Ho Jin Choi
COMETH: Convex Optimization for Multiview Estimation and Tracking of Humans
Aug 28, 2025Abstract:In the era of Industry 5.0, monitoring human activity is essential for ensuring both ergonomic safety and overall well-being. While multi-camera centralized setups improve pose estimation accuracy, they often suffer from high computational costs and bandwidth requirements, limiting scalability and real-time applicability. Distributing processing across edge devices can reduce network bandwidth and computational load. On the other hand, the constrained resources of edge devices lead to accuracy degradation, and the distribution of computation leads to temporal and spatial inconsistencies. We address this challenge by proposing COMETH (Convex Optimization for Multiview Estimation and Tracking of Humans), a lightweight algorithm for real-time multi-view human pose fusion that relies on three concepts: it integrates kinematic and biomechanical constraints to increase the joint positioning accuracy; it employs convex optimization-based inverse kinematics for spatial fusion; and it implements a state observer to improve temporal consistency. We evaluate COMETH on both public and industrial datasets, where it outperforms state-of-the-art methods in localization, detection, and tracking accuracy. The proposed fusion pipeline enables accurate and scalable human motion tracking, making it well-suited for industrial and safety-critical applications. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/PARCO-LAB/COMETH.
On the Feasibility of EEG-based Motor Intention Detection for Real-Time Robot Assistive Control
Mar 13, 2024



Abstract:This paper explores the feasibility of employing EEG-based intention detection for real-time robot assistive control. We focus on predicting and distinguishing motor intentions of left/right arm movements by presenting: i) an offline data collection and training pipeline, used to train a classifier for left/right motion intention prediction, and ii) an online real-time prediction pipeline leveraging the trained classifier and integrated with an assistive robot. Central to our approach is a rich feature representation composed of the tangent space projection of time-windowed sample covariance matrices from EEG filtered signals and derivatives; allowing for a simple SVM classifier to achieve unprecedented accuracy and real-time performance. In pre-recorded real-time settings (160 Hz), a peak accuracy of 86.88% is achieved, surpassing prior works. In robot-in-the-loop settings, our system successfully detects intended motion solely from EEG data with 70% accuracy, triggering a robot to execute an assistive task. We provide a comprehensive evaluation of the proposed classifier.
Towards Feasible Dynamic Grasping: Leveraging Gaussian Process Distance Field, SE(3) Equivariance and Riemannian Mixture Models
Nov 08, 2023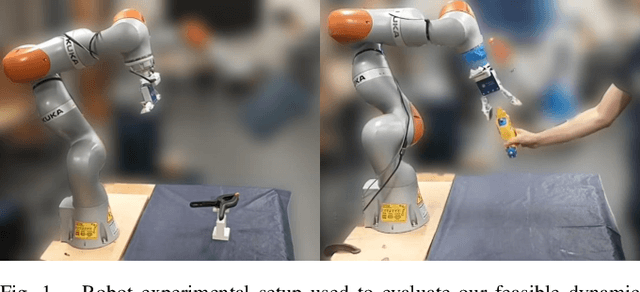
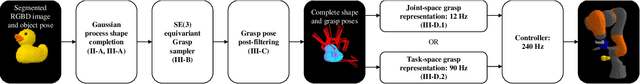
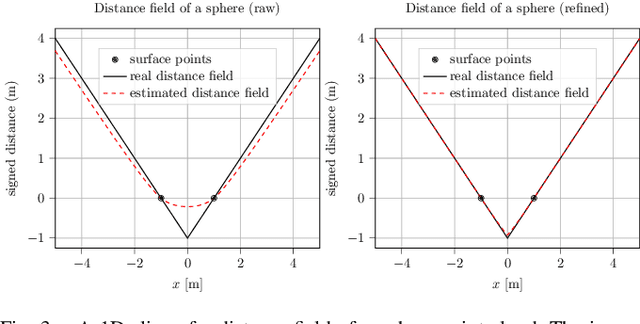

Abstract:In this paper, we present a novel approach towards feasible dynamic grasping by leveraging Gaussian Process Distance Fields (GPDF), SE(3) equivariance, and Riemannian Mixture Models. We seek to improve the grasping capabilities of robots in dynamic tasks where objects may be moving. The proposed method combines object shape reconstruction, grasp sampling, and grasp pose selection to enable effective grasping in such scenarios. By utilizing GPDF, the approach accurately models the shape and physical properties of objects, allowing for precise grasp planning. SE(3) equivariance ensures that the sampled grasp poses are equivariant to the object's pose. Additionally, Riemannian Gaussian Mixture Models are employed to test reachability, providing a feasible and adaptable grasping strategy. The sampled feasible grasp poses are used as targets for novel task or joint space reactive controllers formulated by Gaussian Mixture Models and Gaussian Processes, respectively. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach in generating feasible grasp poses and successful grasping in dynamic environments. (Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wjIVrwTzTOc&t=70s)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge