Get our free extension to see links to code for papers anywhere online!Free add-on: code for papers everywhere!Free add-on: See code for papers anywhere!
Heinz Riener
Safety Synthesis Sans Specification
Nov 27, 2020Figures and Tables: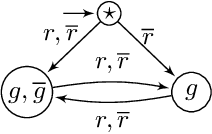
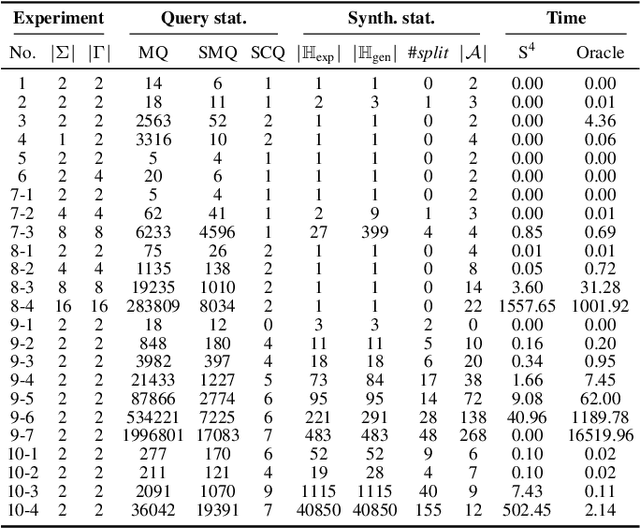
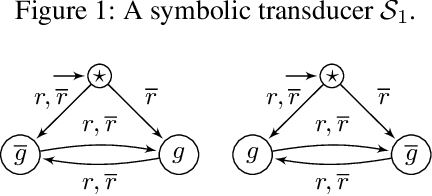
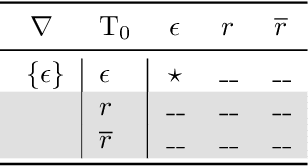




Abstract:We define the problem of learning a transducer ${S}$ from a target language $U$ containing possibly conflicting transducers, using membership queries and conjecture queries. The requirement is that the language of ${S}$ be a subset of $U$. We argue that this is a natural question in many situations in hardware and software verification. We devise a learning algorithm for this problem and show that its time and query complexity is polynomial with respect to the rank of the target language, its incompatibility measure, and the maximal length of a given counterexample. We report on experiments conducted with a prototype implementation.
Via
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge