Haoxuan Kuang
Attention-based Citywide Electric Vehicle Charging Demand Prediction Approach Considering Urban Region and Dynamic Influences
Oct 24, 2024



Abstract:Electric vehicle charging demand prediction is important for vacant charging pile recommendation and charging infrastructure planning, thus facilitating vehicle electrification and green energy development. The performance of previous spatio-temporal studies is still far from satisfactory because the traditional graphs are difficult to model non-pairwise spatial relationships and multivariate temporal features are not adequately taken into account. To tackle these issues, we propose an attention-based heterogeneous multivariate data fusion approach (AHMDF) for citywide electric vehicle charging demand prediction, which incorporates geo-based clustered hypergraph and multivariate gated Transformer to considers both static and dynamic influences. To learn non-pairwise relationships, we cluster service areas by the types and numbers of points of interest in the areas and develop attentive hypergraph networks accordingly. Graph attention mechanisms are used for information propagation between neighboring areas. Additionally, we improve the Transformer encoder utilizing gated mechanisms so that it can selectively learn dynamic auxiliary information and temporal features. Experiments on an electric vehicle charging benchmark dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed approach compared with a broad range of competing baselines. Furthermore, we demonstrate the impact of dynamic influences on prediction results in different areas of the city and the effectiveness of our clustering method.
A physics-informed and attention-based graph learning approach for regional electric vehicle charging demand prediction
Sep 11, 2023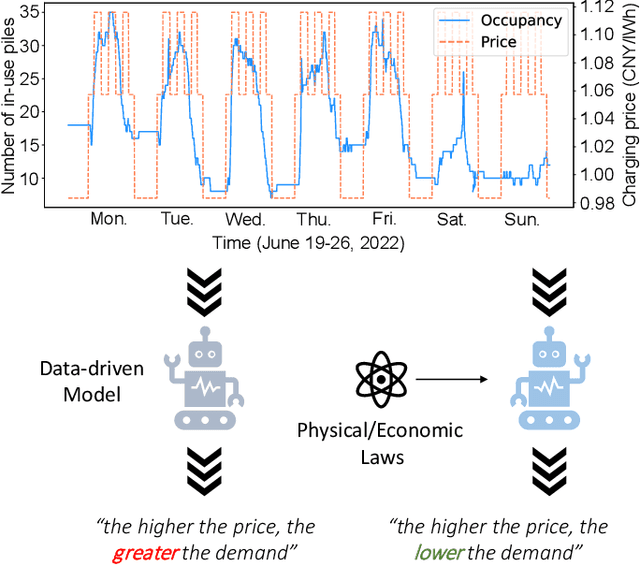
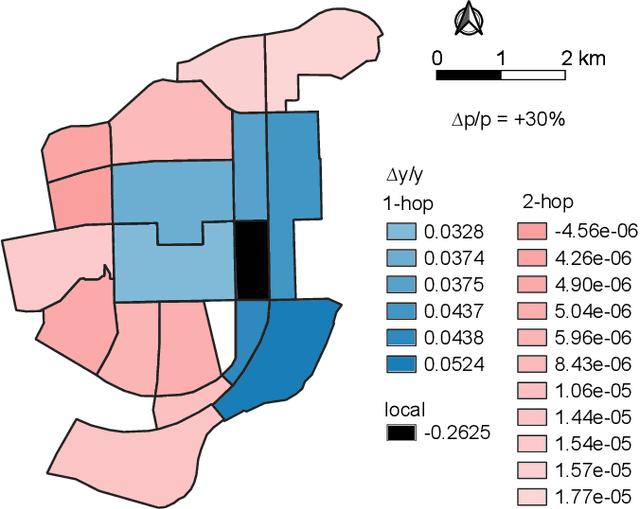
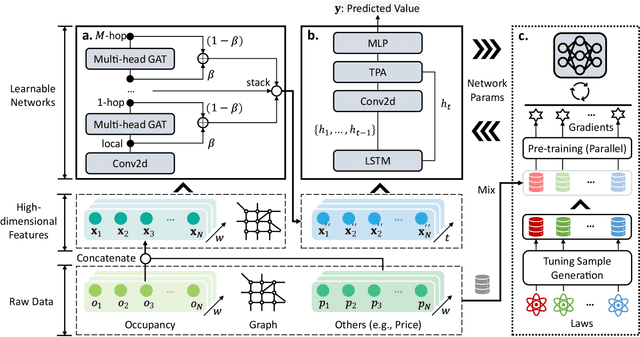
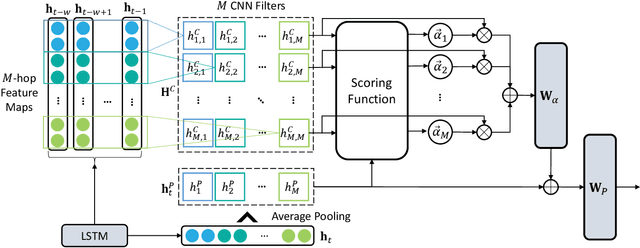
Abstract:Along with the proliferation of electric vehicles (EVs), optimizing the use of EV charging space can significantly alleviate the growing load on intelligent transportation systems. As the foundation to achieve such an optimization, a spatiotemporal method for EV charging demand prediction in urban areas is required. Although several solutions have been proposed by using data-driven deep learning methods, it can be found that these performance-oriented methods may suffer from misinterpretations to correctly handle the reverse relationship between charging demands and prices. To tackle the emerging challenges of training an accurate and interpretable prediction model, this paper proposes a novel approach that enables the integration of graph and temporal attention mechanisms for feature extraction and the usage of physic-informed meta-learning in the model pre-training step for knowledge transfer. Evaluation results on a dataset of 18,013 EV charging piles in Shenzhen, China, show that the proposed approach, named PAG, can achieve state-of-the-art forecasting performance and the ability in understanding the adaptive changes in charging demands caused by price fluctuations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge