass Graph Filter With a Large Number of Edge Rewires
Oct 14, 2021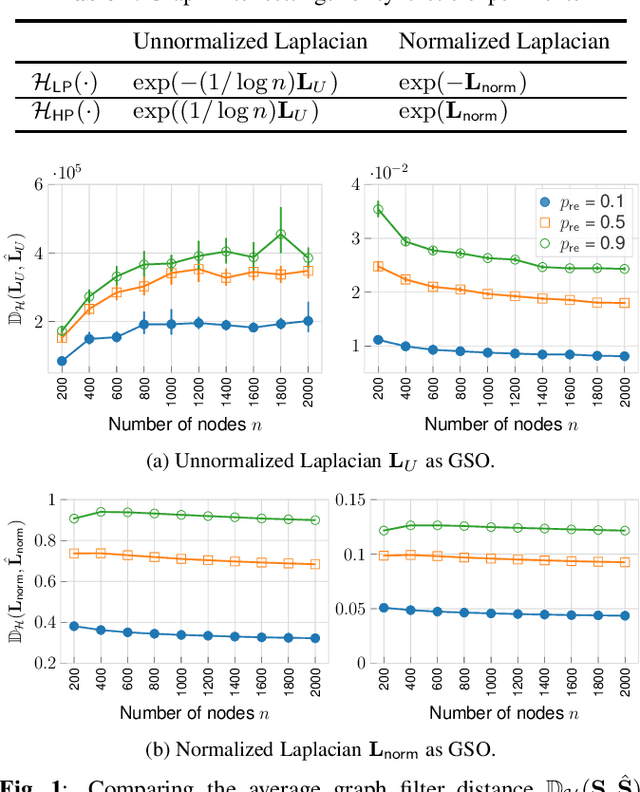
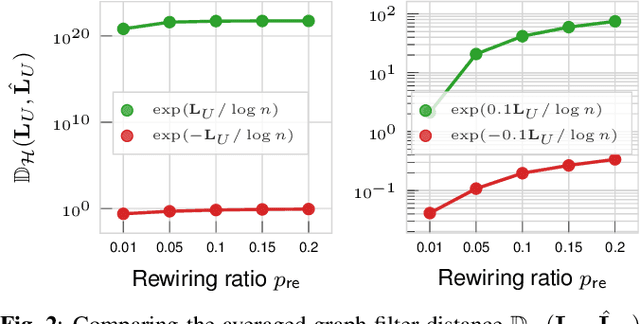
Abstract:Recently, the stability of graph filters has been studied as one of the key theoretical properties driving the highly successful graph convolutional neural networks (GCNs). The stability of a graph filter characterizes the effect of topology perturbation on the output of a graph filter, a fundamental building block for GCNs. Many existing results have focused on the regime of small perturbation with a small number of edge rewires. However, the number of edge rewires can be large in many applications. To study the latter case, this work departs from the previous analysis and proves a bound on the stability of graph filter relying on the filter's frequency response. Assuming the graph filter is low pass, we show that the stability of the filter depends on perturbation to the community structure. As an application, we show that for stochastic block model graphs, the graph filter distance converges to zero when the number of nodes approaches infinity. Numerical simulations validate our findings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge