Ahmed Maalel
General DeepLCP model for disease prediction : Case of Lung Cancer
Sep 15, 2020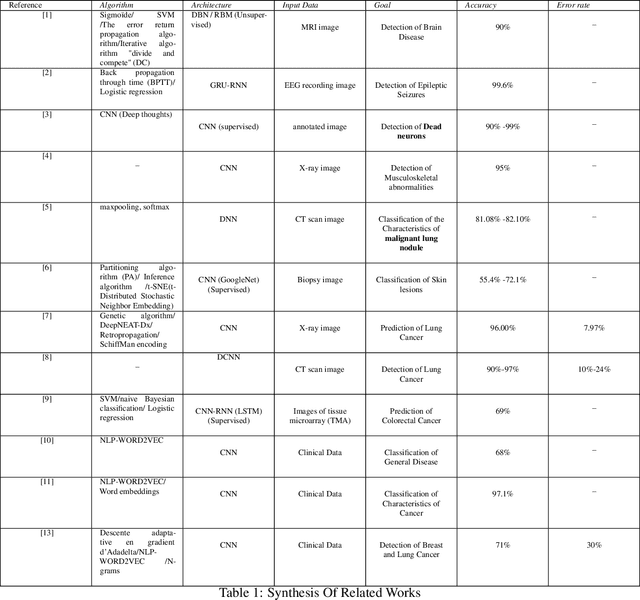
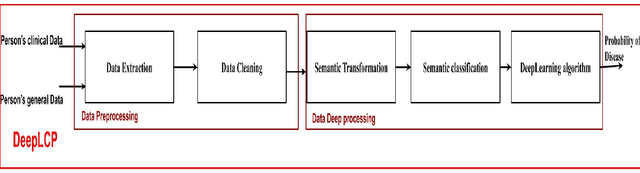
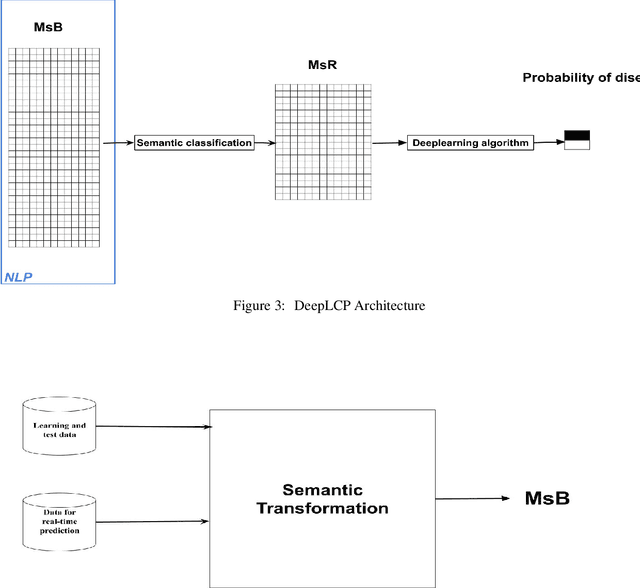
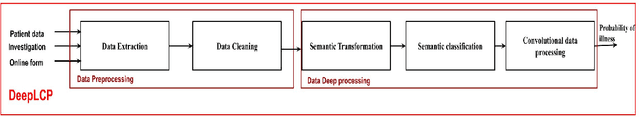
Abstract:According to GHO (Global Health Observatory (GHO), the high prevalence of a large variety of diseases such as Ischaemic heart disease, stroke, lung cancer disease and lower respiratory infections have remained the top killers during the past decade. The growth in the number of mortalities caused by these disease is due to the very delayed symptoms'detection. Since in the early stages, the symptoms are insignificant and similar to those of benign diseases (e.g. the flu ), and we can only detect the disease at an advanced stage. In addition, The high frequency of improper practices that are harmful to health, the hereditary factors, and the stressful living conditions can increase the death rates. Many researches dealt with these fatal disease, and most of them applied advantage machine learning models to deal with image diagnosis. However the drawback is that imagery permit only to detect disease at a very delayed stage and then patient can hardly be saved. In this Paper we present our new approach "DeepLCP" to predict fatal diseases that threaten people's lives. It's mainly based on raw and heterogeneous data of the concerned (or under-tested) person. "DeepLCP" results of a combination combination of the Natural Language Processing (NLP) and the deep learning paradigm.The experimental results of the proposed model in the case of Lung cancer prediction have approved high accuracy and a low loss data rate during the validation of the disease prediction.
Towards a Collaborative Approach to Decision Making Based on Ontology and Multi-Agent System Application to crisis management
Mar 16, 2020



Abstract:The coordination and cooperation of all the stakeholders involved is a decisive point for the control and the resolution of problems. In the insecurity events, the resolution should refer to a plan that defines a general framework of the procedures to be undertaken and the instructions to be complied with; also, a more precise process must be defined by the actors to deal with the case represented by the particular problem of the current situation. Indeed, this process has to cope with a dynamic, unstable and unpredictable environment, due to the heterogeneity and multiplicity of stakeholders, and finally due to their possible geographical distribution. In this article, we will present the first steps of validation of a collaborative decision-making approach in the context of crisis situations such as road accidents. This approach is based on ontologies and multi-agent systems.
* 6 pages, 4 figures
Development of an Ontology to Assist the Modeling of Accident Scenarii "Application on Railroad Transport "
Mar 05, 2012



Abstract:In a world where communication and information sharing are at the heart of our business, the terminology needs are most pressing. It has become imperative to identify the terms used and defined in a consensual and coherent way while preserving linguistic diversity. To streamline and strengthen the process of acquisition, representation and exploitation of scenarii of train accidents, it is necessary to harmonize and standardize the terminology used by players in the security field. The research aims to significantly improve analytical activities and operations of the various safety studies, by tracking the error in system, hardware, software and human. This paper presents the contribution of ontology to modeling scenarii for rail accidents through a knowledge model based on a generic ontology and domain ontology. After a detailed presentation of the state of the art material, this article presents the first results of the developed model.
* 7 pages, 9 figures, Journal of Computing (ISSN 2151-9617); Journal of Computing, Volume 3, Issue 7, July 2011
Contribution of Case Based Reasoning in the Exploitation of Return of Experience. Application to Accident Scenarii in Railroad Transport
Mar 03, 2012



Abstract:The study is from a base of accident scenarii in rail transport (feedback) in order to develop a tool to share build and sustain knowledge and safety and secondly to exploit the knowledge stored to prevent the reproduction of accidents / incidents. This tool should ultimately lead to the proposal of prevention and protection measures to minimize the risk level of a new transport system and thus to improve safety. The approach to achieving this goal largely depends on the use of artificial intelligence techniques and rarely the use of a method of automatic learning in order to develop a feasibility model of a software tool based on case based reasoning (CBR) to exploit stored knowledge in order to create know-how that can help stimulate domain experts in the task of analysis, evaluation and certification of a new system.
* Paper Award, 8 pages, 10 figures,3rd International Conference on Information Systems and Economic Intelligence, 18-20 february 2010, Sousse, Tunisia. http://siie2010.loria.fr/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge