Hadi Seyedarabi
Estimation of Acetabular Version from Anteroposterior Pelvic Radiograph Employing Deep Learning
Nov 14, 2021
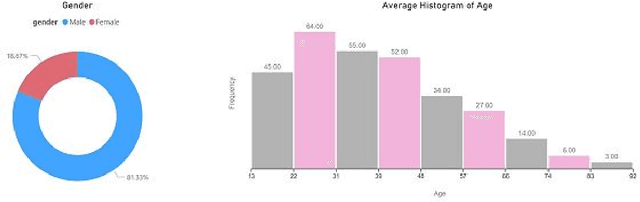

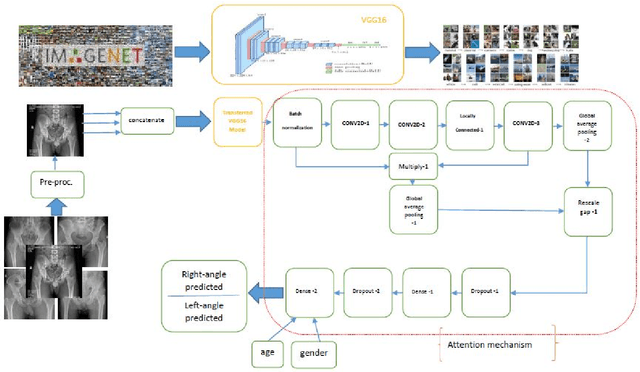
Abstract:Background and Objective: The Acetabular version, an essential factor in total hip arthroplasty, is measured by CT scan as the gold standard. The dose of radiation and expensiveness of CT make anterior-posterior pelvic radiograph an appropriate alternative procedure. In this study, we applied a deep learning approach on anteroposterior pelvic X-rays to measure anatomical version, eliminating the necessity of using Computed tomography scan. Methods: The right and left acetabular version angles of the hips of 300 patients are computed using their CT images. The proposed deep learning model, Attention on Pretrained-VGG16 for Bone Age, is applied to the AP images of the included population. The age and gender of these people are added as two other inputs to the last fully connected layer of attention mechanism. As the output, the angles of both hips are predicted. Results: The angles of hips computed on CT increase as people get older with the mean values of 16.54 and 16.11 (right and left angles) for men and 20.61 and 19.55 for women in our dataset. The predicted errors in the estimation of right and left angles using the proposed method of deep learning are in the accurate region of error (<=3 degrees) which shows the ability of the proposed method in measuring anatomical version based on AP images. Conclusion: The suggested algorithm, applying pre-trained vgg16 on the AP images of the pelvis of patients followed by an attention model considering age and gender of patients, can assess version accurately using only AP radiographs while obviating the need for CT scan. The applied technique of estimation of anatomical acetabular version based on AP pelvic images using DL approaches, to the best of authors' knowledge, has not been published yet.
Automatic Ship Classification Utilizing Bag of Deep Features
Feb 23, 2021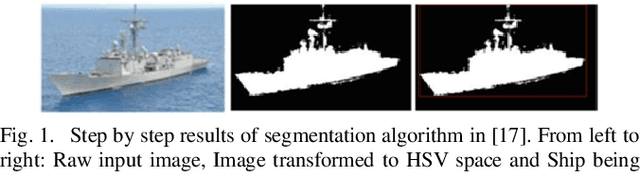
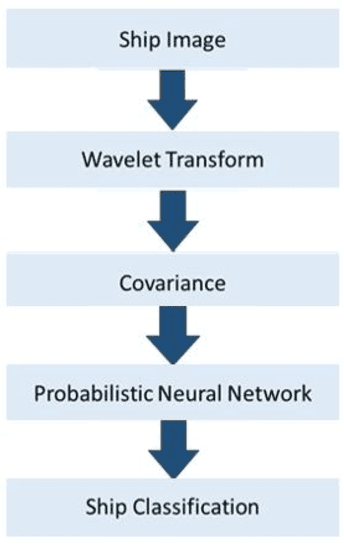
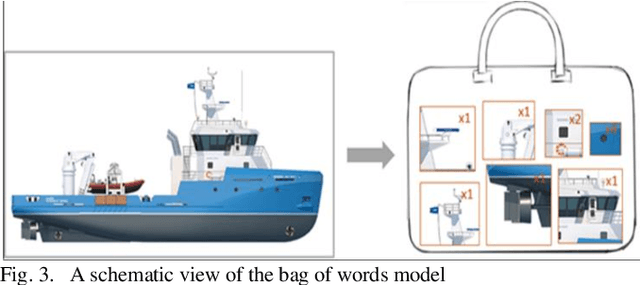
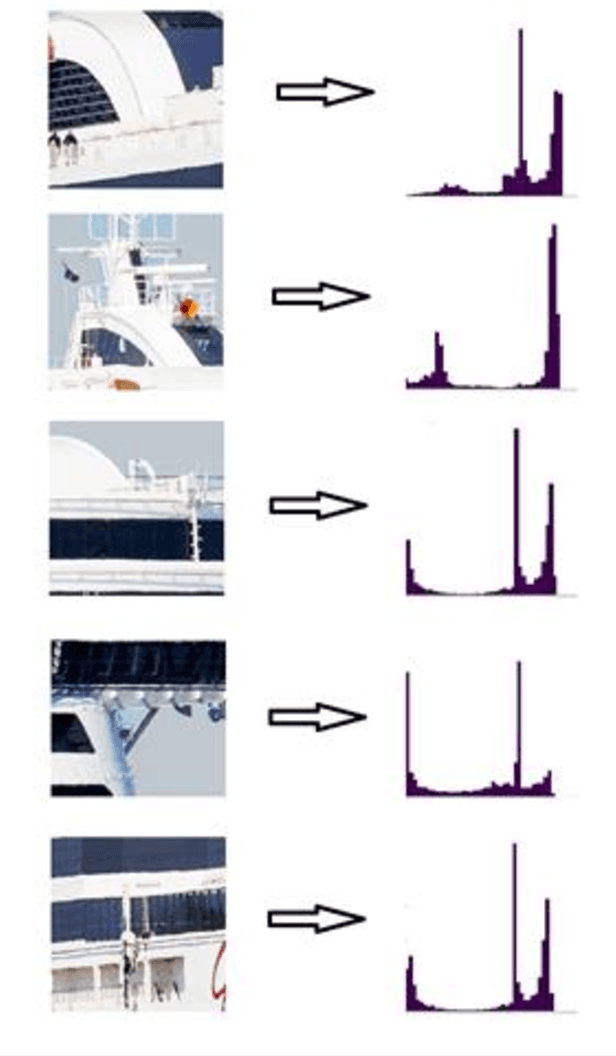
Abstract:Detection and classification of ships based on their silhouette profiles in natural imagery is an important undertaking in computer science. This problem can be viewed from a variety of perspectives, including security, traffic control, and even militarism. Therefore, in each of the aforementioned applications, specific processing is required. In this paper, by applying the "bag of words" (BoW), a new method is presented that its words are the features that are obtained using pre-trained models of deep convolutional networks. , Three VGG models are utilized which provide superior accuracy in identifying objects. The regions of the image that are selected as the initial proposals are derived from a greedy algorithm on the key points generated by the Scale Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT) method. Using the deep features in the BOW method provides a good improvement in the recognition and classification of ships. Eventually, we obtained an accuracy of 91.8% in the classification of the ships which shows the improvement of about 5% compared to previous methods.
Multi-focus Image Fusion for Visual Sensor Networks
Oct 02, 2020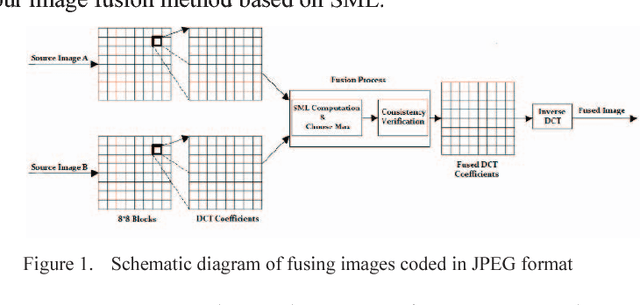
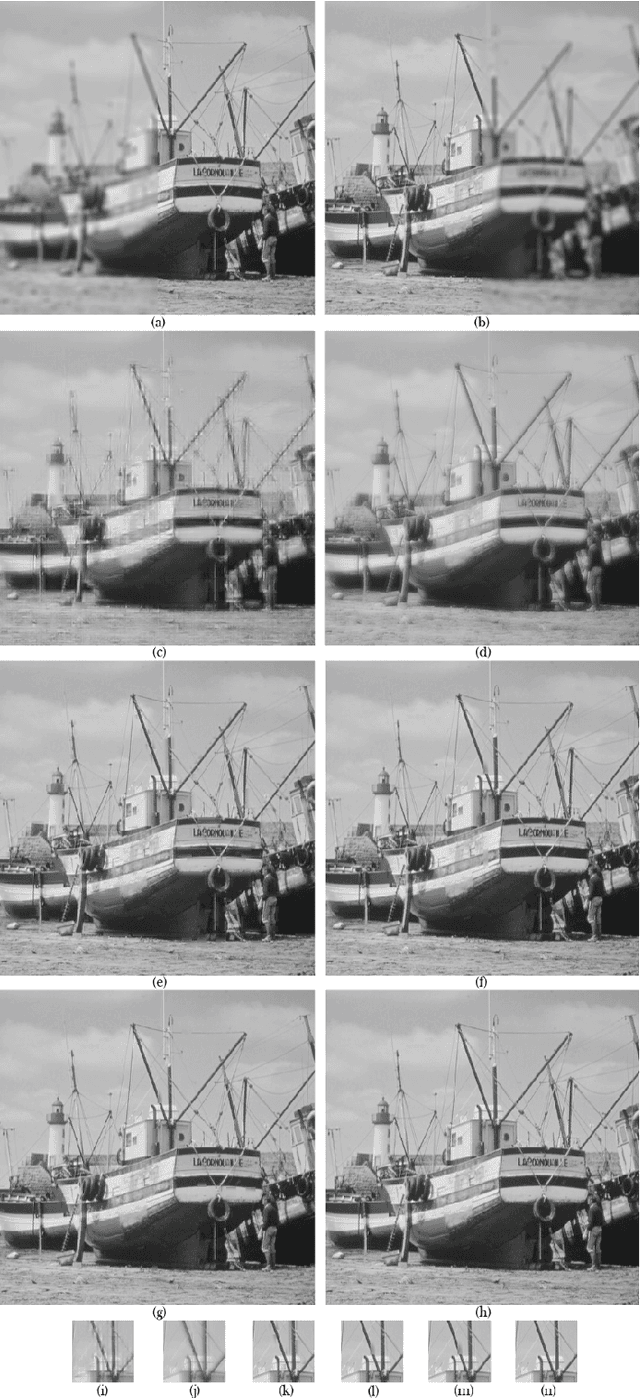


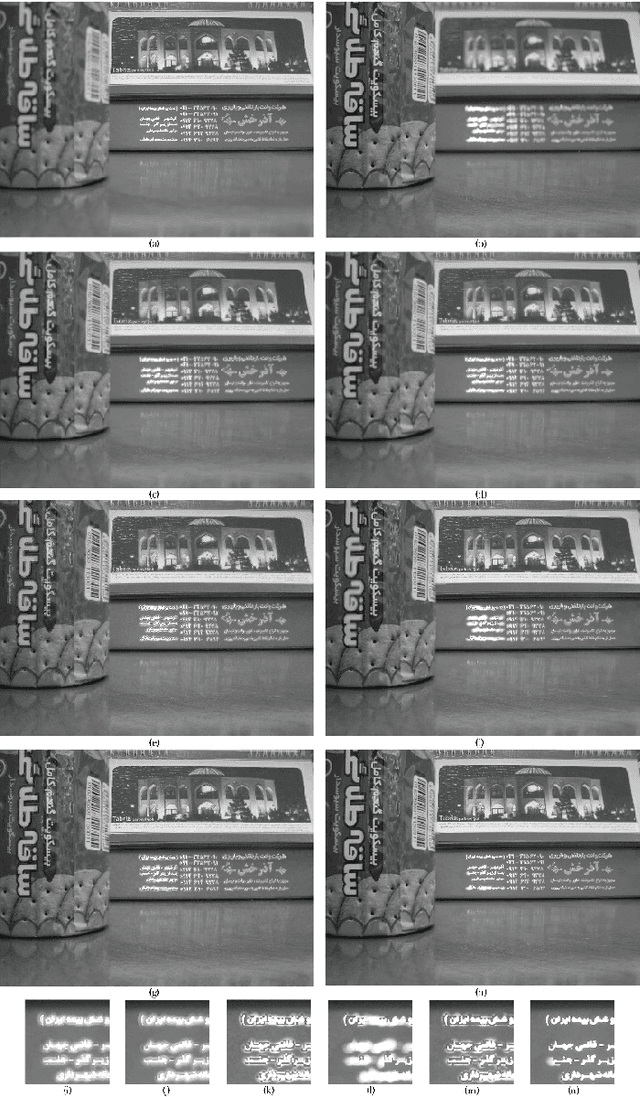
Abstract:Image fusion in visual sensor networks (VSNs) aims to combine information from multiple images of the same scene in order to transform a single image with more information. Image fusion methods based on discrete cosine transform (DCT) are less complex and time-saving in DCT based standards of image and video which makes them more suitable for VSN applications. In this paper, an efficient algorithm for the fusion of multi-focus images in the DCT domain is proposed. The Sum of modified laplacian (SML) of corresponding blocks of source images is used as a contrast criterion and blocks with the larger value of SML are absorbed to output images. The experimental results on several images show the improvement of the proposed algorithm in terms of both subjective and objective quality of fused image relative to other DCT based techniques.
Trajectory-Based Recognition of Dynamic Persian Sign Language Using Hidden Markov Model
Dec 04, 2019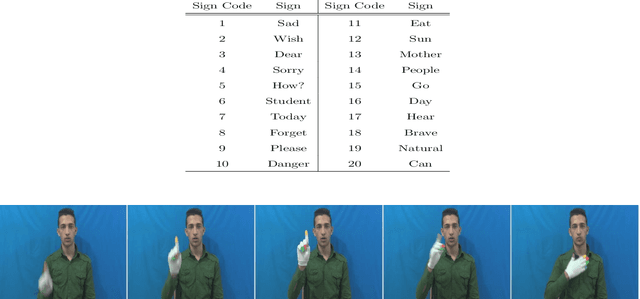
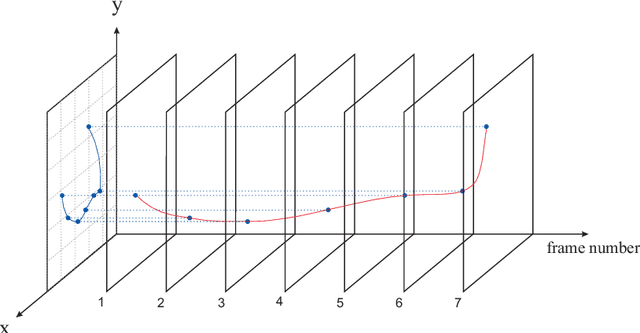
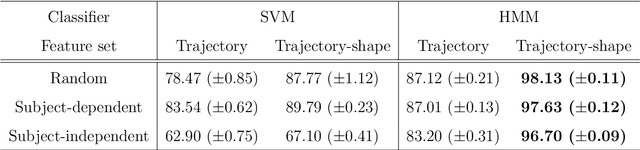

Abstract:Sign Language Recognition (SLR) is an important step in facilitating the communication among deaf people and the rest of society. Existing Persian sign language recognition systems are mainly restricted to static signs which are not very useful in everyday communications. In this study, a dynamic Persian sign language recognition system is presented. A collection of 1200 videos were captured from 12 individuals performing 20 dynamic signs with a simple white glove. The trajectory of the hands, along with hand shape information were extracted from each video using a simple region-growing technique. These time-varying trajectories were then modeled using Hidden Markov Model (HMM) with Gaussian probability density functions as observations. The performance of the system was evaluated in different experimental strategies. Signer-independent and signer-dependent experiments were performed on the proposed system and the average accuracy of 97.48% was obtained. The experimental results demonstrated that the performance of the system is independent of the subject and it can also perform excellently even with a limited number of training data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge