Hairong Tang
Spatial-temporal water area monitoring of Miyun Reservoir using remote sensing imagery from 1984 to 2020
Oct 14, 2021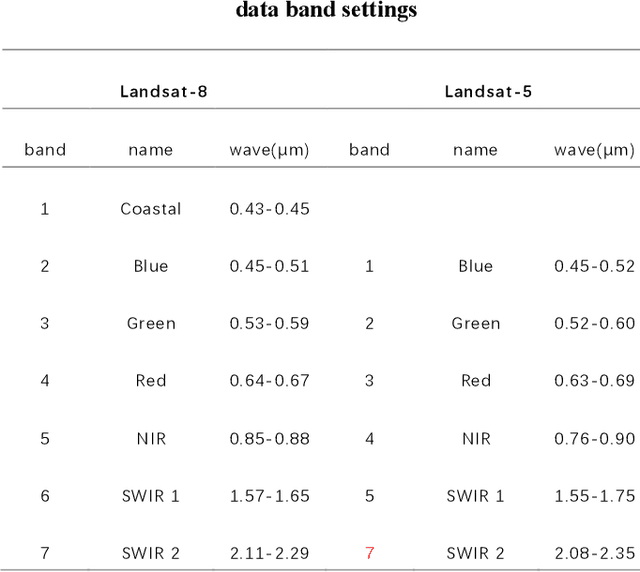
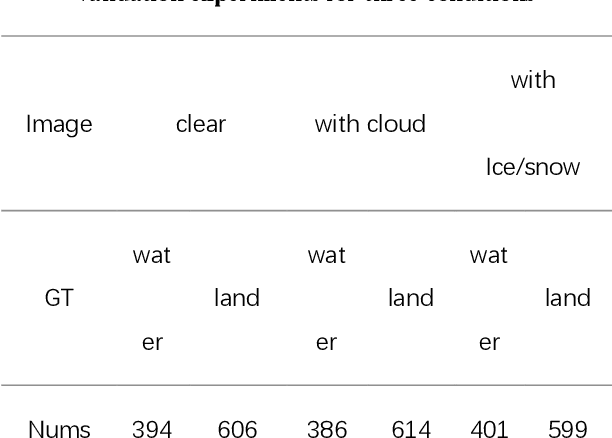
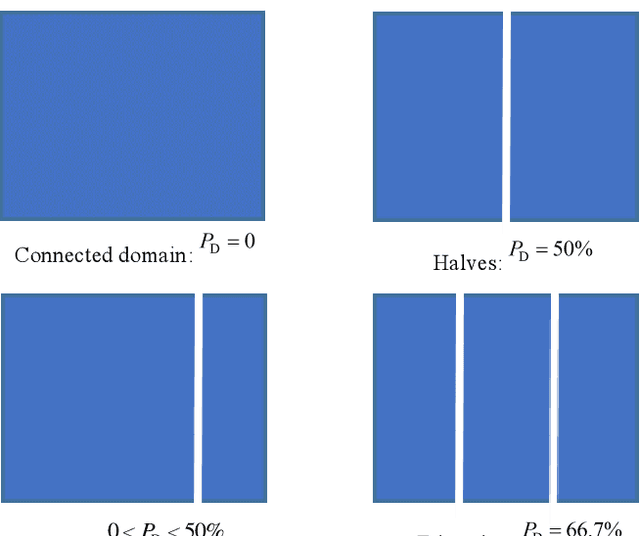
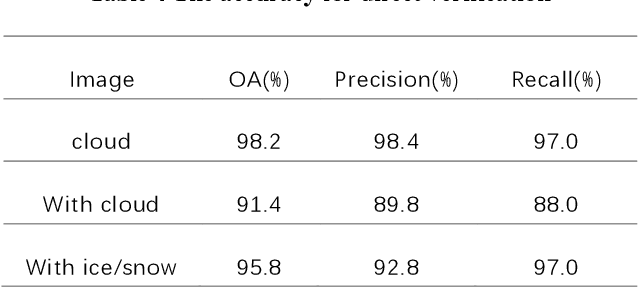
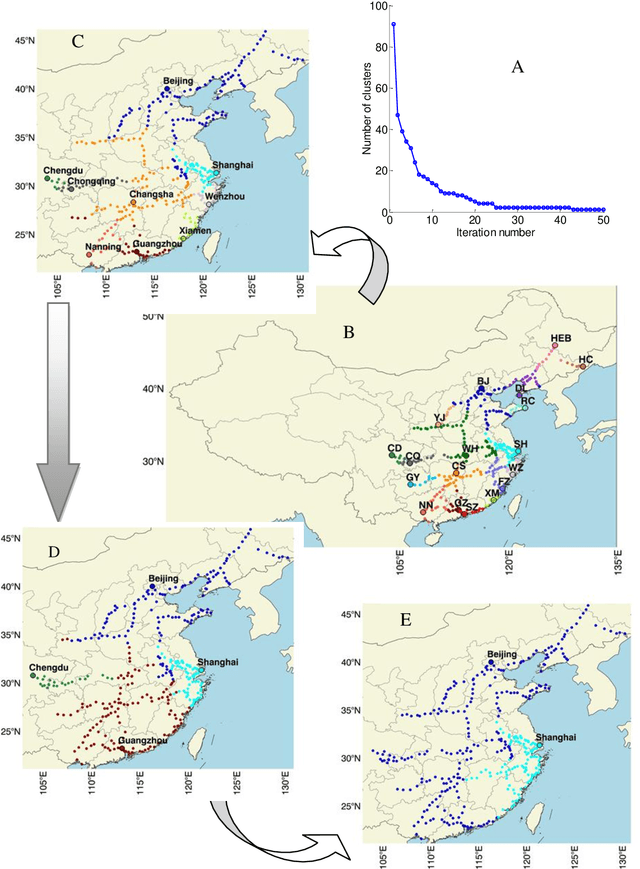
Abstract:Miyun Reservoir has produced huge benefits in flood control, agricultural irrigation, power generation, aquaculture, tourism, and urban water supply. Accurately water mapping is of great significance to the ecological environment monitoring of the Miyun Reservoir and the management of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project. On the 60th anniversary of the completion of the Miyun Reservoir, we took the Miyun Reservoir as the study area and collected all the Landsat-5 and Landsat-8 remote sensing images from 1984 to 2020 for water mapping. Based on the spectral, topographical and temporal-spatial characteristics of water, we proposed an automated method for long-term researvoir mapping, which can solve the problems caused by cloud, shadow, ice and snow pixels. Moreover, it can also deal with 'the same objects with different spectra' and spectral mixed problems. The overall accuracy is as high as 98.2% for the case with no cloud or snow/ice cover. The landscape division index is introduced to analyze the morphological changes of Miyun Reservoir. Based on the mapping results, we analyzed the changes of Miyun Reservoir from 1984 to 2020 and the driving factors of them.
Clustering by connection center evolution
Oct 19, 2016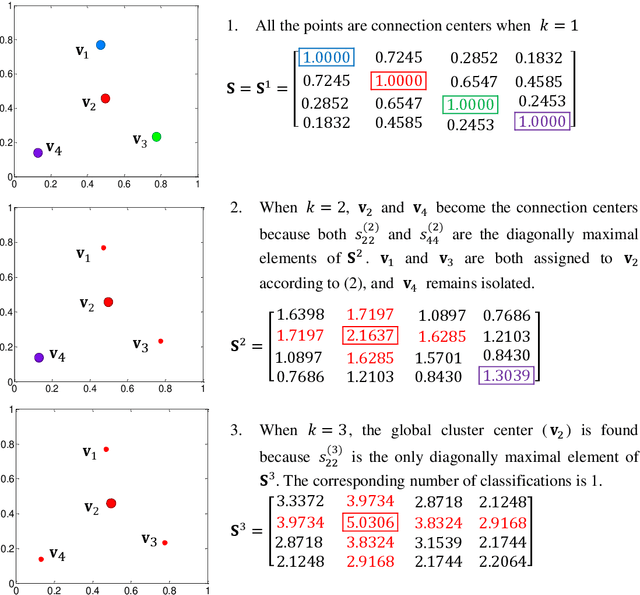
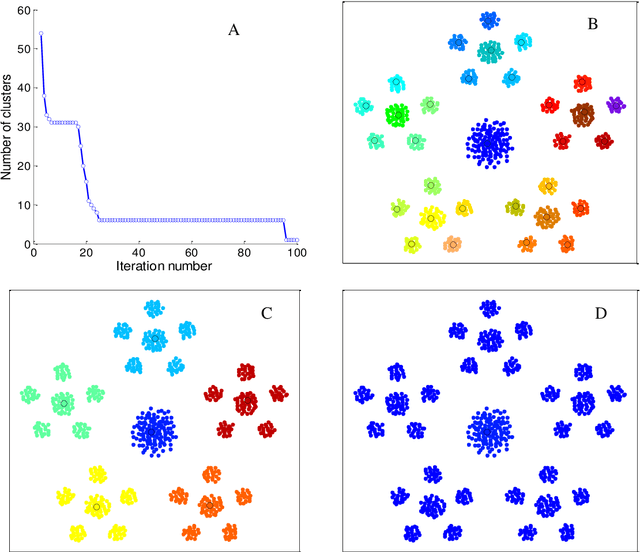
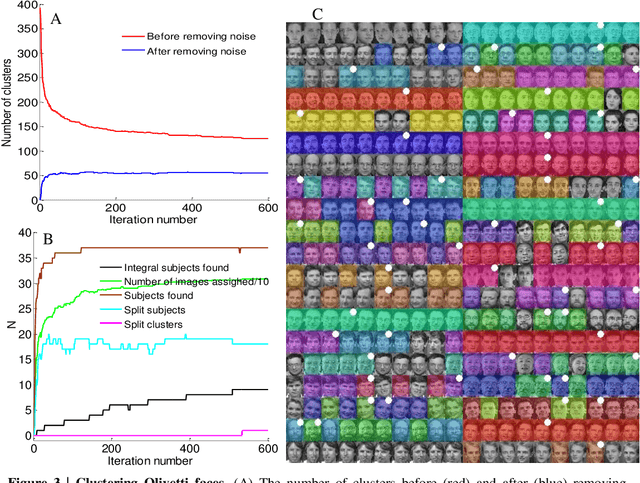
Abstract:The determination of cluster centers generally depends on the scale that we use to analyze the data to be clustered. Inappropriate scale usually leads to unreasonable cluster centers and thus unreasonable results. In this study, we first consider the similarity of elements in the data as the connectivity of nodes in an undirected graph, then present the concept of a connection center and regard it as the cluster center of the data. Based on this definition, the determination of cluster centers and the assignment of class are very simple, natural and effective. One more crucial finding is that the cluster centers of different scales can be obtained easily by the different powers of a similarity matrix and the change of power from small to large leads to the dynamic evolution of cluster centers from local (microscopic) to global (microscopic). Further, in this process of evolution, the number of categories changes discontinuously, which means that the presented method can automatically skip the unreasonable number of clusters, suggest appropriate observation scales and provide corresponding cluster results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge