Henda Ben Ghézala
Randomly Initialized Convolutional Neural Network for the Recognition of COVID-19 using X-ray Images
May 17, 2021



Abstract:By the start of 2020, the novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) has been declared a worldwide pandemic. Because of the severity of this infectious disease, several kinds of research have focused on combatting its ongoing spread. One potential solution to detect COVID-19 is by analyzing the chest X-ray images using Deep Learning (DL) models. In this context, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are presented as efficient techniques for early diagnosis. In this study, we propose a novel randomly initialized CNN architecture for the recognition of COVID-19. This network consists of a set of different-sized hidden layers created from scratch. The performance of this network is evaluated through two public datasets, which are the COVIDx and the enhanced COVID-19 datasets. Both of these datasets consist of 3 different classes of images: COVID19, pneumonia, and normal chest X-ray images. The proposed CNN model yields encouraging results with 94% and 99% of accuracy for COVIDx and enhanced COVID-19 dataset, respectively.
An Enhanced Randomly Initialized Convolutional Neural Network for Columnar Cactus Recognition in Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Imagery
May 10, 2021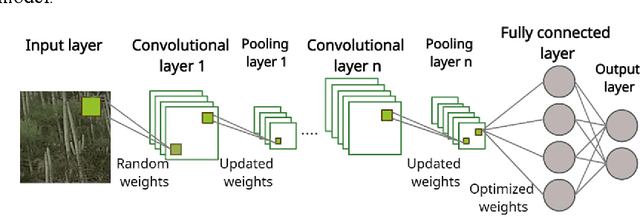
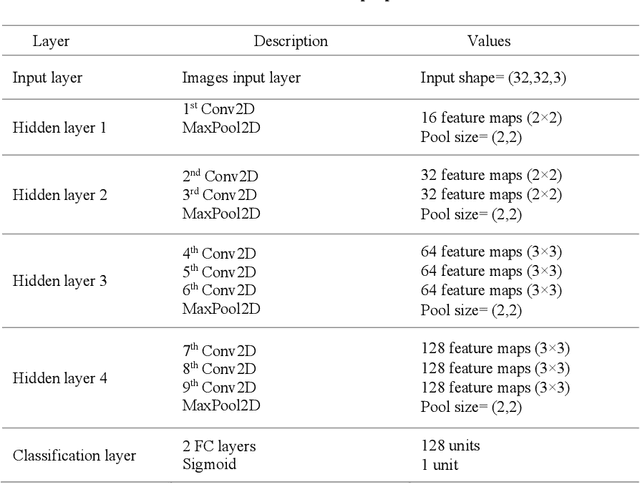

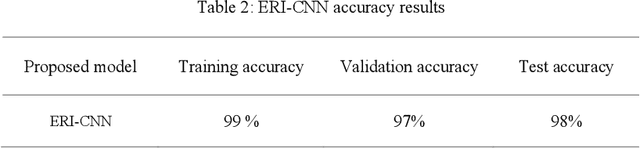
Abstract:Recently, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have made a great performance for remote sensing image classification. Plant recognition using CNNs is one of the active deep learning research topics due to its added-value in different related fields, especially environmental conservation and natural areas preservation. Automatic recognition of plants in protected areas helps in the surveillance process of these zones and ensures the sustainability of their ecosystems. In this work, we propose an Enhanced Randomly Initialized Convolutional Neural Network (ERI-CNN) for the recognition of columnar cactus, which is an endemic plant that exists in the Tehuac\'an-Cuicatl\'an Valley in southeastern Mexico. We used a public dataset created by a group of researchers that consists of more than 20000 remote sensing images. The experimental results confirm the effectiveness of the proposed model compared to other models reported in the literature like InceptionV3 and the modified LeNet-5 CNN. Our ERI-CNN provides 98% of accuracy, 97% of precision, 97% of recall, 97.5% as f1-score, and 0.056 loss.
Towards a Collaborative Approach to Decision Making Based on Ontology and Multi-Agent System Application to crisis management
Mar 16, 2020



Abstract:The coordination and cooperation of all the stakeholders involved is a decisive point for the control and the resolution of problems. In the insecurity events, the resolution should refer to a plan that defines a general framework of the procedures to be undertaken and the instructions to be complied with; also, a more precise process must be defined by the actors to deal with the case represented by the particular problem of the current situation. Indeed, this process has to cope with a dynamic, unstable and unpredictable environment, due to the heterogeneity and multiplicity of stakeholders, and finally due to their possible geographical distribution. In this article, we will present the first steps of validation of a collaborative decision-making approach in the context of crisis situations such as road accidents. This approach is based on ontologies and multi-agent systems.
* 6 pages, 4 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge