Hana Matatov
Examining the Prevalence and Dynamics of AI-Generated Media in Art Subreddits
Oct 09, 2024
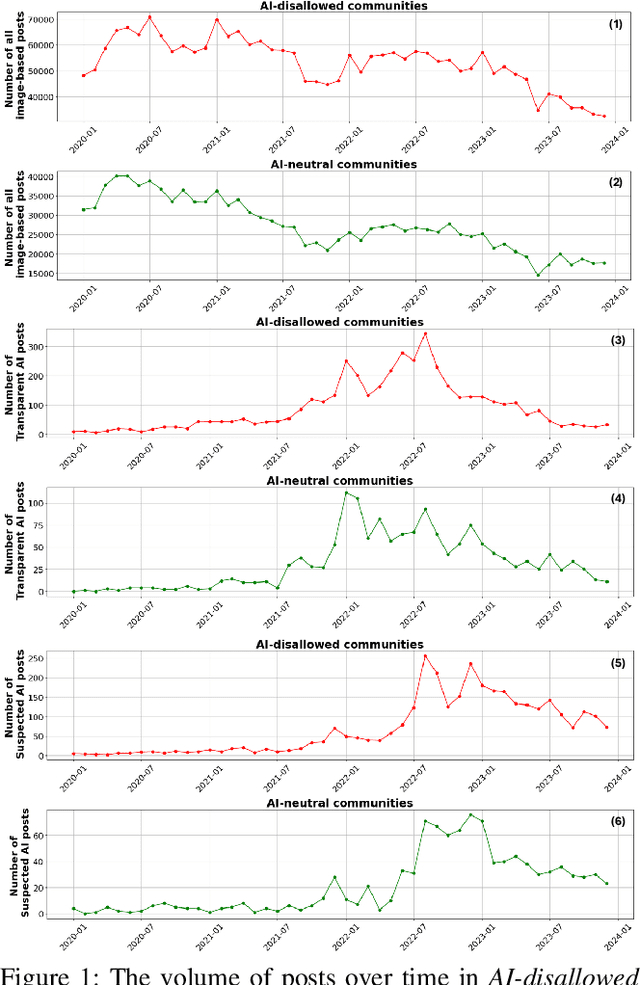
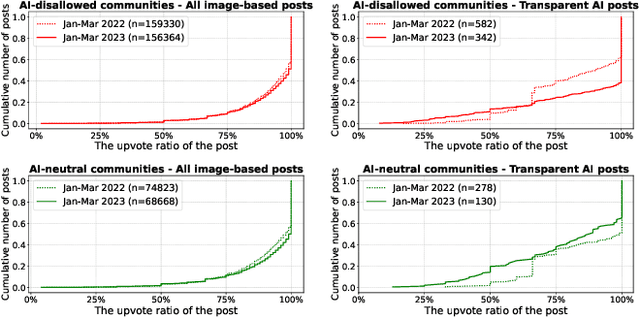
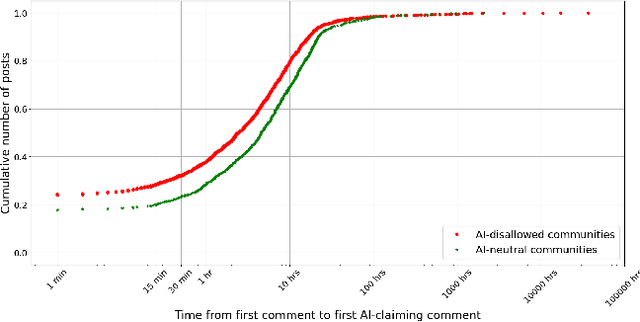
Abstract:Broadly accessible generative AI models like Dall-E have made it possible for anyone to create compelling visual art. In online communities, the introduction of AI-generated content (AIGC) may impact community dynamics by shifting the kinds of content being posted or the responses to content suspected of being generated by AI. We take steps towards examining the potential impact of AIGC on art-related communities on Reddit. We distinguish between communities that disallow AI content and those without a direct policy. We look at image-based posts made to these communities that are transparently created by AI, or comments in these communities that suspect authors of using generative AI. We find that AI posts (and accusations) have played a very small part in these communities through the end of 2023, accounting for fewer than 0.2% of the image-based posts. Even as the absolute number of author-labelled AI posts dwindles over time, accusations of AI use remain more persistent. We show that AI content is more readily used by newcomers and may help increase participation if it aligns with community rules. However, the tone of comments suspecting AI use by others have become more negative over time, especially in communities that do not have explicit rules about AI. Overall, the results show the changing norms and interactions around AIGC in online communities designated for creativity.
Dataset and Case Studies for Visual Near-Duplicates Detection in the Context of Social Media
Mar 14, 2022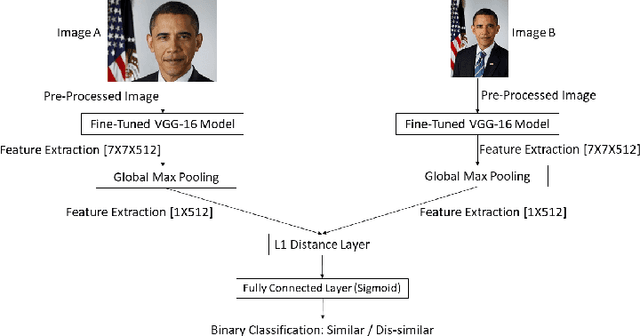
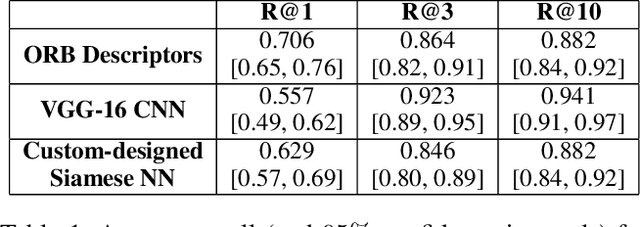

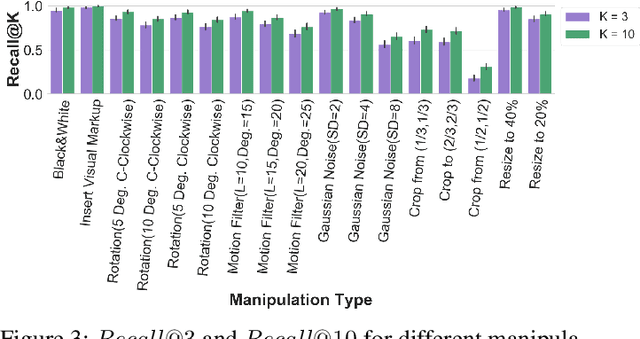
Abstract:The massive spread of visual content through the web and social media poses both challenges and opportunities. Tracking visually-similar content is an important task for studying and analyzing social phenomena related to the spread of such content. In this paper, we address this need by building a dataset of social media images and evaluating visual near-duplicates retrieval methods based on image retrieval and several advanced visual feature extraction methods. We evaluate the methods using a large-scale dataset of images we crawl from social media and their manipulated versions we generated, presenting promising results in terms of recall. We demonstrate the potential of this method in two case studies: one that shows the value of creating systems supporting manual content review, and another that demonstrates the usefulness of automatic large-scale data analysis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge