Hadi Salehi
Efficient MCMC Sampling for Bayesian Matrix Factorization by Breaking Posterior Symmetries
Jun 08, 2020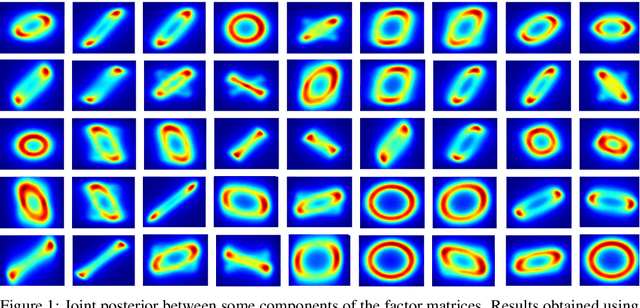
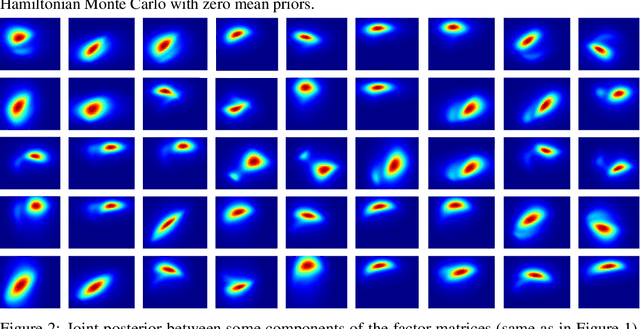
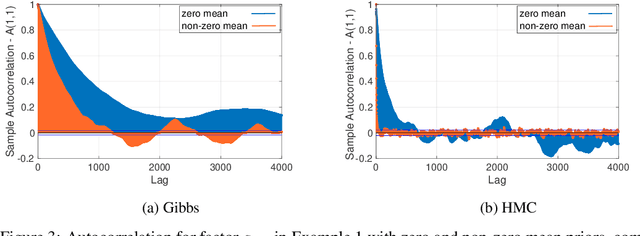
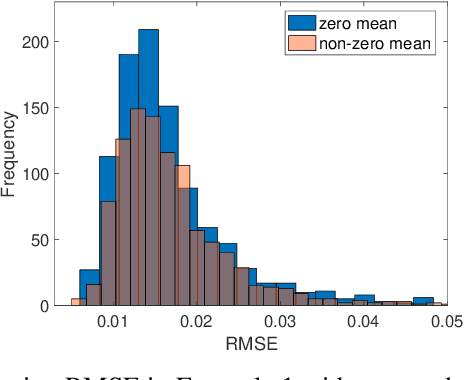
Abstract:Bayesian low-rank matrix factorization techniques have become an essential tool for relational data analysis and matrix completion. A standard approach is to assign zero-mean Gaussian priors on the columns or rows of factor matrices to create a conjugate system. This choice of prior leads to symmetries in the posterior distribution and can severely reduce the efficiency of Markov-chain Monte-Carlo (MCMC) sampling approaches. In this paper, we propose a simple modification to the prior choice that provably breaks these symmetries and maintains/improves accuracy. Specifically, we provide conditions that the Gaussian prior mean and covariance must satisfy so the posterior does not exhibit invariances that yield sampling difficulties. For example, we show that using non-zero linearly independent prior means significantly lowers the autocorrelation of MCMC samples, and can also lead to lower reconstruction errors.
Data-Driven Failure Prediction in Brittle Materials: A Phase-Field Based Machine Learning Framework
Mar 24, 2020



Abstract:Failure in brittle materials led by the evolution of micro- to macro-cracks under repetitive or increasing loads is often catastrophic with no significant plasticity to advert the onset of fracture. Early failure detection with respective location are utterly important features in any practical application, both of which can be effectively addressed using artificial intelligence. In this paper, we develop a supervised machine learning (ML) framework to predict failure in an isothermal, linear elastic and isotropic phase-field model for damage and fatigue of brittle materials. Time-series data of the phase-field model is extracted from virtual sensing nodes at different locations of the geometry. A pattern recognition scheme is introduced to represent time-series data/sensor nodes responses as a pattern with a corresponding label, integrated with ML algorithms, used for damage classification with identified patterns. We perform an uncertainty analysis by superposing random noise to the time-series data to assess the robustness of the framework with noise-polluted data. Results indicate that the proposed framework is capable of predicting failure with acceptable accuracy even in the presence of high noise levels. The findings demonstrate satisfactory performance of the supervised ML framework, and the applicability of artificial intelligence and ML to a practical engineering problem, i.,e, data-driven failure prediction in brittle materials.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge