Haritha Thilakarathne
Group Activity Recognition using Unreliable Tracked Pose
Jan 06, 2024

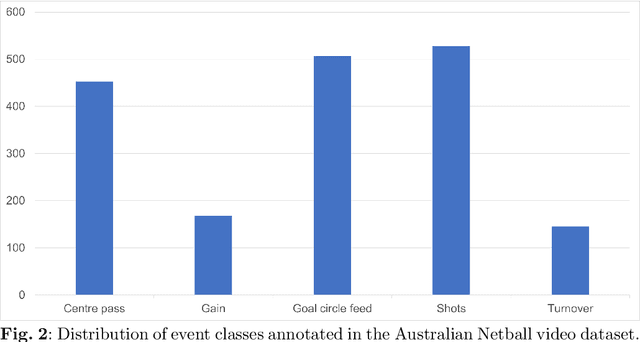
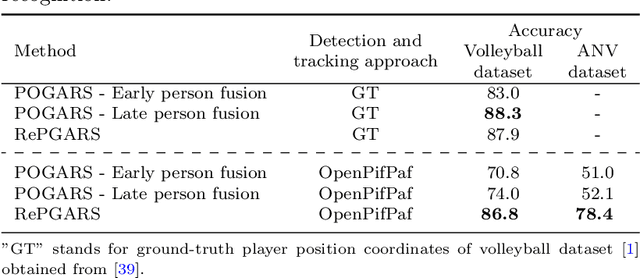
Abstract:Group activity recognition in video is a complex task due to the need for a model to recognise the actions of all individuals in the video and their complex interactions. Recent studies propose that optimal performance is achieved by individually tracking each person and subsequently inputting the sequence of poses or cropped images/optical flow into a model. This helps the model to recognise what actions each person is performing before they are merged to arrive at the group action class. However, all previous models are highly reliant on high quality tracking and have only been evaluated using ground truth tracking information. In practice it is almost impossible to achieve highly reliable tracking information for all individuals in a group activity video. We introduce an innovative deep learning-based group activity recognition approach called Rendered Pose based Group Activity Recognition System (RePGARS) which is designed to be tolerant of unreliable tracking and pose information. Experimental results confirm that RePGARS outperforms all existing group activity recognition algorithms tested which do not use ground truth detection and tracking information.
Pose is all you need: The pose only group activity recognition system
Aug 09, 2021



Abstract:We introduce a novel deep learning based group activity recognition approach called the Pose Only Group Activity Recognition System (POGARS), designed to use only tracked poses of people to predict the performed group activity. In contrast to existing approaches for group activity recognition, POGARS uses 1D CNNs to learn spatiotemporal dynamics of individuals involved in a group activity and forgo learning features from pixel data. The proposed model uses a spatial and temporal attention mechanism to infer person-wise importance and multi-task learning for simultaneously performing group and individual action classification. Experimental results confirm that POGARS achieves highly competitive results compared to state-of-the-art methods on a widely used public volleyball dataset despite only using tracked pose as input. Further our experiments show by using pose only as input, POGARS has better generalization capabilities compared to methods that use RGB as input.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge