Hemant Kumar Singh
Geolocating Earth Imagery from ISS: Integrating Machine Learning with Astronaut Photography for Enhanced Geographic Mapping
Apr 29, 2025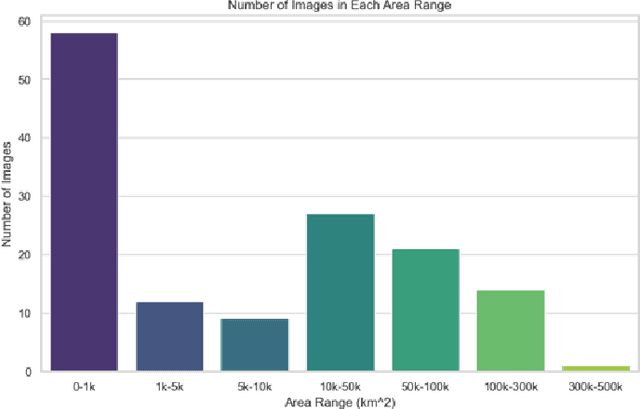
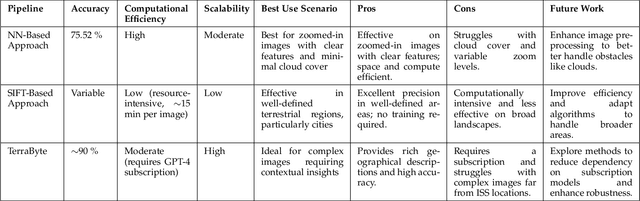
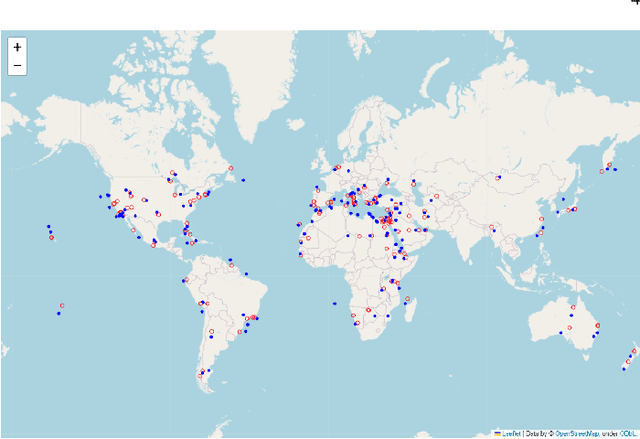
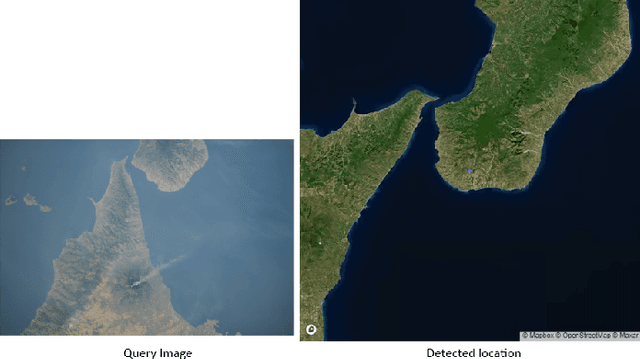
Abstract:This paper presents a novel approach to geolocating images captured from the International Space Station (ISS) using advanced machine learning algorithms. Despite having precise ISS coordinates, the specific Earth locations depicted in astronaut-taken photographs often remain unidentified. Our research addresses this gap by employing three distinct image processing pipelines: a Neural Network based approach, a SIFT based method, and GPT-4 model. Each pipeline is tailored to process high-resolution ISS imagery, identifying both natural and man-made geographical features. Through extensive evaluation on a diverse dataset of over 140 ISS images, our methods demonstrate significant promise in automated geolocation with varied levels of success. The NN approach showed a high success rate in accurately matching geographical features, while the SIFT pipeline excelled in processing zoomed-in images. GPT-4 model provided enriched geographical descriptions alongside location predictions. This research contributes to the fields of remote sensing and Earth observation by enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of geolocating space-based imagery, thereby aiding environmental monitoring and global mapping efforts.
Decomposition of Difficulties in Complex Optimization Problems Using a Bilevel Approach
Jul 03, 2024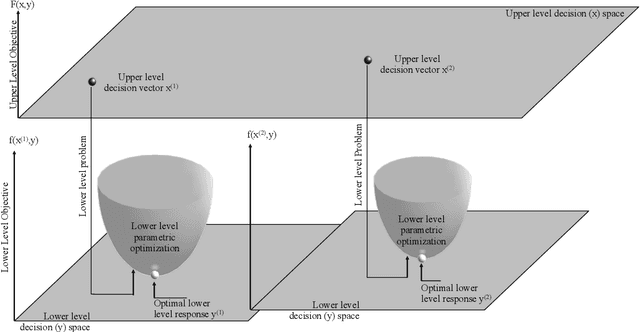
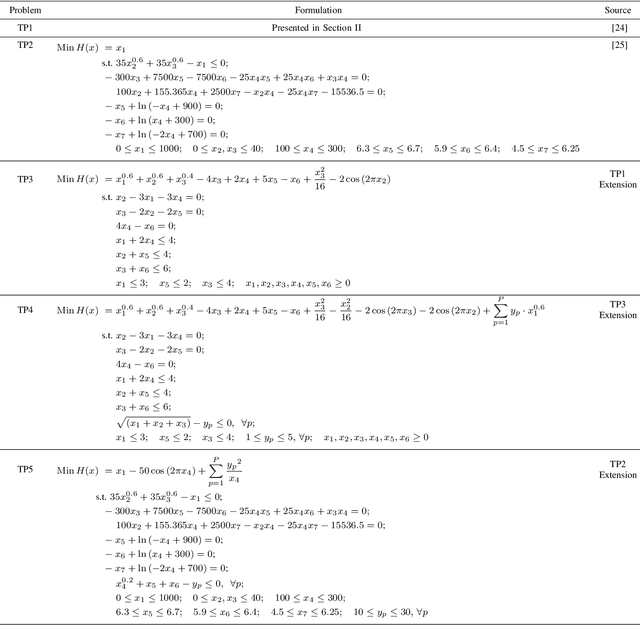

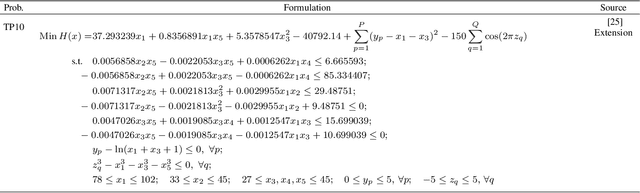
Abstract:Practical optimization problems may contain different kinds of difficulties that are often not tractable if one relies on a particular optimization method. Different optimization approaches offer different strengths that are good at tackling one or more difficulty in an optimization problem. For instance, evolutionary algorithms have a niche in handling complexities like discontinuity, non-differentiability, discreteness and non-convexity. However, evolutionary algorithms may get computationally expensive for mathematically well behaved problems with large number of variables for which classical mathematical programming approaches are better suited. In this paper, we demonstrate a decomposition strategy that allows us to synergistically apply two complementary approaches at the same time on a complex optimization problem. Evolutionary algorithms are useful in this context as their flexibility makes pairing with other solution approaches easy. The decomposition idea is a special case of bilevel optimization that separates the difficulties into two levels and assigns different approaches at each level that is better equipped at handling them. We demonstrate the benefits of the proposed decomposition idea on a wide range of test problems.
A Simple Evolutionary Algorithm for Multi-modal Multi-objective Optimization
Jan 18, 2022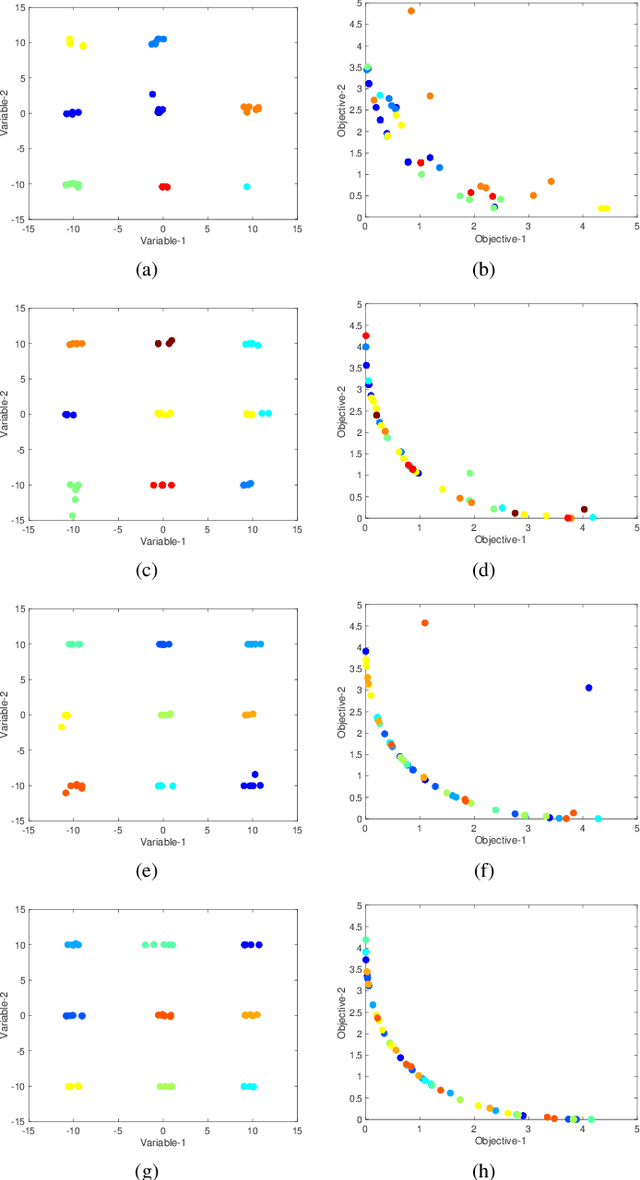
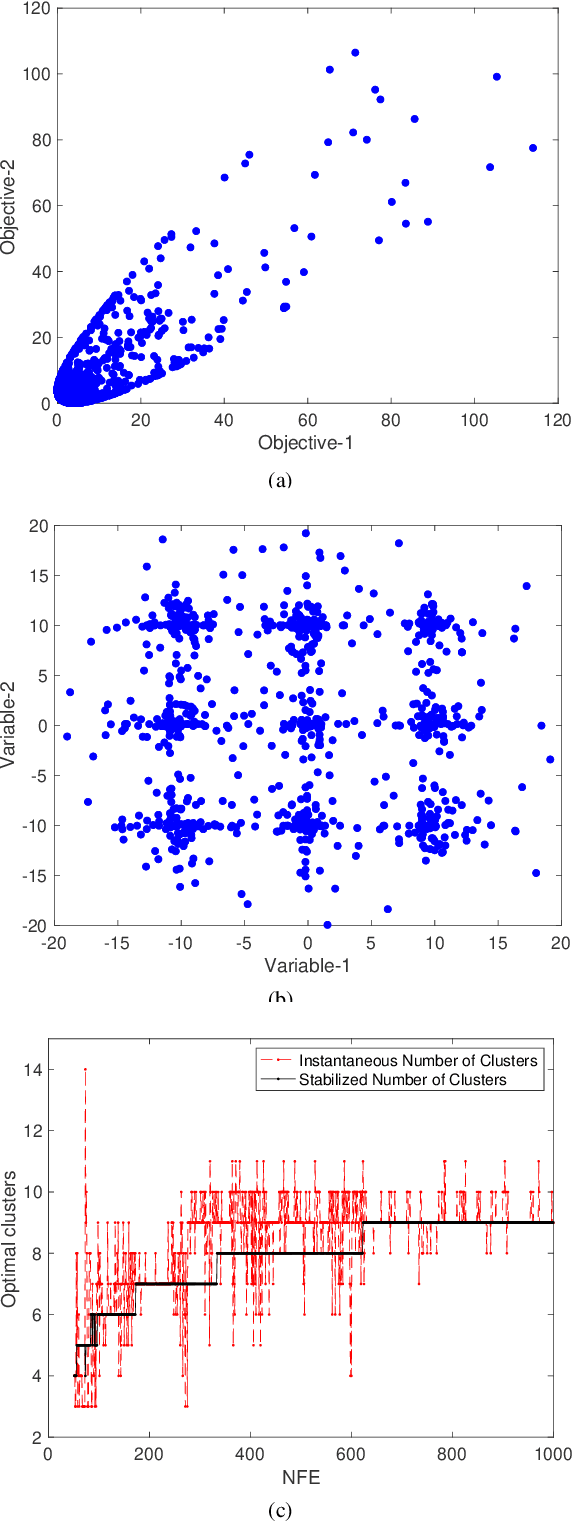
Abstract:In solving multi-modal, multi-objective optimization problems (MMOPs), the objective is not only to find a good representation of the Pareto-optimal front (PF) in the objective space but also to find all equivalent Pareto-optimal subsets (PSS) in the variable space. Such problems are practically relevant when a decision maker (DM) is interested in identifying alternative designs with similar performance. There has been significant research interest in recent years to develop efficient algorithms to deal with MMOPs. However, the existing algorithms still require prohibitive number of function evaluations (often in several thousands) to deal with problems involving as low as two objectives and two variables. The algorithms are typically embedded with sophisticated, customized mechanisms that require additional parameters to manage the diversity and convergence in the variable and the objective spaces. In this letter, we introduce a steady-state evolutionary algorithm for solving MMOPs, with a simple design and no additional userdefined parameters that need tuning compared to a standard EA. We report its performance on 21 MMOPs from various test suites that are widely used for benchmarking using a low computational budget of 1000 function evaluations. The performance of the proposed algorithm is compared with six state-of-the-art algorithms (MO Ring PSO SCD, DN-NSGAII, TriMOEA-TA&R, CPDEA, MMOEA/DC and MMEA-WI). The proposed algorithm exhibits significantly better performance than the above algorithms based on the established metrics including IGDX, PSP and IGD. We hope this study would encourage design of simple, efficient and generalized algorithms to improve its uptake for practical applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge