Harun Siljak
Classical Capacity of Arbitrarily Distributed Noisy Quantum Channels
Jun 28, 2023Abstract:With the rapid deployment of quantum computers and quantum satellites, there is a pressing need to design and deploy quantum and hybrid classical-quantum networks capable of exchanging classical information. In this context, we conduct the foundational study on the impact of a mixture of classical and quantum noise on an arbitrary quantum channel carrying classical information. The rationale behind considering such mixed noise is that quantum noise can arise from different entanglement and discord in quantum transmission scenarios, like different memories and repeater technologies, while classical noise can arise from the coexistence with the classical signal. Towards this end, we derive the distribution of the mixed noise from a classical system's perspective, and formulate the achievable channel capacity over an arbitrary distributed quantum channel in presence of the mixed noise. Numerical results demonstrate that capacity increases with the increase in the number of photons per usage.
Semantic-Functional Communications in Cyber-Physical Systems
May 31, 2023Abstract:This paper explores the use of semantic knowledge inherent in the cyber-physical system (CPS) under study in order to minimize the use of explicit communication, which refers to the use of physical radio resources to transmit potentially informative data. It is assumed that the acquired data have a function in the system, usually related to its state estimation, which may trigger control actions. We propose that a semantic-functional approach can leverage the semantic-enabled implicit communication while guaranteeing that the system maintains functionality under the required performance. We illustrate the potential of this proposal through simulations of a swarm of drones jointly performing remote sensing in a given area. Our numerical results demonstrate that the proposed method offers the best design option regarding the ability to accomplish a previously established task -- remote sensing in the addressed case -- while minimising the use of radio resources by controlling the trade-offs that jointly determine the CPS performance and its effectiveness in the use of resources. In this sense, we establish a fundamental relationship between energy, communication, and functionality considering a given end application.
Mathematical Model of Quantum Channel Capacity
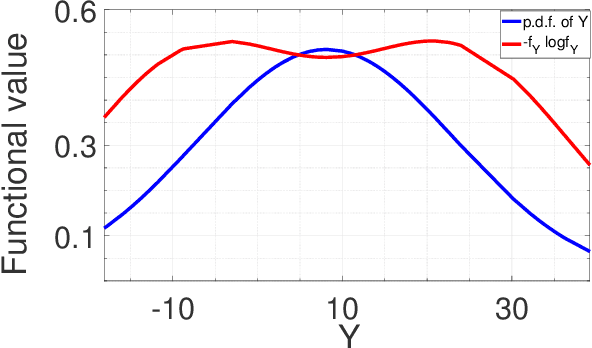
Feb 16, 2023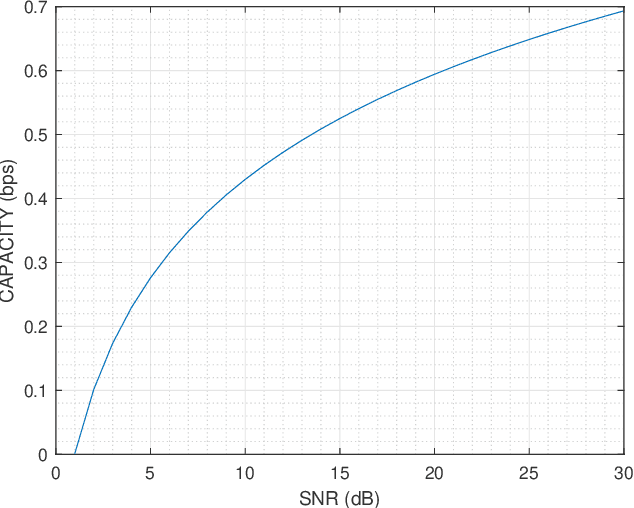
Abstract:In this article, we are proposing a closed-form solution for the capacity of the single quantum channel. The Gaussian distributed input has been considered for the analytical calculation of the capacity. In our previous couple of papers, we invoked models for joint quantum noise and the corresponding received signals; in this current research, we proved that these models are Gaussian mixtures distributions. In this paper, we showed how to deal with both of cases, namely (I)the Gaussian mixtures distribution for scalar variables and (II) the Gaussian mixtures distribution for random vectors. Our target is to calculate the entropy of the joint noise and the entropy of the received signal in order to calculate the capacity expression of the quantum channel. The main challenge is to work with the function type of the Gaussian mixture distribution. The entropy of the Gaussian mixture distributions cannot be calculated in the closed-form solution due to the logarithm of a sum of exponential functions. As a solution, we proposed a lower bound and a upper bound for each of the entropies of joint noise and the received signal, and finally upper inequality and lower inequality lead to the upper bound for the mutual information and hence the maximum achievable data rate as the capacity. In this paper reader will able to visualize an closed-form capacity experssion which make this paper distinct from our previous works. These capacity experssion and coresses ponding bounds are calculated for both the cases: the Gaussian mixtures distribution for scalar variables and the Gaussian mixtures distribution for random vectors as well.
Quantum Channel Modelling by Statistical Quantum Signal Processing
Feb 16, 2023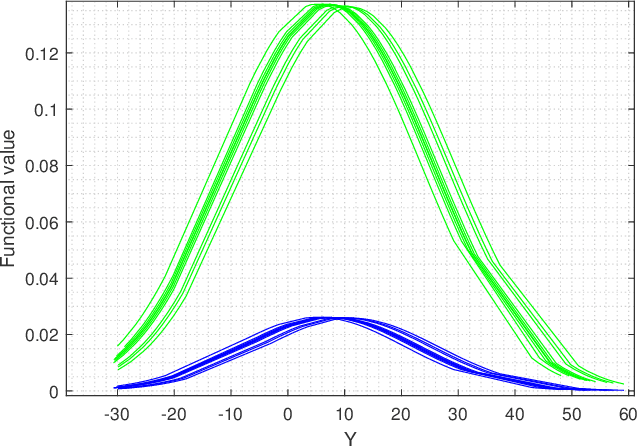
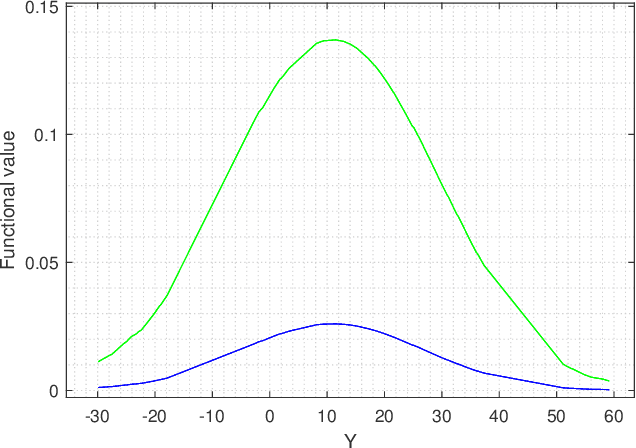
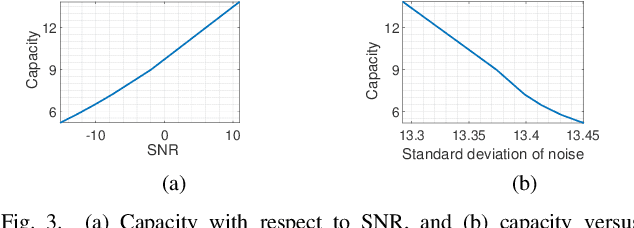
Abstract:In this paper we are interested to model quantum signal by statistical signal processing methods. The Gaussian distribution has been considered for the input quantum signal as Gaussian state have been proven to a type of important robust state and most of the important experiments of quantum information are done with Gaussian light. Along with that a joint noise model has been invoked, and followed by a received signal model has been formulated by using convolution of transmitted signal and joint quantum noise to realized theoretical achievable capacity of the single quantum link. In joint quantum noise model we consider the quantum Poisson noise with classical Gaussian noise. We compare the capacity of the quantum channel with respect to SNR to detect its overall tendency. In this paper we use the channel equation in terms of random variable to investigate the quantum signals and noise model statistically. These methods are proposed to develop Quantum statistical signal processing and the idea comes from the statistical signal processing.
Joint Modelling of Quantum and Classical Noise over Unity Quantum Channel
Jun 08, 2022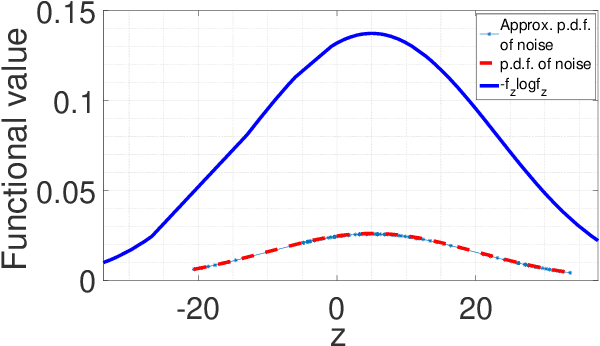
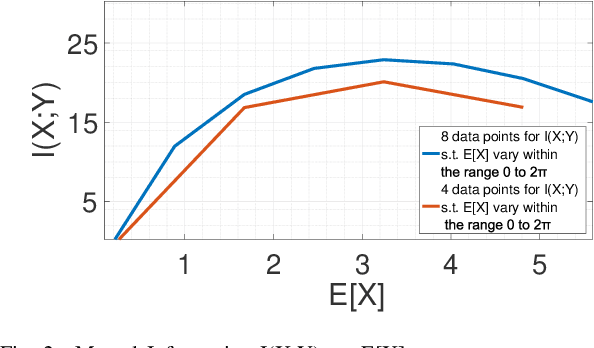
Abstract:For a continuous-input-continuous-output arbitrarily distributed quantum channel carrying classical information, the channel capacity can be computed in terms of the distribution of the channel envelope, received signal strength over a quantum propagation field and the noise spectral density. If the channel envelope is considered to be unity with unit received signal strength, the factor controlling the capacity is the noise. Quantum channel carrying classical information will suffer from the combination of classical and quantum noise. Assuming additive Gaussian-distributed classical noise and Poisson-distributed quantum noise, we formulate a hybrid noise model by deriving a joint Gaussian- Poisson distribution in this letter. For the transmitted signal, we consider the mean of signal sample space instead of considering a particular distribution and study how the maximum mutual information varies over such mean value. Capacity is estimated by maximizing the mutual information over unity channel envelope.
Semantic-functional Communications for Multiuser Event Transmissions via Random Maps
Apr 07, 2022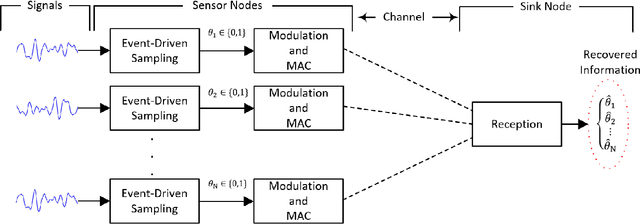
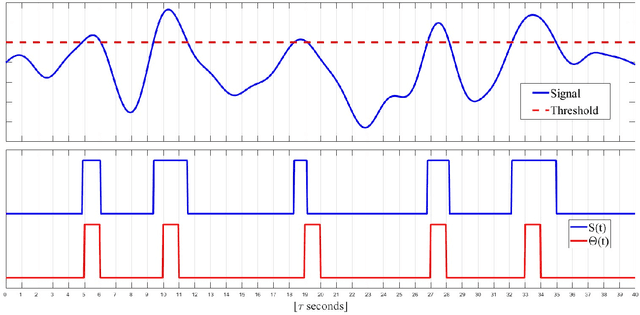
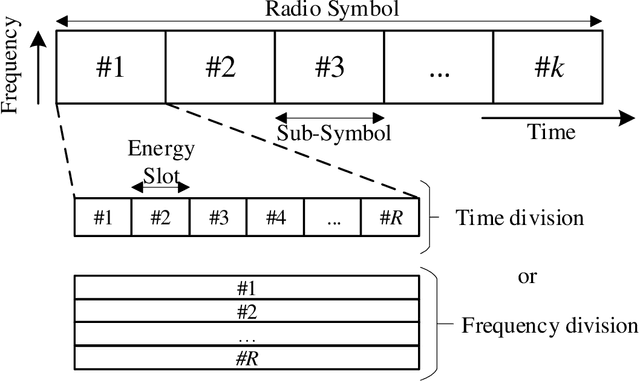
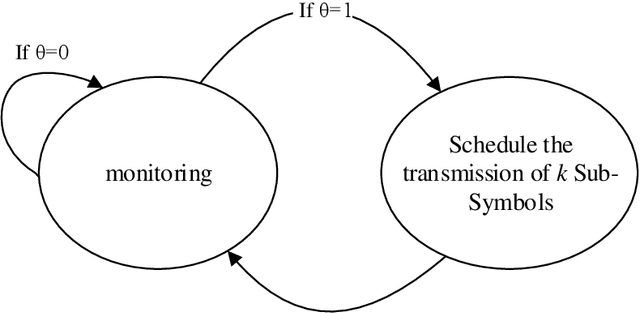
Abstract:This work introduces a new perspective for physical media sharing in multiuser communication by jointly considering (i) the meaning of the transmitted message and (ii) its function at the end user. Specifically, we have defined a scenario where multiple users (sensors) are continuously transmitting their own states concerning a predetermined event. On the receiver side there is an alarm monitoring system, whose function is to decide whether such a predetermined event has happened in a certain time period and, if yes, in which user. The media access control protocol proposed constitutes an alternative approach to the conventional physical layer methods, because the receiver does not decode the received waveform directly; rather, the relative position of the absence or presence of energy within a multidimensional resource space carries the (semantic) information. The protocol introduced here provides high efficiency in multiuser networks that operate with event-triggered sampling by enabling a constructive reconstruction of transmission collisions. We have demonstrated that the proposed method leads to a better event transmission efficiency than conventional methods like TDMA and slotted ALOHA. Remarkably, the proposed method achieves 100\% efficiency and 0\% error probability in almost all the studied cases, while consistently outperforming TDMA and slotted ALOHA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge