Hadi Rahmat-Khah
TB-Net: A Tailored, Self-Attention Deep Convolutional Neural Network Design for Detection of Tuberculosis Cases from Chest X-ray Images
Apr 14, 2021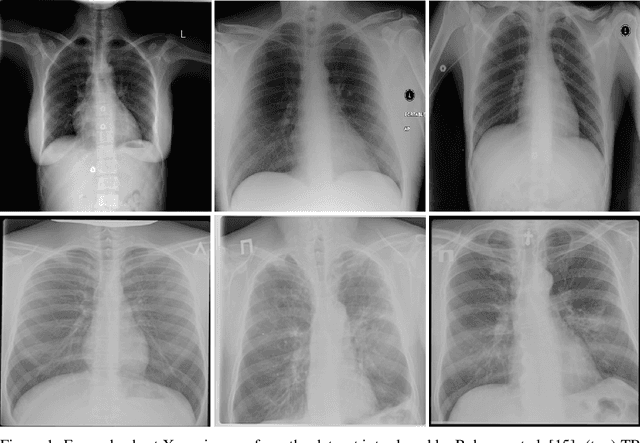
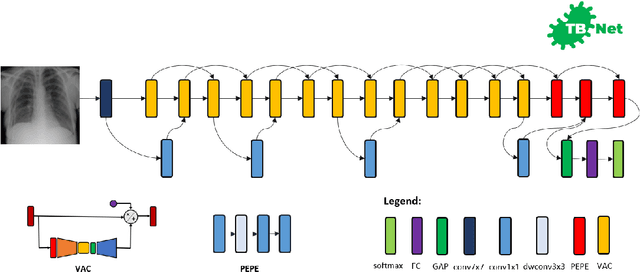
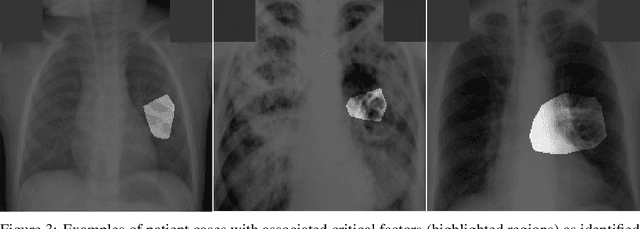
Abstract:Tuberculosis (TB) remains a global health problem, and is the leading cause of death from an infectious disease. A crucial step in the treatment of tuberculosis is screening high risk populations and the early detection of the disease, with chest x-ray (CXR) imaging being the most widely-used imaging modality. As such, there has been significant recent interest in artificial intelligence-based TB screening solutions for use in resource-limited scenarios where there is a lack of trained healthcare workers with expertise in CXR interpretation. Motivated by this pressing need and the recent recommendation by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the use of computer-aided diagnosis of TB, we introduce TB-Net, a self-attention deep convolutional neural network tailored for TB case screening. More specifically, we leveraged machine-driven design exploration to build a highly customized deep neural network architecture with attention condensers. We conducted an explainability-driven performance validation process to validate TB-Net's decision-making behaviour. Experiments on CXR data from a multi-national patient cohort showed that the proposed TB-Net is able to achieve accuracy/sensitivity/specificity of 99.86%/100.0%/99.71%. Radiologist validation was conducted on select cases by two board-certified radiologists with over 10 and 19 years of experience, respectively, and showed consistency between radiologist interpretation and critical factors leveraged by TB-Net for TB case detection for the case where radiologists identified anomalies. While not a production-ready solution, we hope that the open-source release of TB-Net as part of the COVID-Net initiative will support researchers, clinicians, and citizen data scientists in advancing this field in the fight against this global public health crisis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge