Hamid Ghaderi
Discovery of Generalizable TBI Phenotypes Using Multivariate Time-Series Clustering
Jan 15, 2024


Abstract:Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) presents a broad spectrum of clinical presentations and outcomes due to its inherent heterogeneity, leading to diverse recovery trajectories and varied therapeutic responses. While many studies have delved into TBI phenotyping for distinct patient populations, identifying TBI phenotypes that consistently generalize across various settings and populations remains a critical research gap. Our research addresses this by employing multivariate time-series clustering to unveil TBI's dynamic intricates. Utilizing a self-supervised learning-based approach to clustering multivariate time-Series data with missing values (SLAC-Time), we analyzed both the research-centric TRACK-TBI and the real-world MIMIC-IV datasets. Remarkably, the optimal hyperparameters of SLAC-Time and the ideal number of clusters remained consistent across these datasets, underscoring SLAC-Time's stability across heterogeneous datasets. Our analysis revealed three generalizable TBI phenotypes ({\alpha}, \b{eta}, and {\gamma}), each exhibiting distinct non-temporal features during emergency department visits, and temporal feature profiles throughout ICU stays. Specifically, phenotype {\alpha} represents mild TBI with a remarkably consistent clinical presentation. In contrast, phenotype \b{eta} signifies severe TBI with diverse clinical manifestations, and phenotype {\gamma} represents a moderate TBI profile in terms of severity and clinical diversity. Age is a significant determinant of TBI outcomes, with older cohorts recording higher mortality rates. Importantly, while certain features varied by age, the core characteristics of TBI manifestations tied to each phenotype remain consistent across diverse populations.
Identifying TBI Physiological States by Clustering of Multivariate Clinical Time-Series
Mar 30, 2023



Abstract:Determining clinically relevant physiological states from multivariate time series data with missing values is essential for providing appropriate treatment for acute conditions such as Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI), respiratory failure, and heart failure. Utilizing non-temporal clustering or data imputation and aggregation techniques may lead to loss of valuable information and biased analyses. In our study, we apply the SLAC-Time algorithm, an innovative self-supervision-based approach that maintains data integrity by avoiding imputation or aggregation, offering a more useful representation of acute patient states. By using SLAC-Time to cluster data in a large research dataset, we identified three distinct TBI physiological states and their specific feature profiles. We employed various clustering evaluation metrics and incorporated input from a clinical domain expert to validate and interpret the identified physiological states. Further, we discovered how specific clinical events and interventions can influence patient states and state transitions.
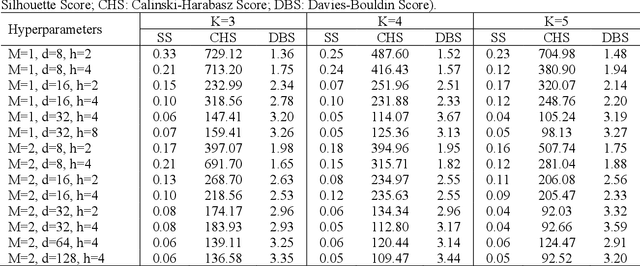
A Self-Supervised Learning-based Approach to Clustering Multivariate Time-Series Data with Missing Values : An Application to Traumatic Brain Injury Phenotyping
Feb 27, 2023



Abstract:Self-supervised learning approaches provide a promising direction for clustering multivariate time-series data. However, real-world time-series data often include missing values, and the existing approaches require imputing missing values before clustering, which may cause extensive computations and noise and result in invalid interpretations. To address these challenges, we present a Self-supervised Learning-based Approach to Clustering multivariate Time-series data with missing values (SLAC-Time). SLAC-Time is a Transformer-based clustering method that uses time-series forecasting as a proxy task for leveraging unlabeled data and learning more robust time-series representations. This method jointly learns the neural network parameters and the cluster assignments of the learned representations. It iteratively clusters the learned representations with the K-means method and then utilizes the subsequent cluster assignments as pseudo-labels to update the model parameters. To evaluate our proposed approach, we applied it to clustering and phenotyping Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) patients in the TRACK-TBI dataset. Our experiments demonstrate that SLAC-Time outperforms the baseline K-means clustering algorithm in terms of silhouette coefficient, Calinski Harabasz index, Dunn index, and Davies Bouldin index. We identified three TBI phenotypes that are distinct from one another in terms of clinically significant variables as well as clinical outcomes, including the Extended Glasgow Outcome Scale (GOSE) score, Intensive Care Unit (ICU) length of stay, and mortality rate. The experiments show that the TBI phenotypes identified by SLAC-Time can be potentially used for developing targeted clinical trials and therapeutic strategies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge